What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Depigmentation of the Skin
- Hypopigmented Patches on the Skin
- Loss of Brown Pigment on the Skin
What is Vitiligo? (Definition/Background Information)
- Vitiligo is a common pigmentary (depigmentation) disorder of unknown cause, in which the skin loses its melanocytes. Melanocytes are cells that make the brown color pigment ‘melanin’
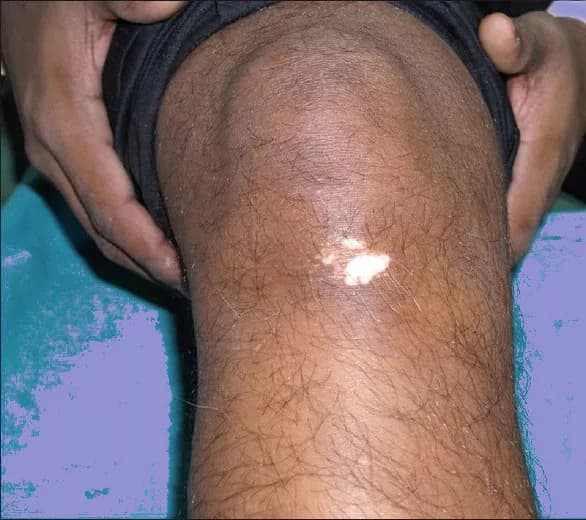
- As a result, when a patch of skin loses the pigment, it becomes white. This condition is progressive in nature; though, many years may pass, without any new patches developing. Vitiligo is neither contagious nor life-threatening
- Vitiligo can either have a focal pattern (white patches seen in one or a few areas), or a segmental pattern (white patches on one side of the body), or a generalized pattern (white patches appearing all over the body)
- The most common pattern is the non-segmental Vitiligo pattern, in which generalized pattern of white patches are noticed, all over the body
- Mild cases of Vitiligo may not require any treatment, though severe cases may be treated using various medical therapies, such as steroids, tacrolimus (immune-suppressant), ultraviolet light, etc.
- Even though there is no complete cure available for Vitiligo, the prognosis is excellent and most individuals are able to lead normal lives
- Vitiligo is a skin condition that cannot be prevented; however, avoiding the direct sun (using sunscreens, lotions, wide-brimmed hats) may lessen its severity
Who gets Vitiligo? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- The incidence of Vitiligo is around 1-2% of the global population
- Most individuals who have Vitiligo, usually develop the condition before they reach 20 years of age
- Vitiligo effects both sexes, across all races, ethnic groups, and communities
What are the Risk Factors for Vitiligo? (Predisposing Factors)
The precise cause of Vitiligo is not well-understood; it may be hereditary. It is commonly noticed in association with the following conditions:
- Adrenocortical insufficiency
- Alopecia areata
- Pernicious anemia
- Premature graying of the hair (before 35 years of age)
- Excessive stress
- A positive family history of Vitiligo
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases one's chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Vitiligo? (Etiology)
- Vitiligo is considered to be an autoimmune disorder, in which the body’s immune system attacks its own melanocytes, though the exact cause of the condition is unknown
- Vitiligo results in white patches. It is not known exactly what triggers this condition
- However, it seems to be a combination of genetic, infectious (usually viral), immunologic, biochemical and neurogenic factors. It can also be hereditary
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Vitiligo?
The signs and symptoms of Vitiligo may include:
- Irregular white patches on the skin, especially on the areas exposed to the sun
- More commonly, depigmented patches of skin are seen on the face, hands, and wrist, and also around the body orifices such as mouth, eyes, nostrils, genitalia, and umbilicus
- Graying of hair: Premature graying (before the age of 35 years) of the hair, eyebrows, eyelashes, and other affected areas, like the retina
- However, it is important to note that not all pale patches may be due to Vitiligo.
How is Vitiligo Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of Vitiligo requires a through physical examination, along with an evaluation of medical history. During this, the physician will try to evaluate:
- If there was any illness or stressful event, prior to the appearance of the white patches
- If there is a family history of Vitiligo
- If there was a rash or a sunburn, in and around the white patch
- If there is a family history of autoimmune disorders
Diagnostic tests that are performed for Vitiligo may include:
- Skin biopsy: A small piece of affected skin is taken and is examined by a pathologist, under the microscope to make a definitive diagnosis
- Examination under wood light/ultraviolet light/black light: Skin with Vitiligo when exposed to this light will appear pearl white
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Vitiligo?
The complications from Vitiligo could include:
- Sunburns
- Skin cancers
- Depression and mood disorders, due to social stigma and isolation
How is Vitiligo Treated?
There is no definitive cure for Vitiligo, though not all cases of the disorder need treatment. The primary goal of the treatment is to slow progression of hypopigmentation. Current treatment options for Vitiligo include:
The use of medical therapies, such as:
- Topical steroid therapy may help return color to one’s skin, particularly if used early in the disease
- Topical calcipotriene: A form of vitamin D
- Tacrolimus and pimecrolimus are medications that suppress the immune system and are effective for people with small area of depigmentation, especially on the face and neck
- Combined medical and light therapy (photopharmacotherapy): Psoralen, a drug which is either given orally or applied to skin, and the individuals are exposed to UVA or UVB (ultraviolet) lights
- Light therapy: This treatment used narrowband UVB light
- Laser therapy: A specific wavelength of UVB light is used, to treat only small areas
- Depigmantation: When Vitiligo is widespread and other treatment options have failed, a drug monobenzone is applied to the unaffected areas of the skin, which gradually lightens them, to blend with the discolored areas
- Surgical therapies include the use of skin grafting, blister grafting, and tattooing (micropigmentation).
How can Vitiligo be Prevented?
- Currently, there are no methods available to prevent Vitiligo
- The use of sun protection gear and sunscreens may help in decreasing the severity of the condition
What is the Prognosis of Vitiligo? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- Vitiligo is a benign condition that cannot be completely cured
- Emphasis is laid on managing the emotional stress and mental trauma an individual undergoes due to Vitiligo
- The affected individuals are able to lead normal and active lives
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Vitiligo:
Individuals with Vitiligo usually have the following co-existing diseases:
- Addison's disease
- Hyperthyroidism
- Vitamin B-12 deficiency anemia (pernicious anemia)
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals


0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.