What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- dcSSc (Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis)
- Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis (dcSSc)
- Systemic Scleroderma, Diffuse Type
What is Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma? (Definition/Background Information)
- Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma is a subtype of Scleroderma that affects the skin and a variety of organs such as the gastrointestinal tract, heart, muscles, and joints, causing severe damage to them
- Scleroderma is a chronic connective tissue disorder of unknown cause. Connective tissues give support to the organs and skin. Individuals with Scleroderma have thick or hard connective tissue
There is currently a debate about how Scleroderma should be classified. A majority believe that it should be classified as an autoimmune rheumatic disorder. Due to this, many researchers believe that the damage is caused by immune cells mistakenly attacking one’s own healthy tissue.
Scleroderma can be classified into 2 broad categories, which include Localized Scleroderma and Systemic Scleroderma:
- Localized Scleroderma:
- It often affects the skin tissues only and does not cause harm to the other major organs
- There are two types of Localized Scleroderma, namely Morphea and Localized Linear Scleroderma
- Systemic Scleroderma:
- It affects the skin, tissues beneath the skin, major organs, and blood vessels
- Systemic Scleroderma also has 2 different types, namely Limited Systemic Scleroderma and Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma
Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma is a type of Systemic Scleroderma of unknown cause.
- Commonly, the organs involved include the esophagus , stomach, small intestines, large intestines, heart, muscles, joints, blood vessels, and kidneys
- The complications of Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma include physical hardening of the organs due to abnormal fibrosis of the tissue. This can severely affect the organ function, scar several organ tissues, and create additional complications due to Raynaud’s phenomenon
- Typically, Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma progresses quickly, resulting in severe signs and symptoms and life-threatening complications
- There is currently no cure for Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma, but medications, therapy, and surgery may be used to control symptoms and prevent complications. The treatment measures are dependent upon the tissues or organs affected
- The way Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma changes and progresses over time vary among individuals. The rapidity of progression of signs and symptoms and the organs involved affects the prognosis. Typically, individuals who respond to treatment have a better prognosis than individuals who do not respond to treatment
Who gets Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Individuals of any age can be affected by Scleroderma; however, this connective tissue disorder usually occurs from ages 25 to 55 years
- A majority of Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma cases often occur in individuals between the age of 25 and 55 years, although even children may be affected
- Like Scleroderma, it is thought that Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma occurs more often in females
- Scleroderma is known to occur worldwide, in all races and ethnic groups. Systemic Scleroderma is more common in Native Americans and African Americans than individuals of European decent
What are the Risk Factors for Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma? (Predisposing Factors)
The risk factors for Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma include:
- Females are more likely than males to have Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma
- Native Americans and African Americans are more susceptible to Systemic Scleroderma than individuals of European decent
- Some studies have shown that individuals who have worked or been exposed to silica dust, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and other hydrocarbon vapors may have an increased incidence
- Having a first degree relative (mother, father, full sibling, or child) with Systemic Sclerosis increases one’s personal risk of getting it by 1.5%; a 10-15-fold increase in risk over the general population
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma? (Etiology)
The exact cause of Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma is unknown. Research is currently being performed, to identify the relevant causal factors.
- Many researchers believe that Scleroderma is an autoimmune disorder, where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues resulting in damage of the tissues and organs
- Many different autoantibodies are found in Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma patients, supporting a significant contribution of autoimmunity in the cause of the disease
- Some studies have revealed that there may be a higher risk for the condition, due to occupational exposure to chemicals such as silica dust and PVC
However, research has established the following on Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma:
- It is not an infectious or contagious condition, which means that it cannot be passed on from one individual to another through contact. It is also not a malignant condition
- It is not a straightforward genetic disorder, yet 1.5 % of Systemic Scleroderma patients have a parent, full sibling, or child with the disease. This calculates to a 10-15 fold increased risk to family members with Systemic Sclerosis, Diffuse or Limited
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma?
The signs and symptoms of Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma can vary greatly from individual to individual. This might create confusion in many, since one may not have all of the signs and symptoms described for the condition. In some cases, Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma can be severe, causing significant signs, symptoms, and complications.
The skin-related signs and symptoms of Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma can include:
- Hardening and tightening of the skin of the fingers, hands, arms, toes and feet. This causes restricted movement of the affected area of the skin. The skin of the remainder of the body can also be affected
- Raynaud’s phenomenon: In Raynaud’s phenomenon, the blood vessels of the hands and feet constrict either due to cold weather or when the individual is anxious. This constriction of blood vessels causes severe pain in the hands and feet. It also results in temporary skin color changes in the fingers and toes, pale white, red, or blue
- The facial skin becomes firmer and tighter. Older patients with Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma have fewer wrinkles than expected for their age. Restriction of opening the mouth can lead to difficulty with dental care, self or by a professional
- Hair loss. The collagen infiltration around the hair follicles constricts growth
- Irregular pigmentation of skin; increased and/or decreased (hypopigmentation or hyperpigmentation
- Ulcer formation at the tips of the fingers or toes from poor blood flow and inflexibility when subjected to trauma
- Telangiectasias (visible superficial broken blood vessels) appear of the face and chest, often numerous
- The skin at the base of the fingernails shows many superficial dilated blood vessels
- Small hard deposits of calcium form on the skin of the fingers
- Joint pain and painful joint movement; pain in the feet
Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis produces many extensive, severe, and rapidly progressive internal organ damage.
- The lungs become stiff with excess collagen, leading to shortness of breath
- Dry cough
- Constipation or diarrhea based on poor intestinal motility
- Difficulty absorbing nutrients
- Difficulty swallowing because of stiffness of the esophagus. Liquids and pureed foods might be required to overcome this
- Decreased renal (kidney) function, with eventual complete renal failure is possible
- The changes in kidney function, as well as arterial involvement, can lead to high blood pressure
- Heart failure can occur because the collagen infiltrating the heart muscle; making the heart so stiff that it cannot dilate normally to fill with an adequate blood volume
- Pulmonary arterial hypertension can put additional strain on the heart and lungs
- Disrupted heart, lung, kidney, or liver function can be life-threatening
In Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma, the progression of the signs and symptoms is usually fast, causing severe and sometimes life threatening complications.
How is Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma Diagnosed?
Scleroderma can be difficult to diagnose, as other conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. The presence of common symptoms or skin that thickens quickly makes it easier to diagnose Scleroderma. The following tests and procedures may be used to diagnose Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma:
- A thorough physical examination along with a complete medical and family history
- Blood tests such as anti-nuclear antibody panel, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, complete blood count, rheumatoid factor levels, antibody testing for other autoimmune disorders, and other tests
- Kidney function tests including creatine level, BUN level, glomerular filtration rate (GFR), and urine analysis
- Chest X-ray and CT scan of the lungs to determine the extent of lung scarring (pulmonary fibrosis)
- Pulmonary function test (PFT)
- Electrocardiogram and echocardiogram to determine heart involvement, caused by heart scarring (cardiac fibrosis)
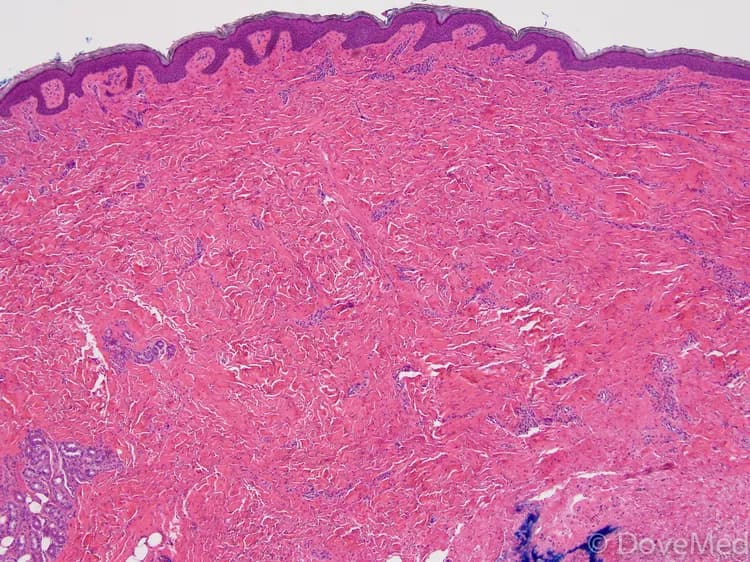
- Skin biopsy: Cells and tissues are examined by a pathologist under a microscope. The pathologist arrives at a diagnosis after analyzing pathology findings along with clinical information of the patient. A pathologist may perform special studies on tissue samples to aid in the final diagnosis
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma?
The hardening of organs due to abnormal fibrosis of the tissue can severely affect the organ function. Complications due to Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma can range from mild to severe and could include:
- Scarring of lung tissue can occur with reduced lung function, lessened ability to breathe, and decreased tolerance for physical activity. This is known as pulmonary fibrosis. One may also develop hypertension (high blood pressure) in the arteries leading to the lungs, known as pulmonary hypertension
- If Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma affects the kidneys, there may be elevated blood pressure and protein in the urine. More severe kidney complications could include renal crisis, leading to rapid kidney failure. For kidney failure, the treatments are dialysis or transplantation
- If Raynaud’s phenomenon that develops from Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma is severe enough then restricted blood flow at the fingertips can cause damage to the tissue, leading to the formation of skin ulcers. In severe cases, amputation may be necessary to avoid gangrene
- Increased blood pressure in the pulmonary arterial system can also raise the pressure on the heart’s right side causing right heart failure. This condition increases the risk for cardiac arrhythmias and congestive heart failure
- Tightening of the facial skin to a great degree can cause the mouth to become narrower and smaller, making it difficult to clean the teeth. It is common for individuals with Scleroderma to produce inadequate amounts of saliva, which also increases the risk for dental decay
- Complications with the digestive system can occur, leading to acid reflux and swallowing difficulties. Alternating episodes of constipation and diarrhea are often seen
- Men may experience erectile dysfunction, whereas women experience decreased lubrication and constriction of the vaginal opening
How is Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma Treated?
Currently, Scleroderma is a condition that has no cure, but is managed through medications, lifestyle modifications, therapy, and surgery. These measures can help control symptoms and prevent complications. Systemic Scleroderma usually worsens over time, as it affects the internal organs.
The treatment options for Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma include:
- Occupational or physical therapists can help individuals with Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma manage pain, increase their strength, and uphold their independence in their everyday lives
- Surgery is considered to be a last resort. Amputation may be necessary in patients whose finger ulcers have developed gangrene. Those with high blood pressure in the lung arteries due to Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma may need lung transplants
The following are the treatment measures for Raynaud’s phenomenon:
- Cessation of smoking: Smoking causes constriction of blood vessels, which causes an increase in symptoms due to Raynaud’s phenomenon
- Keeping hands and feet warm (particularly in colder temperatures), taking medications for anxiety, taking medications that open up the small blood vessels, all are factors that cause a better blood flow to the hands and feet (vasodilators)
- Regular exercise can also help with blood flow to the hands and feet
Treatment measures for painful joints with or without restricted movements include:
- Regular exercise and stretching that helps loosen up the joints
- Pain medication to reduce joint pain
Treatment measures for skin signs and symptoms include:
- Regular use of sunscreen, avoiding hot showers, and regular exercising
- For individuals living in a dry climate with low humidity, the use of a humidifier can help with the signs and symptoms
- Antibiotic ointment for fingertip ulcers
- Plastic surgery may be an option for cosmetic issues; a plastic surgeon can advise on the available treatment options
- It is always important to follow the physician’s advice and take the prescribed medication regularly
- A therapist or certain support groups may be consulted on the variety of social issues that can be caused by Scleroderma, which include self-esteem issues, depression, anxiety, and relationships with friends, family, and partners
- There is evidence that UVA1 phototherapy helps with the skin issues in Systemic Scleroderma. This form of treatment requires a significant infrastructure cost. It is not widely available
Treatment measures for dry mouth and dental issues include:
- Individuals with Scleroderma could experience tightening of the facial skin that may prevent adequate oral care; this can result in the development of tooth decay
- The following measures can help decrease the signs and symptoms:
- Regular brushing and flossing of teeth
- Regular dental check-ups
- Keeping mouth wet by frequently sipping water
- Avoid mouthwash that contains alcohol, since alcohol in mouthwashes can cause dryness of the mouth
Individuals with Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma can have a variety of gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea, constipation, excess gas formation, difficulty in swallowing, and heartburn. The following treatment measures can help in such cases:
- Medication for heart burn, diarrhea, and constipation
- Eating small and frequent meals, which helps with movement of the food and digestion
- Avoidance of spicy and fatty foods, alcohol, and caffeinated drinks
- Avoiding food items that are hard and difficult to swallow
Individuals with Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma can have a variety of signs and symptoms related to the lungs, which include difficulty in breathing due to excessive scarring and high blood pressure in the lungs (pulmonary hypertension). Lung infection, in an individual with poor lung function, may result in severe complications such as severe pneumonia:
The following treatment options may be beneficial:
- It is important to see a pulmonologist on a regular basis to manage one’s signs and symptoms
- Getting regular flu shots and pneumonia shots will help mitigate or avoid infection
Individuals with heart and kidney symptoms should get regular health check-ups from a cardiologist and nephrologist respectively.
How can Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma be Prevented?
Currently, there are no specific methods or guidelines to prevent Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma. However, through proper dietary and lifestyle changes, some of the signs and symptoms may be controlled.
What is the Prognosis of Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- The prognosis for individuals with Systemic Scleroderma (both Limited and Diffuse types) is worse than with Localized Scleroderma (both Morphea and Linear types)
- The manner in which Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma changes and progresses over time varies amongst individuals. The rapidity of progression of signs and symptoms and the types of organs involved affects the prognosis
- Some individuals respond well to treatment and generally have a better prognosis than those who do not respond well to treatment
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma:
- Research is currently underway to identify and understand more about Scleroderma. Studies are being completed to understand the genes that may be involved with the development of the condition, medicines to prevent the skin from thickening, and to treat the kidney/lung conditions, as well as medicines to completely treat Diffuse Systemic Scleroderma.
- Scleroderma used to be called progressive systemic sclerosis, but this term is no longer used since Scleroderma does not always progress by nature. This means that the signs and symptoms do not progress with equal severity in all individuals
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals


0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.