What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Abrikossoff Tumor of Colon
- GCT of Colon
- Mucosal Granular Cell Tumor of Colon
What is Granular Cell Tumor of Colon? (Definition/Background Information)
- Granular Cell Tumor (GCT) of Colon is a rare, benign, non-cancerous lesion that forms in the colon (large intestine). Granular cell tumors are not pre-malignant - meaning that individuals are not at an increased risk for developing colon cancer
- It can occur in middle-aged and older men and women aged around 50 years and over
- In most cases, no significant signs and symptoms or complications are present. Occasionally, some Granular Cell Tumors of Colon are known to transform into malignant tumors
- In a majority of individuals, a complete surgical removal of Granular Cell Tumor of Colon results in a cure. The prognosis is generally excellent and it does not usually recur after removal
- However, in rare cases of a malignant transformation of the tumor, the prognosis of Granular Cell Tumor of Colon depends on the stage of the tumor
Who gets Granular Cell Tumor of Colon? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Granular Cell Tumor of Colon usually arise in older adults; most commonly they are found in individuals aged 50 years and over
- However, they can be found in individuals of all ages
- Granular Cell Tumors of Colon have been found in both men and women. It is slightly more common in women than in men
- No racial or ethnic group predilection is observed
What are the Risk Factors for Granular Cell Tumor of Colon? (Predisposing Factors)
The specific risk factors of Granular Cell Tumor of Colon are unknown. However, the general risk factors for formation of other types of colon polyps include:
- Colonic epithelial injury (injury to the epithelial lining cells of the colon)
- A diet which is high in fat and low in fiber
- Smoking
- Lack of exercise
- Weight gain
- Inflammatory bowel disease
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Granular Cell Tumor of Colon? (Etiology)
The exact cause of Granular Cell Tumor of Colon is unknown.
- Researchers have documented certain genetic changes within the tumor. However, cases where these specific genetic mutations have been observed are rare. Thus, studies regarding genetic changes are limited
- GCT is not associated with any known congenital syndrome
- Some researchers believe that Granular Cell Tumor of Colon are formed in response to colon injury or irritation
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Granular Cell Tumor of Colon?
Majority of Granular Cell Tumors of Colon do not cause any significant symptoms. They are often found incidentally during a colonoscopy, which may be performed for other health conditions.
Rarely, the signs and symptoms of GCT of Colon may include:
- Presence of small lesions/polyps in the colon, typically less than 3-4 cm in size
- Bleeding from the anus
- Mucus mixed with stools
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
How is Granular Cell Tumor of Colon Diagnosed?
A diagnosis of Granular Cell Tumor of Colon would involve:
- Physical exam and evaluation of medical history
- Screening colonoscopy: Granular Cell Tumors of Colon are diagnosed during colonoscopies. A colonoscopy is a test that allows the physician to look at the inner lining of the colon and rectum. A typical colonoscopy involves using a thin, flexible tube (called a colonoscope), with an attached video camera, to view the colon and rectum. A polyp will show up as a bump and can be removed during the colonoscopy and sent for testing
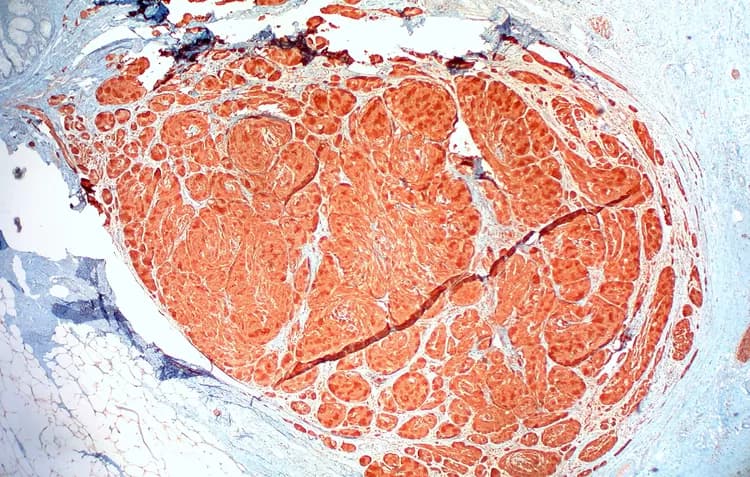
- A tissue biopsy of the tumor (polyp) is performed and sent to a laboratory for a pathological examination
- A pathologist examines the biopsy under a microscope. If it is indeed a polyp, a distinct appearance is noted by the pathologist. After putting together clinical findings, special studies on tissues (if needed) and with microscope findings, the pathologist arrives at a definitive diagnosis
- Examination of the biopsy under a microscope by a pathologist is considered to be gold standard in arriving at a conclusive diagnosis
- Biopsy specimens are studied initially using Hematoxylin and Eosin staining. The pathologist then decides on additional studies depending on the clinical situation
- Sometimes, the pathologist may perform special studies, which may include immunohistochemical stains, molecular testing, and very rarely, electron microscopic studies to assist in the diagnosis
A differential diagnosis may be performed to exclude other tumor types before arriving at a diagnosis. This may include:
- Perineuriomas
- Granular cell tumors
- Inflammatory fibroid polyp
- Ganglioneuroma
- Schwannoma
- Neurofibroma
- Mucosal prolapse (cloacogenic polyp)
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Granular Cell Tumor the Colon?
- Granular Cell Tumors of Colon is normally not harmful, due to their benign nature. Therefore, any complications arising from such polyps are typically minimal
- Nevertheless, in rare cases, GCT of Colon may be malignant. In such cases, the tumor may spread to others part of the body
How is Granular Cell Tumor of Colon Treated?
Due to predominantly benign (non-cancerous) nature of Granular Cell Tumor of Colon, they do not require any treatment other than a complete removal through surgery.
- Typically, they are removed during a colonoscopy and sent for testing, in order to ensure that they are not cancerous or harmful
- In majority of individuals, a complete surgical resection of the tumor usually results in cure
Sometimes, it is difficult to distinguish between a benign GCT and a malignant GCT. Hence, a complete removal of the tumor is often recommended.
How can Granular Cell Tumor of Colon be Prevented?
Currently, no known preventive methods exist for Granular Cell Tumor of Colon.
- One can lower one’s risk of developing polyps by eating a healthy diet and maintaining a healthy lifestyle
- This includes eating lots of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains; high fat foods should be consumed less
- One must exercise for at least 30 minutes each day
- In general, folic acid and calcium supplements may also reduce the risk of formation of colon polyps
What is the Prognosis of Granular Cell Tumor of Colon? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- The prognosis for most individuals with Granular Cell Tumor of Colon is generally good
- Most individuals with benign GCTs of Colon are able to carry on with a normal quality of life
- Since, there is a minimal risk of these polyps developing into malignant granular cell tumor (cancer), the prognosis of malignant GCTs depend upon the extent of tumor spread and other factors
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Granular Cell Tumor of Colon:
The following article link will help you understand colonoscopy screening procedure.
https://www.dovemed.com/common-procedures/procedures-surgical/colonoscopy/
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.