Liver Cirrhosis
What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Cirrhosis of the Liver
- Fibrosis of the Liver
- Scarring of the Liver
What is Liver Cirrhosis? (Definition/Background Information)
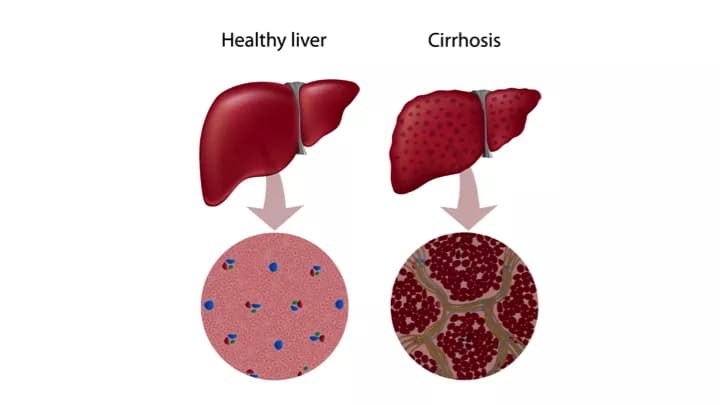
- Liver Cirrhosis is a condition that is caused by a sudden or continuous damage to the liver tissue. Scar tissue forms in the liver when damage occurs. This tissue replaces healthy liver tissue and blocks the normal flow of blood to the liver. The liver cannot heal itself once extensive damage and scarring have occurred
- This condition is commonly seen in adults with excessive alcohol consumption, due to viral infections (hepatitis B or C infection), obesity, and abuse of certain drugs and medications
- Early signs and symptoms of liver cirrhosis include fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, and the development of spider-like veins. As the condition progresses, more severe signs and symptoms arise that may include jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), edema (fluid accumulation), pale stools, and uncontrolled bleeding
- Portal hypertension (high blood pressure in the portal vein), spleen enlargement, and excessive bleeding are some of the common complications of Cirrhosis of the Liver
- The treatment of Liver Cirrhosis is undertaken to control the signs and symptoms of the disorder and to ensure that the cirrhosis does not progress and worsen. Some of the treatment options may include the use of medication, endoscopy, or even a liver transplantation
- Preventative measures to reduce the likelihood of developing the condition include drinking alcohol in moderation, bringing about healthier diet and lifestyle changes, taking vaccinations against viral infections, and practicing safe sex
Who gets Liver Cirrhosis? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Cirrhosis of the Liver can occur in individuals of all ages. It is, however, more common in adults than children
- No racial, ethnic, or geographical predominance is observed
What are the Risk Factors for Liver Cirrhosis? (Predisposing Factors)
The risk factors of Liver Cirrhosis include:
- Alcohol abuse, heavy consumption of alcohol
- Chronic hepatitis B and hepatitis C infection
- The overuse of certain drugs and medications can overburden the liver and cause them to become toxic to the liver. This can result in the development of Liver Cirrhosis
- Obesity and excess fat deposits around the abdomen can increase one’s risk of developing the condition
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases one's chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Liver Cirrhosis? (Etiology)
Liver Cirrhosis is the formation of scar tissue on the liver caused by sudden or continuous damage of the liver tissue. It is a serious, progressive, and irreversible condition in which healthy liver tissue is replaced by scar tissue that blocks the normal flow of blood to the liver.
Cirrhosis of the Liver can be caused by a variety of factors and conditions, which may include:
- Heavy alcohol consumption (typically the most common cause of Liver Cirrhosis) can overwhelm the liver such that it is unable to properly filter and breakdown alcohol. This can damage the liver and result in cirrhosis
- Chronic hepatitis B and C infections are viral infections that attack the liver. Continuous attack on the liver can wear it down, leading to liver damage and cirrhosis
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease can result in fat accumulation in the liver cell. This can impair liver function and cause damage to the liver tissue, resulting in scarring and cirrhosis
- Injury to the bile ducts, which can occur in conditions such as primary biliary cirrhosis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, and biliary atresia, can also cause Liver Cirrhosis to develop
Certain genetic disorders may also cause Liver Cirrhosis. These include:
- Wilson’s disease: This condition leads to the accumulation of excess copper in the liver, brain, kidneys, and corneas, which can become toxic for the liver and cause cirrhosis
- Hemochromatosis: This condition causes the accumulation of iron in the liver and other organs that is toxic to the liver, resulting in Liver Cirrhosis
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Liver Cirrhosis?
Early symptoms of Liver Cirrhosis can include:
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Nausea
- Stomach pain
- Development of spider-like veins
As the liver becomes damaged further and the cirrhosis progresses, the liver function worsens. This can lead to symptoms that may include:
- Edema; fluid buildup in the legs
- Ascites; fluid accumulation in the abdomen
- Redness of the palms
- Easy bruising
- Abnormal bleeding
- Pale stools
- Jaundice; yellowing of the skin and eyes
Females with Liver Cirrhosis may additionally experience menstrual abnormalities including irregular or absent periods. Males with Liver Cirrhosis may moreover experience impotence, loss of sexual drive, and breast enlargement.
How is Liver Cirrhosis Diagnosed?
A diagnosis of Liver Cirrhosis may include:
- Evaluation of the individual’s medical (and family) history with a thorough physical examination. An evaluation of medical history can help determine the presence of predisposing factors such as alcohol abuse, hepatitis B or C infection, or any associated genetic disorder
- Blood tests that include:
- Liver function tests: These provide information about the state of the individual’s liver. The levels of albumin, bilirubin, liver transaminases (AST and ALT), and alkaline phosphatases are determined
- Excess bilirubin and excess levels of various liver enzymes can indicate that liver damage has occurred
- Viral serology to check for the presence of hepatitis B and C infection
- Ultrasound, MRI, and CT scans may be used to image the liver and determine if cirrhosis has occurred
- Liver biopsy is the most definitive diagnostic tool to establish Liver Cirrhosis
In a liver biopsy procedure, the physician removes a sample of liver tissue and sends it to the laboratory for histopathological examination, where a pathologist examines the biopsy sample under a microscope. The pathologist arrives at a definitive diagnosis on a thorough evaluation of the clinical and microscopic findings, as well as by correlating the results of special studies on tissues (if any performed).
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions in order to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Liver Cirrhosis?
Complications associated with Liver Cirrhosis depend on the severity of the condition, which may include:
- Portal hypertension: Increased pressure in the blood vessels of the liver
- Enlarged veins in the esophagus, stomach, and anal canal that can bleed easily
- Bleeding disorders
- Enlargement of the spleen (splenomegaly)
- Fluid accumulation in the abdomen (ascites) and secondary infection of the fluid
- Kidney failure
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (a type of liver cancer)
- Hepatic encephalopathy: Mental confusion or changes in the level of consciousness due to the accumulation of toxins in blood that are not cleared by the damaged liver
How is Liver Cirrhosis Treated?
There is no cure for Liver Cirrhosis. The treatment is directed at controlling the signs and symptoms of the disorder. The various treatment methods used depend on the set of symptoms observed. These include the use of:
- Water pills (diuretics) to get rid of excess fluid
- Vitamin K and blood products to prevent excess bleeding
- Medicines (such as lactulose) to remove toxins from the blood of individuals with hepatic encephalopathy
- Antibiotics to control infections
- Endoscopic treatment of enlarged vessels in the esophagus and stomach
- Removal of excess fluid from the abdominal cavity by a procedure called paracentesis
If the liver is severely damaged and the symptoms can no longer be controlled using conservative measures, then a liver transplantation may be required.
How can Liver Cirrhosis be Prevented?
Some of the risk factors of Liver Cirrhosis may be controlled and chances of development of the condition lowered. Such preventive measures can include:
- Drinking alcohol in moderation (no more than 2 drinks per day for men and 1 drink per day for women)
- Get vaccinated against the hepatitis infections
- Practice safe sex to lower the risk of contracting hepatitis B
- Avoid sharing needles to lower the risk of contracting both hepatitis B and C infections
- Eat a healthy and balanced diet and avoid obesity
What is the Prognosis of Liver Cirrhosis? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- The prognosis of Liver Cirrhosis depends on the severity of liver damage
- The condition cannot be cured or reversed. Once the liver is damaged and scarred, it cannot be healed completely
- If cirrhosis progresses and worsens, it can lead to serious complications that include liver cancer and may even result in death
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Liver Cirrhosis:
- Liver Cirrhosis is the tenth leading cause of death amongst males and the twelfth leading cause of death amongst females
- Hepatitis C Infection is a viral infection that causes inflammation and injury to the liver. It is caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV)
The following article link will help you understand hepatitis C infection:
http://www.dovemed.com/diseases-conditions/hepatitis-c-infection/
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.