What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Aseptic Necrosis of the Hip
- Avascular Necrosis of the Hip
- Ischemic Bone Necrosis of the Hip
What is Osteonecrosis of the Hip? (Definition/Background Information)
- Osteonecrosis is a serious disorder characterized by the temporary or permanent disruption of blood supply to the bone, which causes cells within the affected bone to die
- Osteonecrosis of the Hip is a gradual disorder that may affect one or more joints of the hip. Individuals begin to experience joint pain that usually progresses slowly
- Excess consumption of alcohol may lead to development of the condition. Middle-aged men have the highest rate of incidence
- Treatment associated with Osteonecrosis of the Hip includes both nonsurgical and surgical methods
Who gets Osteonecrosis of the Hip? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Osteonecrosis of the Hip may occur in individuals of all age, race, ethnic group, and belonging to any gender
- A high percentage of individuals who develop the condition are middle-aged men
What are the Risk Factors for Osteonecrosis of the Hip? (Predisposing Factors)
Common risk factors associated with Osteonecrosis of the Hip include:
- Excess consumption of alcohol may lead to its development
- Individuals, who sustain a hip dislocation or a hip fracture, while participating in sports such as football
- Systemic lupus erythematosus: Autoimmune systemic inflammatory conditions that occur when an individual’s immune system create antibodies, which accidentally attack healthy tissues and organs within the body
- Decompression sickness: A disorder characterized by abnormal formation of nitrogen bubbles within the blood and tissues, usually seen in divers, when they move up from the water (high-pressure medium) to the surface (low-pressure medium) too soon
- Sickle cell anemia: An inherited condition characterized by crescent-shaped red blood cells in the body, obstructing blood flow and causing reduced amounts of oxygen transportation
- Gaucher’s disease: A rare inherited disorder caused by excessive accumulation of fatty substances (lipid) in the cells and certain organs. This excess build-up of fatty substances can prevent the liver, spleen, lungs, bone marrow, and in rare cases the brain, from functioning properly
- Crohn’s disease: A disease causing inflammation of the digestive tract lining
- Arterial embolism: Blood flow obstruction to an organ or body part, caused due to an embolus (a blood clot or fat particle) within the artery
- Thrombosis: Blood clot that occurs within blood vessels
- Vasculitis: A condition that causes inflammation of blood vessels
- Prolonged consumption of a steroidal medication, such as prednisone
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases one's chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Osteonecrosis of the Hip? (Etiology)
Causes associated with Osteonecrosis of the Hip include:
- Individuals, who suffer injuries, while participating in sports
- Excess alcohol intake
- Perthes disease: Children who develop a rare childhood hip disorder caused by the temporary loss of blood flow to the ball portion of the hip joint
- Peripheral vascular disease: The contraction and hardening of blood vessels within the legs and feet
- Slipped capital femoral epiphysis: Adolescents develop this unusual condition, due to a weakness of the growth plate, causing the femur/thighbone head, to slip backwards
- Sickle cell anemia: A genetic condition caused by odd-shaped red blood cells that tend to obstruct the flow of blood to different body parts
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (or lupus): An auto-immune systemic inflammatory condition that occurs when an individual’s immune system create antibodies that accidentally attack healthy tissues and organs within the body
- Decompression sickness: A disorder characterized by abnormal formation of nitrogen bubbles within the blood and tissues, usually seen in divers, when they move up from the water to the surface too soon
- Radiation therapy, which uses high-energy beams to shrink tumors and destroy cancer cells
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Osteonecrosis of the Hip?
Signs and symptoms of Osteonecrosis of the Hip include:
- Noticeable pain and tenderness in the hip
- Swelling of tissue (due to inflammation) around the hip joint
- Stiffness, reduced mobility of the hip joint
- Difficulty walking
How is Osteonecrosis of the Hip Diagnosed?
Diagnostic methods that a physician may use to help diagnose Osteonecrosis in the Hip include:
- Physical examination and evaluation of medical history
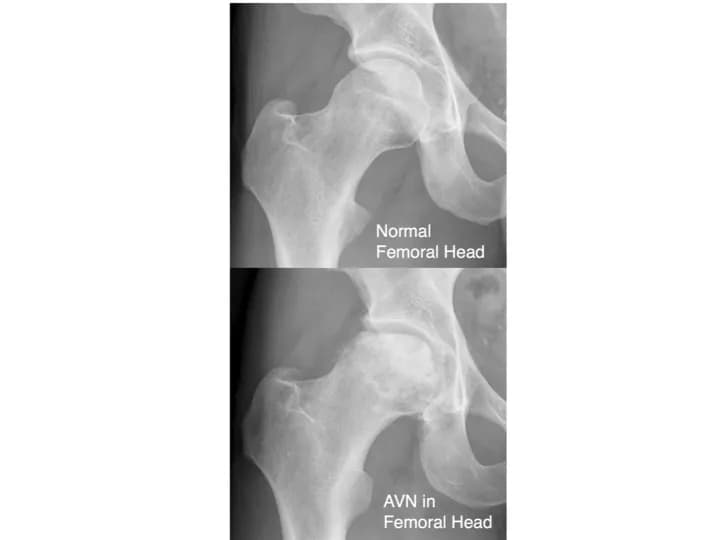
- X-ray of hip: X-rays are utilized to visualize images of the hip. It can also help the physician rule out other possible causes of hip discomfort. During the early stages of osteonecrosis, it is difficult to locate the appearance of any abnormal bone changes. However, x-rays can usually identify the presence of Osteonecrosis of the Hip, during the later stages
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): An MRI is an imaging technique that creates images of soft tissues and bones, which helps detect any bone abnormalities, during the early stages of osteonecrosis
- Bone scan: A bone scan is a diagnostic method used to identify any bone abnormalities by injecting tiny amounts of radioactive material into the bloodstream
- Computerized tomography (CT):A CT scan takes a series of x-ray images from several different angles, which are then merged to create cross-sectional images of bones and soft tissues of the body. This allows a physician to examine the hip joint and its surrounding structures
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Osteonecrosis of the Hip?
A few complications associated with Osteonecrosis of the Hip could include:
- Deterioration of the hip bone
- If left untreated, the hip bone may collapse
- Chronic disability
How is Osteonecrosis of the Hip Treated?
The treatment of Osteonecrosis in the Hip includes nonsurgical and surgical methods. A healthcare provider may start with non-surgical treatment methods before adopting surgical procedures and techniques. These include
- Applying ice to the hip can help reduce the pain and swelling
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory oral medications, such as Ibuprofen and naproxen, may be used to help decrease hip pain and swelling
- Medications for osteonecrosis may decrease the progression of this condition
- Corticosteroid injections help provide temporary relief of symptoms, and in improving the range of motion. It is important to note that corticosteroid injections only give temporary relief. Prolonged episodes of such injections, may injure the joints in the long-run
- After the symptoms has decreased, it is important to begin some light motion exercises. Physical therapy may help restore strength, as well as provide flexibility, to the muscles
Surgical treatment measures include:
- Partial hip replacement: Partial hip replacement is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of one part of the hip joint. This surgical procedure is recommended, if the disorder is confined to a certain area of the hip. A part of the hip is then removed and replaced using a prosthetic implant
- Total hip arthroplasty: Total arthroplasty involves the complete removal of cartilage within the hip joint. The hip joint (acetabulum and femoral head) is then removed and replaced by a metal and plastic prosthetic implant. A physician will recommend this surgical procedure, if the disorder affects the entire hip joint
- Cartilage grafting: Cartilage grafting is a surgical procedure to replace the damaged hip cartilage, which may be damaged due to osteonecrosis, or any traumatic injury
- Core decompression: Core decompression is used to treat early stage osteonecrosis. In this surgical procedure the pressure within the bone is decreased by removing a part of the bone causing the abnormal pressure
How can Osteonecrosis of the Hip be Prevented?
A few recommendations to help prevent Osteonecrosis of the Hip include:
- Avoid excessive intake of alcoholic beverages
- Individuals, who participate in any high-risk sports, such as football, should wear appropriate safety equipment to help prevent a serious injury
- Undertake a proper treatment of lupus
- Wear proper equipment while scuba-diving to avoid decompression sickness
- Monitor consumption of steroidal medications
- Maintain a low cholesterol diet
- Avail proper treatment that can help control or minimize blood vessel damage, associated with vasculitis
- Proper treatment of Crohn’s disease will help prevent the development of Osteonecrosis of the Hip
- Treatments that improve the blood flow to organs or any other body part
- Proper treatments of blood clots that occur within blood vessels
What is the Prognosis of Osteonecrosis of the Hip? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- If treated early, a high percentage of individuals, who develop Osteonecrosis of the Hip, may show an improvement and experience favorable outcomes
- The amount of bone damaged by this disorder significantly affects its prognosis
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Osteonecrosis of the Hip:
Osteoarthritis of the hip is a gradual progressive degenerative disorder that affects one or more joints of the hip. Individuals, who develop the condition, begin to experience pain and stiffness within the hip that usually increase with age.
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.