What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Benign Bone Spurs
- Osteophytes
What is Bone Spurs? (Definition/Background Information)
- Bone Spur is an abnormal bone growth that can develop on the surface of bones. Usually, Bone Spurs are not painful by themselves, but may cause pain when they rub against the nerves and press surrounding tissue
- Bone Spurs may develop on the surface of any bone. It most commonly involves the bones of the feet, elbow, and spine. Joint damage caused by degenerative joint disease, such as osteoarthritis, is the primary cause of Bone Spur in the joints
- Individuals with Bone Spurs rarely experience any signs or symptoms. However, in some cases, individuals may experience pain depending on the location of the Bone Spur
- A majority of Bone Spurs grow very slowly and are stable. However, in some cases, the growth is more rapid and unpredictable. In these cases, the healthcare provider may recommend surgery to remove the Bone Spurs
- Over-the-counter oral medications, such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen, are recommended if the condition is painful. Surgery may be required, if Bone Spurs reduce an individual's range of motion in the affected joint, presses on nerves, or if the pain is not controlled by medication
- The prognosis of Bone Spurs is usually good and conservative methods are usually effective in treating many individuals. However, occasionally, a recurrence of the condition is noted
Who gets Bone Spurs? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Bone Spurs may occur in individuals of all ages, races, ethnic groups, and genders
- In individuals over the age of 60 years old, it is common for Bone Spurs to develop on the spine
- No geographical localization has been noted
What are the Risk Factors for Bone Spurs? (Predisposing Factors)
The common risk factors for Bone Spurs include:
- Advanced age
- Repetitive stress on the affected area and participation in high-impact sports
- Excessive body weight associated with obesity
- Unhealthy diet
- Poor posture
- Degenerative joint disease such as osteoarthritis
- Previous injury at the site affected by Bone Spurs
- Heredity predisposition; a family history of Bone Spurs
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases one’s chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Bone Spurs? (Etiology)
- Bone Spurs are usually caused by a disease or condition that results from a degeneration of the cartilage
- Excess bone formation occurs as a result of the body’s response to abnormal pressure on the affected area of the bone
In other words, Bone Spurs are caused as part of a reactive process to a bone injury.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Bone Spurs?
In many individuals, Bones Spurs are not painful by themselves and cause no significant signs or symptoms. However, in some, severe symptoms may occur depending on the location of the Bone Spurs.
The signs and symptoms of Bone Spurs based on its location include:
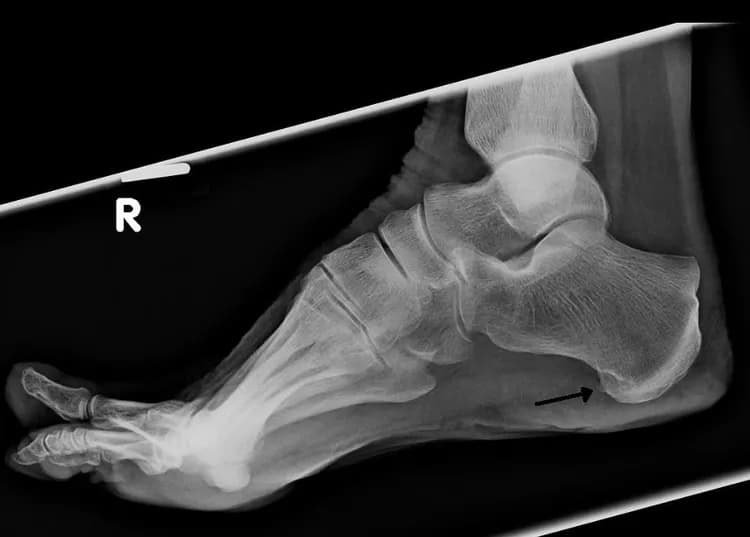
- Foot: Any Bone Spur in the foot or heel may cause pain when the individual applies weight/pressure to the affected area
- Knee:
- Individuals, who develop Bone Spurs in the knee, may experience pain when extending or bending the leg
- Numbness, feeling of weakness, tingling sensations of the knee joint may be observed, if the surrounding nerves are pinched
- Decreased range of motion in the affected knee
- Spine:
- Bone Spurs that develop on the spine can narrow the space between the vertebrae. This can pinch the spinal cord or nerve roots, resulting in weakness or numbness in the arms or legs
- Severe uncontrollable pain in the back
- Difficulty walking
- A painful and burning sensation felt in the shoulders, neck, or arm
- Decreased range of motion in the back
- Hip:
- Bone Spurs on the hip can be painful, and the pain may also extend to the knees
- The range of motion in the hip may be affected
- Numbness, feeling of weakness, tingling sensations of the hip joint may be observed, if the surrounding nerves are pinched
- Shoulder:
- Bone Spurs in the shoulder can affect the rotator cuff, which form a group of muscles and tendons that support the shoulder joint and control shoulder movement
- Severe uncontrollable pain in the shoulder
- Numbness, feeling of weakness, tingling sensations of the shoulder joint may be observed, if the surrounding nerves are pinched
- Fingers:
- Bone Spurs in the finger appear as a bony mass under the skin
- Uncontrollable pain in the affected hand
- Numbness, feeling of weakness, tingling sensations in the hands may be observed, if the surrounding nerves are pinched
- Decreased range of motion in the fingers
- If the nerves surrounding the Bone Spur are pinched, the affected muscles may show weakness
How is Bone Spurs Diagnosed?
Bone Spurs may be diagnosed by the following observations and tests:
- A complete physical examination with thorough evaluation of medical history
- X-ray of the affected region: X-rays are noninvasive medical tests that use radiation to produce images of the bone
- Computerized tomography (CT) scan of the affected region: A CT scan takes a series of X-ray images from several different angles. These images are then merged to create cross-sectional images of bones and soft tissues with the body
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan of the affected region: An MRI is a more detailed scan that uses radio waves and a magnetic field that generates thorough images of interior bones and soft tissues
- Electromyography (EMG): An EMG shows the electrical activity of the muscle during rest and muscle contraction. This test may be performed if the signs and symptoms indicate that there is muscle or nerve damage
- Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) studies: Nerve conduction velocity shows the speed at which electrical signals move through the affected nerve. Slow nerve signal speed may indicate nerve damage
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Bone Spurs?
The possible complications of Bone Spurs include:
- Without treatment, in some individuals, Bone Spurs can cause severe uncontrollable pain, by impinging on surrounding structures such as the tendons and nerves
- Individuals, who develop Bone Spurs in the heel, may experience pain while walking
- Surgery to remove Bone Spurs may lead to the following complications:
- Infection at the site of surgery
- Poor wound closure
- Anesthetic complications
- Permanent damage to the affected nerves
- Occasionally, relief from surgery may only be temporary, since Bone Spurs may grow back (recurrent Bone Spurs)
How is Bone Spurs Treated?
The methods for treating Bone Spurs depend on the severity of the signs and symptoms. Conservative methods for individuals with mild to moderate pain may include:
- Rest: Any activity that aggravates the condition further should be avoided. The healthcare provider may advise individuals to refrain from participating in certain activities, until the symptoms get better
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory oral medications, such as ibuprofen, naproxen, and acetaminophen may be used to treat Bone Spurs. These medications can help decrease pain and swelling
- Corticosteroid injections help provide temporary relief of symptoms, and in improving the range of motion. It is important to note that corticosteroid injections only give temporary relief. Prolonged episodes of such injections may injure the joints in the long-run
- Physical therapy exercises that include strengthening and improving flexibility in the affected area can help reduce discomfort. It can also help decrease pressure on the nerves
Surgical treatment for Bone Spurs: Bone Spurs may occur in any joint or bone, and if conservative treatments are unsuccessful, surgery may be recommended. Common decompression surgical procedures may include:
- Bone spur removal: This procedure involves the surgical removal of any abnormal bony growth from the affected region
- Cheilectomy for Bone Spurs of the toes: Cheilectomy is a surgical procedure that involves removing Bone Spurs from the base of the big toe
- Laminectomy for Bone Spurs of the spine: Laminectomy is a surgical procedure intended to relieve pressure on the spinal cord and/or nerves by removing the lamina, in order to widen the spinal cord. During a laminectomy procedure, the lamina (the small section of the bony roof in the spine) is removed, to create additional space for the surrounding nerves within the spinal canal. A bone graft material is then used to fill the empty space, and two or more vertebrae of the spine are fused together to create stability
- Laminotomy for Bone Spurs of the spine: Laminotomy, is a surgical procedure that is performed by removing a small portion of the lamina of the vertebral bone
- Foraminotomy for Bone Spurs of the spine: Foraminotomy is a surgical procedure performed to relieve pressure on the spinal cord and/or nerves by widening an intervertebral foramen (a passage in the bone). Bone Spurs that develop around the foramina can impinge on spinal nerve roots. By removing the foramina, pain due to the compressed nerve root may decrease. This procedure can be performed with a laminectomy or laminotomy surgical procedure
- Facet thermal ablation for Bone Spurs of the Spine: This surgical procedure is performed if Bone Spurs have developed in a facet joint. Facet joints are joints in the spine that help with the flexibly of the back
How can Bone Spurs be Prevented?
Bone Spurs is a condition that cannot be prevented in most individuals. However, in some cases, following certain guidelines may help reduce the risk of developing Bone Spurs.
- Maintain a healthy body weight through a healthy diet and regular exercise
- Maintain correct posture while standing, sitting, or working on the computer
- Limit activities that may involve repetitive stress; wear appropriate safety equipment when participating in any (high-impact) sports. Significant stress on the joints may lead to the development of Bone Spurs
What is the Prognosis of Bone Spurs? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- In a majority of cases, the prognosis of Bone Spurs is good and symptoms are resolved with suitable conservative treatment
- However, there is still a risk that the Bone Spur will continue to grow. In these cases, a healthcare provider will recommend surgery to treat the condition
- Occasionally, recurrent Bone Spurs may be observed and the relief obtained from surgery may only be temporary
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Bone Spurs:
- Bone Spurs that develop on the heel are found in around 21% of the individuals with plantar fasciitis
Please visit the following link for more information on bone spur removal surgical procedure that may be performed if Bone Spurs develop on any surface of the bones.
http://www.dovemed.com/common-procedures/procedures-surgical/bone-spur-removal/
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.