What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Brain Attack causing stroke
- Cerebrovascular Disease causing stroke
- Cerebral Hemorrhage
What is Brain Stroke? (Definition/Background Information)
- A Brain Stroke is a medical condition that occurs when blood supply to the brain is reduced or blocked, resulting in oxygen deprivation to the brain tissue. When oxygen levels are severely depleted, brain cells begin to die and result in the symptoms of a stroke
- When brain cells die, the functions that are controlled by that area of the brain are lost. Usually, the first abilities that are lost are speech, movement, and memory. The severity of damage depends on where in the brain the stroke originated and how much of the brain was damaged
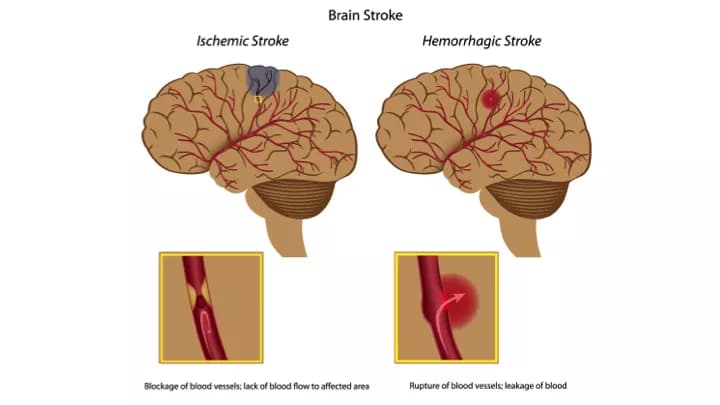
- Two major categories of Brain Stroke exist: Those caused by blood blockages (ischemic) and those caused by bleeding into the brain (hemorrhagic)
Who gets Brain Stroke? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Brain Strokes can occur in males and females. Men are 25% more likely to be affected from strokes than women
- Strokes can occur in people of all ages. However, as people get older, their risk for a stroke increases
- Studies have found that 95% of all strokes occur in people over the age of 45 years and 65% of all strokes occur in people over the age of 65 years
What are the Risk Factors for Brain Stroke? (Predisposing Factors)
Common risk factors of Brain Strokes include:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- Heavy alcohol consumption
- Obesity
- Any cardiovascular diseases (heart failure, heart defects, and abnormal heart rate)
- Family history
- Age (individuals over the age of 45 years are at the highest risk)
- Race (African Americans are at a higher risk for a stroke)
- Gender (males have a higher risk for strokes than females)
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases one’s chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Brain Stroke? (Etiology)
Brain Strokes occur when the flow of blood to the brain is reduced or blocked. A lack of blood flow to the brain deprives the brain of oxygen. When brain cells do not receive oxygen, they begin to die, resulting in a loss of function in that area of the brain.
- Ischemic Brain Strokes are caused by blood blockages to the brain. This accounts for 85% of strokes. Ischemic strokes occur when the arteries to the brain narrow or become blocked, reducing blood flow to the area. Usually, a blood clot, fatty deposits, or other debris bloods the arteries
- Hemorrhagic strokes occur when blood vessels rupture or begin to leak into the brain. When this happens, blood seeps into the brain tissue and damages the brain cells. Typically, these strokes are caused by high blood pressure or aneurysms, blood of which damage blood vessels
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Brain Stroke?
The common signs and symptoms of Brain Strokes include:
- Difficulty walking
- Dizziness
- Loss of coordination
- Lack of balance
- Speech problems (slurred words, incoherent speech)
- Paralysis/numbness, typically worse on one side of the body than the other
- Vision problems
- Headache
- Personality/mood changes
Usually, these symptoms develop suddenly and without any warning. It is important to seek immediate medical treatment if any of these signs unexpectedly arise, so as to minimize brain damage.
How is Brain Stroke Diagnosed?
- Brain Strokes are usually diagnosed based on the presenting signs and symptoms and physical examinations. During the physical examination, your doctor will check your blood pressure and listen to your heart. They will also gather a medical history
- A CT or MRI scan is the most effective test to diagnose a brain stroke. It can image the brain and show if a hemorrhaging is present, if a tumor is obstructing a blood pathway, etc.
- Cerebral angiogram highlights the blood vessels in the brain
- An ophthalmoscope can also be used to make a diagnosis. It is used to check for small cholesterol crystals in the blood vessels and in the back of the eyes. If crystals are found, a stroke is likely occurring
- Blood tests to help gather information on how quickly one's blood clots, whether blood sugar levels are at normal levels, and the level of certain blood chemicals
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Brain Stroke?
Brain Strokes can often cause permanent damage to the body, and a host of complications that may include:
- Paralysis is the most common complication that arises from strokes. When too little oxygen reaches certain parts of the brain, brain cells die and the function the control is lost. This often results in paralysis and/or loss of muscle function. This can often be severe, resulting in difficulties walking, eating, getting dressed, etc.
- Talking, swallowing, and other mouth controls may also be lost due to stroke. People can experience slurred speech, incoherent speech, and difficulty reading or writing
- Memory loss is also common amongst stroke patients. The parts of the brain that were oxygen deprived and involved in controlling memory may be damaged, leading to a memory loss
How is Brain Stroke Treated?
- The treatment for Brain Stroke varies depending on the nature of the stroke - whether ischemic stroke or hemorrhagic stroke has occurred. Once the type of stroke is determined, specific treatments are administered
- To treat an ischemic stroke:
- Use of thrombolytics (clot-breaking or blood thinning drugs) - these drugs are most effective if administered within 4-5 hours of the stroke
- Tissue plasminogen activator (TPA) - this is a drug that dissolves blood clots; it is administered intravenously
- Mechanical brain clot removal using a catheter
- Carotid endarterectomy - surgery to remove fatty plaque deposits from the carotid arteries
- To treat an ischemic stroke:
- Medications to prevent blood clot formation (such as Coumadin and Plavix)
- Surgery to repair the ruptured blood vessels
- Treatment must be continued after a stroke has occurred. This helps people regain their strength and function so that they can return to their normal life. This often involves medications, physical therapy, and speech therapy
How can Brain Stroke be Prevented?
The most effective method of preventing a Brain Stroke is by controlling the associated risk factors.
- It is important to take measures to control high blood pressure. This involves regular exercise, managing stress, limiting sodium intake, limiting alcohol consumption, and including more potassium in one's diet
- Lowering cholesterol is another preventative measure that can be taken against strokes. A diet low in saturated and trans fats is important, though your doctor may also prescribe medications to further help you
- It is also important to stop smoking, as it improves one's lung and artery quality
- Preventative medications also exist to reduce one's risk for a Brain Stroke. These include:
- Anti-platelet drugs to help make the blood cells less sticky so that they will not clot
- Anticoagulants, which are blood thinners that help prevent the blood from clotting
What is the Prognosis of Brain Stroke? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
The prognosis of individuals with Brain Stroke depends on the type of stroke that occurred, the extent of brain damage, and how quickly treatment was received.
- Most people receive treatment quickly enough that over the course of months and sometimes years, they are able to restore most of the body function and resume their day-to-day (regular) activities
- Over half of those who suffer from a stroke are able to improve so much that they can resume their lives at home without other people helping care for them
- People who have had ischemic strokes have a higher chance of surviving than those who have had hemorrhagic strokes
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Brain Stroke:
The following DoveMed website link is a useful resource for additional information:
https://www.dovemed.com/health-topics/neurological-institute/
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.