What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Fetal Meconium Aspiration Syndrome
- Meconium Aspiration Pneumonitis
- Neonatal Meconium Aspiration Syndrome
What is Meconium Aspiration Syndrome? (Definition/Background Information)
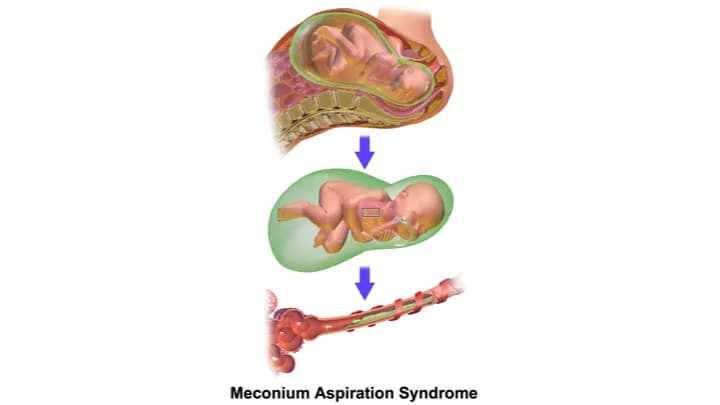
- Meconium Aspiration Syndrome (MAS) is when a newborn baby breathes-in a fluid containing amniotic fluid with meconium into his/her lungs during the time of delivery. Meconium is the dark green feces from the first bowel movement of the baby
- Meconium Aspiration Syndrome can also be defined as the presence of any meconium below the level of the vocal cords in the baby. Babies, who are under stress, due to reduced blood flow and oxygen from the placenta, may pass meconium while in the uterus. This may potentially result in MAS during birth
- Some risk factors for Meconium Aspiration Syndrome include a ‘past the due date’ pregnancy, certain health conditions of the mother (such as hypertension and diabetes), and a long labor
- The condition may cause breathing difficulties in the infant, a low heart rate, or blue-colored skin. Meconium Aspiration Syndrome may lead to complications that include hearing loss, infection, or even a collapsed lung
- Treatment for Meconium Aspiration Syndrome often involves clearing the airway, or aiding the infant during respiratory distress when breathing is difficult. The prognosis is very good in most cases with appropriate treatment
- Meconium Aspiration Syndrome may be prevented by staying healthy throughout the pregnancy and adhering to the advice of the healthcare provider during the prenatal period. It is also important that certain health issues of the expectant mother (such as diabetes, low blood pressure), if any, be kept under control
Who gets Meconium Aspiration Syndrome? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- It is estimated that up to 25% of the newborns may have meconium present in the amniotic fluid during the time of birth
- It is also estimated that up to 10% of the babies may aspirate the fluid, meaning that Meconium Aspiration Syndrome occurs in about 1 in 10 cases of childbirth
- The condition affects both sexes equally and no preference is noted
- MAS is a common condition that is observed around the world; no particular racial or ethnic preference is noted
What are the Risk Factors for Meconium Aspiration Syndrome? (Predisposing Factors)
The risk factors for Meconium Aspiration Syndrome may include:
- The expectant mother having diabetes and/or high blood pressure (hypertension)
- Pregnant women who are heavy (cigarette) smokers
- A long labor or delivery issues
- Aging of the placenta; if the pregnancy exceeds the due date (beyond 42 weeks)
- Post-term delivery or post-mature delivery with indications of long nails, yellow-stained nails, yellowing of the skin/umbilical cord, etc.
- Fetal distress, which can be caused by disrupted blood flow to the baby during childbirth
- Complications of the umbilical cord caused by other medical conditions
- Pregnant women having cardiovascular disease or respiratory conditions
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases the chance of getting a condition in comparison to an individual without any risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
At the same time, not having a risk factor does not mean one will not get a condition. For more clarity, discuss with your healthcare provider the effects of risk factors.
What are the Causes of Meconium Aspiration Syndrome? (Etiology)
Meconium Aspiration Syndrome is caused by the newborn baby breathing-in meconium, which is early feces (stool) passed by the baby right after birth.
- Babies could pass meconium while still in the uterus. This can happen when babies are “under stress” when blood and oxygen flow decrease, due to placental abnormalities or defects
- An inhalation of meconium occurs, if the baby gasps while in the womb or during the initial breaths following delivery. The inhaled meconium can block the baby’s airways. Following birth, breathing problems can occur because of swelling (inflammation) of the baby’s lungs
- If there is a medical issue, such as an infection or lack of flow in the umbilical cord, the baby may not be able to get enough oxygen
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Meconium Aspiration Syndrome?
Some signs and symptoms of Meconium Aspiration Syndrome that are observed in the newborn baby may include:
- Bluish-colored skin (cyanosis)
- Difficulty in breathing, rapid breathing, or no breathing (fetal apnea)
- The infant is limp at birth due to poor muscle tone
- Green streaks or stains in the amniotic fluid or on the baby’s skin
- The fetus has low heart rate during the period immediately before birth
- The baby has a low Apgar score; low Apgar scores indicate severe stress during the birthing process
- Any signs that show the baby is overdue, such as the presence of long nails, called over term pregnancy
- Infants exposed to meconium for a length of time may have yellow skin or nails
How is Meconium Aspiration Syndrome Diagnosed?
After the healthcare provider documents a thorough medical history and physical examination, Meconium Aspiration Syndrome may be diagnosed through the following tests:
- The fetus has a slow heart rate, as seen on a monitor device
- Meconium is visible in the amniotic fluid or on the newborn (further examination must be performed)
- A stethoscope may be used to listen to the newborn baby’s breathing; abnormal, irregular or crackled breathing may be heard
- Analysis of blood may show lowered oxygen levels and increased carbon dioxide levels
- A chest X-ray is used to see if there are streaky or patch-like areas in the infant’s lungs
- The most accurate test that a healthcare provider can use is a laryngoscope to see meconium staining on the infant’s vocal cords. A laryngoscope is a scope that is inserted into the throat to observe the vocal cords
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Meconium Aspiration Syndrome?
The possible complications of Meconium Aspiration Syndrome include:
- The infant may have to be placed on a breathing machine
- The baby’s breathing can be affected because of irritation to the lung tissue, due to a meconium plug that blocks the airway, or by an infection. This may also lead to inactivation of the pulmonary surfactant (a natural substance coating the lungs that allows it to be properly filled)
- Collapsed lung
- Babies who are severely affected are at risk of chronic lung disease
- Severely affected infants may lose their sense of hearing or may have developmental abnormalities
- If oxygen is cut-off for too long, it may lead to brain damage
In extremely rare cases, Neonatal Meconium Aspiration Syndrome may be fatal.
How is Meconium Aspiration Syndrome Treated?
The specific treatment for Meconium Aspiration Syndrome depends on the amount of meconium inhaled, the length of time the infant was exposed to the same, and the severity of respiratory distress. Meconium Aspiration Syndrome can be treated by aiding the infant with breathing immediately after birth.
If traces of meconium are present in the amniotic fluid, a specialized medical team (preferably consisting of a neonatologist) should be present to help in the treatment process. This is because intensive care may be required in babies showing signs of MAS.
- In case there is an obstruction in the airways, the healthcare provider may gently tap on the chest of the baby to loosen the obstruction
- If required, during delivery, a laryngoscope may be inserted into the infant’s throat to remove any remaining meconium
- A face mask with a bag may be used to help the infant breathe. This will give the baby oxygen to inflate the lungs
- A radiant warmer may be used to maintain the baby’s body temperature
- If necessary, a breathing machine or ventilator can help keep the baby’s lungs full of air and supply oxygen
- Antibiotics may be administered in case of an infection following birth of the child
If required, the newborn may have to be placed in neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) for a few days to be monitored and treated.
- In the case of severe aspiration, the treatments may include:
- Surfactant therapy may be used, which can help keep the air sacs open
- High-frequency oscillatory ventilation: A procedure using a type of ventilator to deliver oxygen-rich air to the infant’s lungs
- A technique called rescue therapy may be used to help the baby with breathing adequate oxygen. Rescue therapy is a procedure of using nitric oxide in the ventilator machine, which lets more blood and oxygen reach the lungs
- If all the above therapies do not work, extra-corporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), which is a form of cardiopulmonary bypass (an artificial lung and heart) will be used to supply blood to the infant
Note: If the baby is active and crying, even when meconium is present, no additional treatment is generally needed, because the airways are not blocked.
How can Meconium Aspiration Syndrome be Prevented?
Meconium Aspiration Syndrome can be potentially dangerous. It can be prevented through adequate prenatal care, which includes staying healthy throughout one’s pregnancy and strictly adhering to the medical advice of a healthcare provider.
- Preventive methods also include anticipation of conditions that would place the baby at an increased risk for MAS. Healthcare providers will prepare ahead for meconium presence, if the following conditions are noted:
- The expectant mother’s amniotic sac has ruptured at home (i.e., the water broke) and the presence of a green or brown substance was observed in it, or the fluid was clear
- Prenatal tests taken during pregnancy indicates possible health issues
- Any signs of distress that is noted while the fetus is being monitored
- Amniofusion treatment can help decrease the incidence of Meconium Aspiration Syndrome
- In this treatment procedure, saline is injected into the amniotic cavity around the fetus during childbirth. This procedure is used after the membranes have ruptured
- Amniofusion helps dilution of the meconium in the amniotic fluid; washing-out the meconium before the infant inhales the fluid
What is the Prognosis of Meconium Aspiration Syndrome? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- The prognosis of Meconium Aspiration Syndrome is very good in most cases
- Some breathing issues may occur in severe cases, but these are often known to disappear within 2-4 days
- Rapid breathing may continue for several days in severe cases. However, the necessity to use a breathing machine is generally uncommon
- In very rare cases, permanent lung damage is seen to occur
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Meconium Aspiration Syndrome:
- Sometimes, the presence of meconium is seen, because there may be some other health issue concerning the baby
- A serious condition of blood circulation, to and from the lungs, is called persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN). Due to this, the infant may not have the ability to get enough blood into the lungs and to the rest of the body
- Some studies have shown that infants with Meconium Aspiration Syndrome may have a higher risk for diseases affecting the airways such as asthma
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.