What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Accelerating Angina
- New-Onset Angina
- Progressive Angina
What is Unstable Angina? (Definition/Background Information)
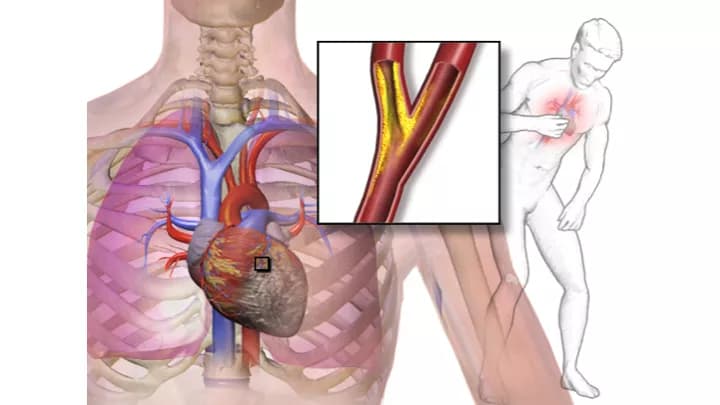
- Unstable Angina is a severe unexpected pain or discomfort felt within the chest, typically when an individual is resting. In this condition, the heart does not get sufficient amount of blood and oxygen, predisposing an individual to a heart attack. Thus, an Unstable Angina can be indicative of a serious heart disease
- The chief cause of Unstable Angina is coronary artery disease because of fat build-up in the arterial walls. This plaque build-up clogs the coronary artery, which supplies blood to the heart. The pain and discomfort felt by an individual is due to reduced blood flow to the heart muscles
- The risk factors for developing Unstable Angina include a positive family history of heart condition, having a young family member who had had a heart attack, high cholesterol and blood pressure levels, including smoking and heavy alcohol drinking
- The symptoms of the heart condition include chest pain, pain along the jaw, shoulder and arm, sweating, and breathlessness, typically, when the individual is resting. The sudden chest pain might last a period of 15-20 minutes and may coexist with reduced blood pressure levels
- A healthcare professional may undertake a physical examination, symptoms assessment, study one’s family medical history, and potentially conduct an electrocardiography, echocardiography, and blood tests, to diagnose Unstable Angina
- The treatment options for Unstable Angina may include medication to stabilize the heart rhythm, blood-thinners to help regulate blood pressure levels, and procedures to open a blocked/narrowed artery with a stent. In case of severe blockage, an open-heart surgery may be performed
- The prognosis is determined by its severity. In cases where damage to the heart is limited, the outcome can be good, with appropriate medical care and lifestyle changes. If there is extensive damage to the heart, Unstable Angina can be fatal
- Unstable Angina can be prevented through certain lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, avoiding smoking, drinking in moderation, exercising, and maintaining good glycemic control for diabetes
Who gets Unstable Angina? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Unstable Angina is most commonly seen among older individuals who have history of the condition
- Both males and females are affected
- There are no reported racial and ethnic biases in the occurrence of this condition; Unstable Angina is seen worldwide
What are the Risk Factors for Unstable Angina? (Predisposing Factors)
The following are some risk factors for developing Unstable Angina:
- A family history of the condition
- Close relatives who have had a heart attack before the age of 55 years
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- High cholesterol, particularly high LDL and low HDL cholesterol
- Obesity, sedentary lifestyle
- Smoking
- Heavy alcohol drinking
- Improper diet, lacking in fresh vegetables and fruits
- Individuals with conditions, such as poorly-controlled diabetes, with poor glycemic control
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases one’s chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Unstable Angina? (Etiology)
Unstable Angina is caused by the following conditions:
- Coronary artery disease: Coronary artery disease develops, as a result of atherosclerosis, which is the formation of plaques in and on the arterial walls. The plaques can cause blockages in the arteries. When the blockage occurs in the coronary artery, which supplies blood to the heart, the heart muscles do not function properly, leading to the symptoms
- Rarely, the condition can also be caused by:
- Coronary artery spasm that results in a tightening of the coronary arterial wall
- Microvascular dysfunction, which is the aberrant functioning of tiny branches of an artery
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Unstable Angina?
The signs and symptoms associated with Unstable Angina are as follows:
- Sudden pain and discomfort in the chest, while resting
- Pain in the chest, lasting till about 20 minutes
- Breathlessness
- Pain in the jaw, shoulder, arm, neck or back
- Drop in blood pressure level
- Sweating
- The pain may not go away with nitroglycerin (a medicine that is normally taken, to dilate the blood vessels)
How is Unstable Angina Diagnosed?
A healthcare professional may perform the following tests and exams, to arrive at an accurate diagnosis of Unstable Angina:
- A thorough physical examination and an assessment of symptoms
- An evaluation of personal and family medical history
- Electrocardiography, to check for electrical activity of the heart
- Echocardiography, to check the flow of blood through the heart
- Coronary angiography, to visualize the coronary arteries using a dye
- Blood tests to evaluate heart enzymes
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Unstable Angina?
The complications associated with Unstable Angina include:
- Arrhythmia
- Heart failure
- Heart attack
All of the above complications can be fatal in some cases.
How is Unstable Angina Treated?
The treatment for Unstable Angina is dependent upon the severity of symptoms and underlying conditions. The treatment options include:
- Plenty of rest, preferably in a hospital-setting; also, to enable a battery of tests
- Painkillers, to treat pain
- Blood-thinners to prevent blood clots
- Medications to treat high blood pressure and address high cholesterol levels
- Angioplasty: A procedure to place a stent in a blood vessel, to release blockage and enable free flow of blood. Sometimes, a stent with medication may be placed, to prevent the artery from closing over a period of time
- Heart bypass surgery: A healthcare professional may make a determination, if this surgery is necessary, based on the number, extent, location, and severity of blockages. The blocked parts of coronary artery are replaced with blood vessels from another part of the body
How can Unstable Angina be Prevented?
It is possible to prevent Unstable Angina through certain lifestyle changes such as:
- Losing weight
- Exercising regularly
- Including fruits and vegetables in the diet
- Smoking cessation
- Moderate drinking of alcohol
- Taking medication for high blood pressure, keeping regular track of changes in blood pressure
- Taking medication for high cholesterol levels
- Maintaining good glycemic index
- Getting routine physical examination done, especially in case of a previous history of the condition
What is the Prognosis of Unstable Angina? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
The prognosis of Unstable Angina is dictated by the extent and seriousness of blockage in the coronary artery.
- If the blockage is minor, lifestyle changes may help an individual manage his/her condition
- If the blockages are severe, it can result in arrhythmia, heart failure, and/or heart attack. Such complications may severely affect the prognosis of the individual
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Unstable Angina:
Current studies indicate that approximately 6 million individuals, in the United States alone, have Unstable Angina.
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.