What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- GM2 Gangliosidosis
- Hexosaminidase A Deficiency Disease
- Infantile Amaurotic Familial Disease
What is Tay-Sachs Disease? (Definition/Background Information)
- Tay-Sachs Disease (TSD) is an enzyme deficiency, or a complete absence of the enzyme called beta-hexosaminidase A, disorder
- Gangliosides are fatty acid derivatives that are broken down by the enzyme Hexosaminidase A, in the absence of which, the gangliosides accumulate in the nerve cells of the brain causing brain degeneration
- This is caused due to genetic mutation in the HEXA gene on chromosome 15
- If both parents are carriers of the defective gene, then a child has a 25% chance of developing the disease. If only one parent passes the defective gene to the child, the child becomes a carrier and remains unaffected; even though they will have the potential to pass on the disorder to their children
- There are three types of Tay-Sachs Disease: Infantile (the most common one, in which neurodegeneration sets even as the child is in the womb), Juvenile, and Adult
Who gets Tay-Sachs Disease? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Tay-Sachs Disease usually occurs in infants and toddlers
- There is no specific sexual predilection; both males and females are equally prone to the condition
- This disease is observed more commonly in Eastern European and among the Ashkenazi Jews
What are the Risk Factors for Tay-Sachs Disease? (Predisposing Factors)
Risk factor for Tay-Sachs Disease include:
- Children born to TSD-affected or carrier parents
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Tay-Sachs Disease? (Etiology)
- Tay-Sachs Disease is caused, when the child receives two affected HEXA genes on chromosome 15; one from each parent. This type of genetic transmission is called autosomal recessive
Autosomal Recessive: Autosomal recessive conditions are traits or disorders that occur when two copies of an abnormal gene have been inherited on a non-sex chromosome. If both parents have an autosomal recessive condition, there is a 100% likelihood of passing on the mutated genes to their children. If, however, only one mutant copy of the gene is inherited, the individual will be a carrier of the condition, but will not be present with any symptoms. Children born to two carriers, have a 25% chance of being homozygous dominant (unaffected), a 50% chance of being heterozygous (carrier), and a 25% chance of being homozygous recessive (affected).
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Tay-Sachs Disease?
Most of the Tay-Sachs Disease signs and symptoms are linked to the nervous system. These vary with age of disease onset:
- Blindness
- Deafness
- Loss of muscle strength
- Delayed developmental milestones
- Difficulty swallowing
- Speech disturbances
- Atrophy and paralysis of muscles
- Gait instability
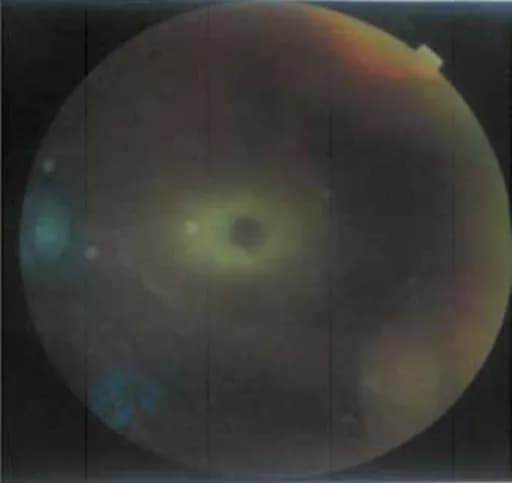
- Eye examination shows cherry red spots in the retina (macula)
- Dementia
- Seizures
- Irritability
How is Tay-Sachs Disease Diagnosed?
A diagnosis of Tay-Sachs Disease would include:
- Physical examination
- Evaluation of family history
- Testing Beta-Hexosaminidase A levels in the blood
- Eye Exam; shows cherry red spots in the retina (macula)
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Tay-Sachs Disease?
Complications due to Tay-Sachs Disease include:
- Spasticity (stiffness), atrophy and paralysis of the muscles
- Seizures
- Mental deterioration
- TSD can be fatal in advanced stages
How is Tay-Sachs Disease Treated?
Treatment measures for Tay-Sachs Disease include:
- A definitive treatment for Tay-Sachs Disease does not exist
- Treatment is symptomatic and is directed towards preventing/treating the complications and keeping the patient comfortable
- Maintaining proper nutrition and hydration
How can Tay-Sachs Disease be Prevented?
- Currently, there are no specific methods or guidelines to prevent Tay-Sachs Disease genetic condition
- Genetic testing of the expecting parents (and related family members) and prenatal diagnosis (molecular testing of the fetus during pregnancy) may help in understanding the risks better during pregnancy
- If there is a family history of the condition, then genetic counseling will help assess risks, before planning for a child
- Active research is currently being performed to explore the possibilities for treatment and prevention of inherited and acquired genetic disorders
What is the Prognosis of Tay-Sachs Disease? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- Tay-Sachs Disease prognosis is very poor with the infantile and juvenile onset types
- Death usually occurs before age 4 with the infantile type and between 5-15 years with the Juvenile type
- Adult-onset Tay-Sachs Disease has a slower progression. But, the condition gets complicated with psychiatric and motor neuron disease; the affected individuals may become wheel-chair dependent
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Tay-Sachs Disease:
The following DoveMed website link is a useful resource for additional information:
https://www.dovemed.com/diseases-conditions/congenital-genetic-disorders/
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.