What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Broken Talus
- Fractured Talus
- Osteochondral Fracture of the Talar Dome
What is Talus Fracture? (Definition/Background Information)
- The talus bone, also referred to as the ankle bone, is part of a group of small bones that are located between the heel bone and the two bones of the lower leg (the fibula and tibia)
- A Talus Fracture is a break or crack occurring in the talus bone
- Talus Fractures are usually caused by high-energy impacts, resulting from an athletic sport, a motor vehicle accident, or a fall from a substantial height
Who gets Talus Fracture? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Talus Fractures are non-specific fractures, and as such, may occur in individuals of any age, race, ethnic group, and gender
- It is generally seen that young athletes (who participate in a high-impact sports) or adult men, have the highest rates of occurrence of this fracture
- Men are twice more likely to experience a Talus Fracture, than women
What are the Risk Factors for Talus Fracture? (Predisposing Factors)
Common risk factors associated with a Talus Fracture include:
- Participation in high-risk contact sports, such as football or basketball
- Young athletes and adult men have a higher risk
What are the Causes of Talus Fracture? (Etiology)
Some common causes of a Talus Fracture include:
- Falling from a significant height; especially landing on one’s feet (or the fracture occurring since the individual is overweight)
- Direct trauma to the ankle due to an automobile accident
- Taking part in any rough or high-impact sport
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Talus Fracture?
Signs and symptoms of a Talus Fracture include:
- Severe and immediate pain at the site, where the injury occurred.
- Swelling; tender sensation to touch
- Noticeable bruising, abnormal deformity of the ankle
- Inability to apply weight, or bear any pressure on the foot
How is Talus Fracture Diagnosed?
Diagnostic methods that a physician may use to help diagnose a Talus Fracture include:
- Physical examination: A thorough physical examination is important in identifying any noticeable deformities, swelling, contusions, in the foot/ankle. Individuals are also expected to provide an explanation of the circumstances that caused the injury. In addition to this, a complete medical history can aid in arriving at a definitive diagnosis
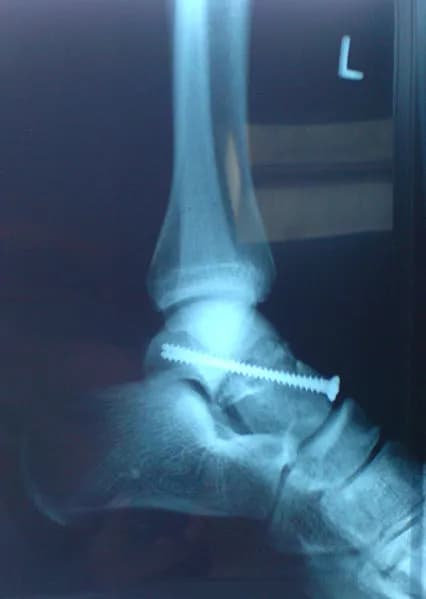
- X-ray: X-rays are the most common methods to evaluate a fracture, especially if the bone has been displaced. This diagnostic test will provide a clear image of the bone, identify the exact location of the injury, and determine the extent of the fracture
- Computerized tomography (CT) scan: A CT scan takes a series of x-ray images from several different angles. These images are then merged to create cross-sectional images of bones and soft tissues of the body, which then allows a physician to examine the foot and surrounding structures
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): An MRI is a more detailed scan that uses radio waves and a magnetic field to generate thorough images of the interior bones and soft tissues
- Bone scan: A bone scan is a diagnostic method used to identify any bone abnormalities. It is performed by injecting tiny amounts of radioactive material into the bloodstream
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Talus Fracture?
Complications associated with a Talus Fracture include:
- Osteonecrosis: A serious disorder characterized by a temporary or permanent disruption of blood flow to the bones
- Prolonged and chronic pain
- Infection of the bone (osteomyelitis)
- Permanent disability; abnormal deformity of the ankle
How is Talus Fracture Treated?
A high percentage of Talus Fractures require surgery. However, this injury may also be treated non-surgically. The nonsurgical treatment measures include:
- Any activity that aggravates the ankle/foot condition should be avoided. The physician may advise the individual to refrain from participating in any physical activities, till the pain or symptoms get better
- Applying ice to the ankle can help reduce pain and swelling
- Complete immobilization of the ankle/foot with a cast, may be required to restrict movement
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory oral medications, such as indomethacin and naproxen, may be used to treat a Talus Fracture. These medications can help decrease the pain and swelling
- Individuals are likely to need physical therapy exercises after the cast is removed. The goals of these exercises are to strengthen the foot muscles, improve flexibility, and decrease stiffness. It may take several months for an individual to complete the physical therapy program and regain full strength and functionality
Surgical treatment methods include:
- Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF): Open reduction is a surgical procedure to realign the fractured bone, to its original position. Surgical hardware (such as plates, screws, or rods) is then used to stabilize the fractured bone under the skin
How can Talus Fracture be Prevented?
To prevent a Talus Fracture, individuals should be careful and consciously aware, while performing any physical activities, such as sports, or even some normal daily activities that could lead to situations involving accidents. Children must be provided a safe environment to work, study, or play. Any possible dangers should also be anticipated and appropriate safety measures adopted.
A few ways to further help prevent unwanted injuries or a Talus Fracture include:
- Individuals, who participate in any high-risk sports, should wear appropriate safety equipment to help prevent the possibility of such fractures
- Wearing appropriate footwear (such as the proper shoe size), may help prevent accidents
- Consuming foods rich in calcium, such as milk, yogurt, and cheese, help build bone strength. Regular diet with appropriate calcium-intake is recommended, even after a Talus Fracture. For women, the recommended amount of calcium, increases with age and menopause
- Perform weight-bearing exercises to strengthen bones
What is the Prognosis of Talus Fracture? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- A high percentage of Talus Fractures heal without any serious complications
- A full recovery and a return to sports or normal daily activities usually require a few weeks to several months, depending on the severity of the injury
- When properly treated and rehabilitated, usually under the guidance of a physiotherapist/specialist, a high percentage of individuals regain their full strength and range of motion in the injured ankle/foot
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Talus Fracture:
A Calcaneus Fracture is a disabling injury that occurs when one or more bones of the heel, fractures. Hence, this fracture is also known as a Heel Bone Fracture (of the calcaneus).
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.