What are other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Genital Yeast Infection
- Monilial Vaginitis
- Vulvovaginal Candidiasis
What is Genital Candidiasis? (Definition/Background Information)
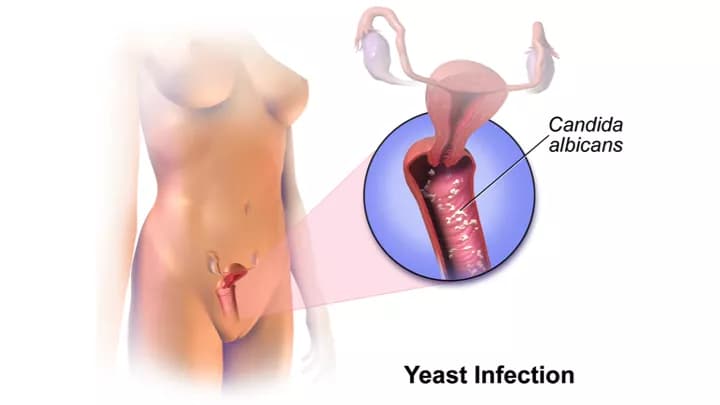
- Genital Candidiasis, generally referred to as a yeast infection, is common infection that about 75% of women worldwide are known to have at least once in their lifetime
- A woman who is pregnant or who has altered hormonal or chemical balance due to antibiotics or medication is at a higher risk for Genital Candidiasis
- A chemical imbalance in the genital region causes the yeast Candida to grow more rapidly, which is the main causal agent for Genital Candidiasis
- Genital Candidiasis may present signs and symptoms of itching and burning rash around the genitals accompanied by a white curd-like vaginal discharge. It does not typically present any complications
- A healthcare specialist can diagnose Genital Candidiasis after a careful physical examination of the pelvic region followed by tests of the vaginal discharge for the causative pathogen
- Genital Candidiasis may be treated using antifungal creams/ointments and oral medication. The prognosis for individuals diagnosed with this yeast infection is typically good with treatment
Who gets Genital Candidiasis? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Genital Candidiasis is very common worldwide and over three-fourths of all adult women may be affected at least once during their lifetime
- Genital Candidiasis is typically a vaginal infection and therefore females are affected much more than males; only very rare cases of infection in males are noted
- Women of any race, ethnicity, or geographic location are prone to Genital Candidiasis
What are the Risk Factors for Genital Candidiasis? (Predisposing Factors)
A woman is more at risk for developing Genital Candidiasis if she has a weakened immune system, or if she experiences the following conditions:
- Pregnancy: Being pregnant increases the risk for Genital Candidiasis due to the changes in hormonal levels
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- Use of higher dose of estrogen hormone replacement pills
- Use of broad-spectrum antibiotics, in some cases
- Immunodeficiency due to factors, such as HIV infection, or other illnesses
- Use of corticosteroids
- Severe iron deficiency anemia
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases one’s chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What Are the Causes of Genital Candidiasis?
Genital Candidiasis is caused by an increased growth of the yeast called Candida.
- Candida is always present on the body in small amounts; an overgrowth causes Genital Candidiasis as a result of a hormonal or chemical imbalance around the vagina
- Estrogen is responsible for the lining of the vagina to mature and contain glycogen, which is a necessary substrate for Candida to grow rapidly. Abnormal estrogen levels create an environment that promotes the yeast growth
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Genital Candidiasis?
The signs and symptoms of Genital Candidiasis can include:
- Itching or burning feeling in the genital area
- A white curd-like vaginal discharge
- A red rash that forms on and around the genitals that may spread to involve a wider area
- In males, the symptoms of Genital Candidiasis may include an itchy red rash on or around the penis
The signs and symptoms may persist for hours, days, or longer, and a medical professional should be contacted if these symptoms are evidently present/noted.
How is Genital Candidiasis Diagnosed?
Genital Candidiasis is diagnosed following a physical (pelvic) examination and a careful examination of the individual’s medical history. The physical appearance of Genital Candidiasis is similar to that of other genital infections, so it is sometimes difficult for a physician to make a diagnosis without further testing. Such tests may include:
- After a physical examination of the pelvic region, a healthcare specialist may place an instrument into the vagina to hold it open and examine the inner walls and cervix
- Samples of vaginal secretions are usually collected in order to determine if there are an abnormally high amount of Candida organisms by looking at the sample under a microscope
- The samples of vaginal secretions can also be tested to identify the fungus that causes the infection, and this can be used to help in treating recurring cases of Genital Candidiasis
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Genital Candidiasis?
Generally, the complications from yeast infections are minimal and typically only involve skin irritation during treatment. Thus, if treatment for Genital Candidiasis is not sought, complications can include persistent uncomfortable symptoms and a potential to pass on the infection to sex partners
With treatment, the complications from Genital Candidiasis may include:
- Cracked skin from continuous itching leading to superimposed skin infections
- Repeat infections directly after treatment or infections that do not respond well to treatment may be indicative of early diabetes
How is Genital Candidiasis Treated?
The treatment for Genital Candidiasis is typically using antifungal creams, ointments, or supplements (that may be even bought at a local pharmacy/drugstore without visiting a medical professional).
Treatment and advice for Genital Candidiasis may typically include:
- Prescription of antifungal medications, creams, and ointments
- Keeping the genital area clean and dry
- Avoiding having sexual interaction until completion of treatment
- Avoiding wearing wet or sweaty clothing for an extended period of time; change of dress and after single use
- Keep blood sugar levels under control for diabetics
Although Genital Candidiasis can be treated without seeking medical attention, it is preferable to visit a medical professional. It is also important to contact a medical professional if symptoms are recurrent, or if over the counter treatments are not effective any longer.
Treatment at home is not always recommended but can be sufficient if the woman is not pregnant, and:
- The symptoms are mild and do not include pelvic pain
- It is a first time yeast infection and there is no history of yeast infections in the individual
- There is no concern of a sexually-transmitted disease (STD)
How can Genital Candidiasis be Prevented?
Preventing Genital Candidiasis requires avoiding factors that may cause a hormonal or biochemical imbalance, specifically in the genital regions. Such measures include:
- Avoidance of high doses of estrogen replacement supplements or broad-spectrum antibiotics
- Wearing cotton underwear
- Taking oral or intravaginal probiotics
- Avoiding excessive use of corticosteroids
What is the Prognosis of Genital Candidiasis? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
The prognosis for an individual with Genital Candidiasis is usually very good with treatment.
- The infection can be treated easily with medication and ointment and typically requires no invasive procedures
- One can fully recover from yeast infections with no complications being generally noted; medication typically clears up Genital Candidiasis usually within 7 days or so
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Genital Candidiasis:
According to medical literature, about 20% of the women between ages 15 and 55, who are not pregnant, typically have a yeast infection.
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.