What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Fiebre Manchada
- Rickettsia Rickettsii Infection
- Sao Paulo Fever
What is Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever? (Definition/Background Information)
- Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF) is a serious and life-threatening infectious disease caused by the bacteria Rickettsia rickettsii belonging to the Rickettsiaceae family
- Rickettsial diseases are caused by bacteria, which reside inside the cells of another living entity (a host such as ticks). These bacteria then cause an infection in humans, when transmitted through the host/carrier bites
- The bacteria causing Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever are carried by American dog ticks (called Dermacentor variabilis), wood ticks (called Dermacentor andersoni), and brown dog ticks called Rhipicephalus sanguineus
- Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever is generally seen in parts of North, Central, and South America. The disease is commonly reported in children, elderly adults, and alcoholics. Individuals belonging to the African-American community are reported to have a genetic predisposition for contracting the disease
- People, who have pets at home, or spend significant amounts of time outdoors, or travel to regions with high incidence rates of RMSF, also have a higher risk
- Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever is characterized by the onset of sudden headache, fever, muscle pain, and skin rashes. Several immunological, biochemical, and/or organ function assays or tests may be employed to accurately diagnose RMSF
- Severe cases of infection can lead to failure of vital organs, such as the kidneys, brain, heart, or lungs. Meningitis, or inflammation of the membrane covering the brain and spinal cord; and pneumonitis, or inflammation in the lungs, have also been reported as complications
- Prompt treatment of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever with antibiotics is recommended, if the healthcare provider suspects a Rickettsia rickettsii infection. It is also recommended that treatment be initiated within 5 days of the start of symptoms. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment can help cure the condition. However, a delay in treatment can potentially lead to complications and fatalities
- Presently, there is no vaccine available for Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever. However, infection with Rickettsia rickettsii can be prevented by avoiding tick bites using insect repellents, wearing full-sleeved shirts that are tucked into full pants when venturing outdoors, and seeking prompt medical attention if any symptoms are observed
Who gets Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever? (Age and Sex Distribution)
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever can infect individuals of any age group and both male and female genders. However, the infection is more common in the following categories:
- Individuals living or traveling to the endemic (tick-infested) regions of south, central, and north Americas
- Children and teenagers below the age of 15 years
- Severe infection is seen in the following groups:
- Elderly people
- Alcoholics
- African-Americans
The disease can occur all over the USA; although, it is more commonly observed in Oklahoma, Arkansas, Tennessee, Missouri, and North Carolina.
What are the Risk Factors for Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever? (Predisposing Factors)
The following are some risk factors known to be associated with Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever:
- Traveling to an area with a high incident rate of RMSF
- Being in tick-infested areas in the summer, since ticks are seen in more numbers during the summer months
- Being outdoors more often: Individuals, who frequently visit forests or wooded areas for camping/hiking or undertaking field studies
- Owning pets: Pet dogs that are allowed to roam outdoors, can get infected with ticks and carry them inside the house, increasing the likelihood of human infection
- Elderly adults have a higher risk for infection
- Alcoholics have a higher susceptibility to RMSF
- Belonging to the African-American community: An inherited enzyme deficiency is reported to make them more vulnerable to RMSF
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases one’s chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever? (Etiology)
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever is caused by the bacterium Rickettsia rickettsii, of the Rickettsiaceae family.
- These bacteria reside in carrier ticks and infect humans through bite
- RMSF is carried by American dog ticks (Dermacentor variabilis), wood ticks (Dermacentor andersoni) and brown dog ticks (Rhipicephalus sanguineus)
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever?
The signs and symptoms of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever generally appear within 2-14 days after an individual gets bitten by the carrier ticks. RMSF can affect the respiratory system, central nervous system, gastrointestinal system, and renal system.
The signs and symptoms may include:
- Fever and muscle pain
- Lack of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Severe headaches
- Feeling thirsty
- Diarrhea
- Light-sensitivity (or photophobia)
- Hallucinations
- Parotitis, or salivary gland infection
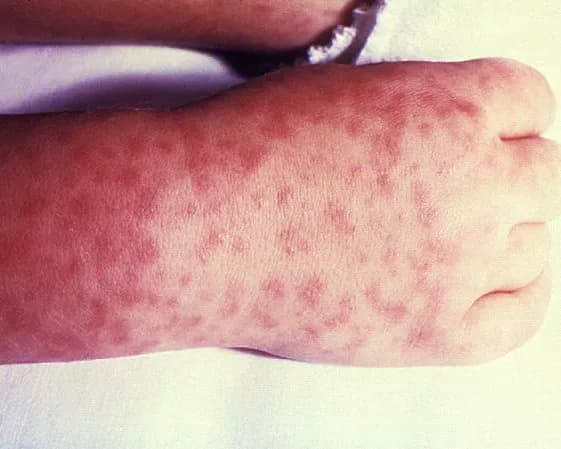
- The formation of small, flat, pink, non-itchy spots or rashes usually on the wrist, forearm, and ankles
- Conjunctivitis
- Neurological symptoms such as:
- Stiff neck
- Hearing difficulty
- Confusion
- Weakness and paralysis
If the infection is severe, additional symptoms such as the following, may be observed:
- Drop in blood platelets level (a condition known as thrombocytopenia)
- Hyponatremia, or a condition where there is deficiency of sodium in the body fluids
- Elevated liver enzyme levels
How is Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever Diagnosed?
A healthcare provider may employ one or more of the following tests for an accurate diagnosis of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever and complications arising from the condition:
- A physical examination of the individual, and a thorough assessment of his/her symptoms
- Complement fixation tests: Immunological tests used to detect the presence of specific antibody to the infecting bacterium
- Immunofluorescence techniques to detect the antibodies
- Complete blood tests to check blood counts, as well as ascertain the level of antibodies to the bacterium, using immunofluorescence techniques such as:
- Immunofluorescence assay (IFA)
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR), to check for the presence of genetic material of the bacteria
- Kidney function tests to assess the extent of infection in the kidneys
- Partial thromboplastin time test, to check for bleeding problems and blood clots
- Prothrombin time test, to check time taken for the liquid portion of blood to clot
- If deemed medically necessary, skin biopsy of rash specimen
- Urinalysis, to check for blood or protein in urine
- Immunohistochemistry to check for the bacterium in affected tissue
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever?
Some potential complications in individuals with Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever include:
- Neurological symptoms including lethargy, confusion, seizures, and delirium
- Heart and lung failure, which could be fatal
- Kidney failure
- Gangrene formation leading to possible amputation of the fingers and toes
- Formation of blood clots causing severe complications
- Meningitis: Infection in the membrane covering the brain and spinal cord
- Pneumonitis (a lung inflammation)
- Shock
A delayed or lack of treatment may lead to more serious complications such as:
- Paralysis of the lower extremities
- Hearing loss
- Loss of bowel or bladder control
- Movement disorders
- Language disorders
- Damage to blood vessels
How is Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever Treated?
It is normally recommended that the treatment for Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever begin within 5 days of appearance of the symptoms. Generally, RMSF is treated with antibiotics such as:
- Tetracycline (Doxycycline)
- Doxycycline is not used in children less than 8 years old, as it can cause staining of the teeth
- It is not prescribed for pregnant women, because it may harm the fetal development and growth
- Chloramphenicol: It is an alternate drug that is used when some individuals develop an allergy to Doxycycline
How can Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever be Prevented?
At the present time, no vaccine is available for prevention of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever. However, one can adopt certain safety measures, to avoid infection and reduce its spread and intensity, such as:
- Minimizing exposed skin to limit tick bites, by wearing long-sleeved shirt, long pants, and socks. Tucking-in shirt (inside pants) and pants (inside socks) may help avoid/reduce tick bites
- Wearing light-colored clothing when going outdoors, so the ticks are more visible
- Using suitable insect repellents while venturing outdoors
- Keeping the surroundings clean, such as the area around one’s house
- When frequenting tick-infested areas, checking for tick bites on pets and self (intermittently checking for ticks), and promptly removing any adhering ticks from the body
- Removing adherent ticks using tweezers: Removing them with bare hands may lead to direct contact with the ticks, thereby increasing the chances of an infection
- Applying antiseptic cream to the affected area after removing the ticks
- Seeking medical attention as soon as symptoms become apparent
What is the Prognosis of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
The prognosis of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever is generally reported to be good.
- Prompt treatment upon presentation of the typical symptoms can leads to a complete recovery
- Even though complications are very rare, there is a reported fatality rate of 3%. Also, if the infection is left untreated, about three-fourths of cases result in death (especially among the highly-vulnerable population group)
Additional and Relevant Useful information for Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever:
Please visit our Infectious Diseases Health Center for more physician-approved health information:
http://www.dovemed.com/diseases-conditions/infection-center/
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.