What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Peripheral Ameloblastoma
- Solid Ameloblastoma
- Unicystic Ameloblastoma
What is Ameloblastoma? (Definition/Background Information)
- An Ameloblastoma is a rare tumor involving excess tissue growths around the jaw. It can occur either in the lower jaw or upper jaw bones. Commonly, the tumor occurs near the un-erupted teeth of the molars
- Statistically, only 1% of all jaw tumors are Ameloblastomas and in most cases the growth is usually benign (non-cancerous) and non-metastatic (they do not spread). However, these tumors may be locally very aggressive, causing bone destruction at the tumor site
- The abnormal growths are formed from cell parts that in normal cases would have turned into tooth enamel. If the condition is severe, then the tissue growth may even cause facial deformity
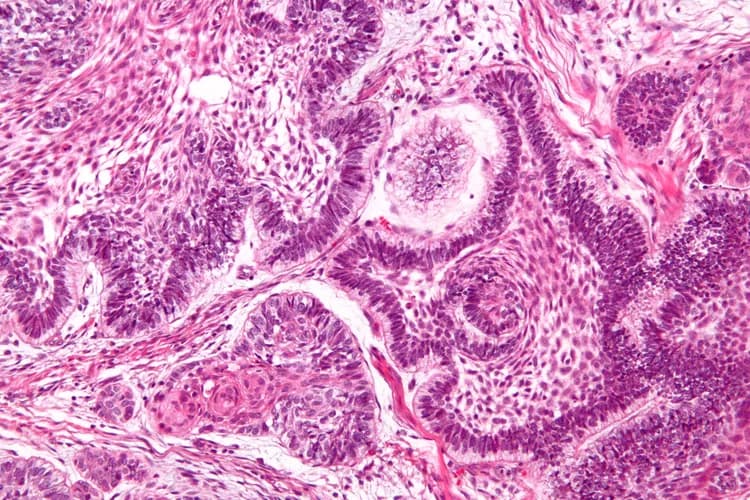
- A diagnosis of Ameloblastoma is made through radiology imaging and biopsy of the tumor
- Generally, a surgical removal of the tumor is the preferred treatment method; though, recurrence of Ameloblastoma after surgery is a possibility
There are 3 types of Ameloblastoma and these are:
Multicystic/Conventional Ameloblastoma (also known as Solid Ameloblastoma):
- A majority of all Ameloblastomas are Multicystic/Conventional Ameloblastomas (over 80%)
- The tumor is usually seen in middle-aged adults, around the age of 40 years
- It is more prevalent among African Americans
Unicystic Ameloblastoma (also known as Cystic Ameloblastoma):
- About 20% of all Ameloblastomas are Unicystic Ameloblastomas
- It affects men more than women, with 65% of the affected individuals being males
- It is usually seen in younger individuals with an average age of 25 years
- A majority of these tumors occur in the lower jaw (over 90%)
- The prognosis for Unicystic Ameloblastoma is better than Conventional Ameloblastoma, because they are less aggressive in growth
- However, they can recur after surgery, like Conventional Ameloblastomas
Peripheral Ameloblastoma:
- Generally, around 2% of Ameloblastomas are of this type
- Peripheral Ameloblastoma typically affect individuals aged between 40-60 years
- Both men and women are equally affected
- The common sites of tumor occurrence include:
- Soft tissues of jaw
- Gingiva
- Buccal mucosa
- They are generally less aggressive than intraosseous tumors that arise in the bones (Intraosseous Ameloblastoma tumors)
Who gets Ameloblastoma? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Ameloblastoma usually occur in adults, who are in their 40s and 50s; median age of 39 years. The condition is rarely diagnosed in children
- Most of the time when this condition develops, the presence of unerupted teeth (teeth that are still entirely in the gums) has been observed
- Both males and females are affected; though, the tumor is much more common in males, than in females. Also, for unknown reasons, the tumors appear to be larger in females, than in males
- There is no particular racial or ethnic preference. However, the condition is observed more often in African Americans
What are the Risk Factors for Ameloblastoma? (Predisposing Factors)
The potential risk factors for Ameloblastoma include:
- The presence of an unerupted tooth is often seen in association with the tumor
- If the individual has Gorlin-Goltz syndrome, then the incidence of Ameloblastoma is increased
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Ameloblastoma? (Etiology)
- Ameloblastoma is often associated with the presence of an unerupted teeth (impacted teeth) or a dentigerous cyst (a follicular cyst)
- No specific genetic mutation is currently reported that increases the risk in development of this jaw tumor
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Ameloblastoma?
The signs and symptoms of Ameloblastoma include:
- Lesions/growths occur in the lower jaw (mandible) or upper jaw (maxilla). Lesions are more common in the lower jaw, than in the upper jaw
- In 80% of the cases, the posterior mandible (lower jaw bone) is involved; in 20% cases, the posterior maxilla (upper jaw bone) is involved
- Mouth sores, gum disease
- Loose teeth
- Painless swelling, in many cases
- Facial deformity
- Swelling and numbness of the jaw - the size of the swelling may be very (or even extremely) large
- Dentures or bridges that do not fit
- In occasional cases, pain surrounding the teeth or jaw may be felt
- Abnormal growths may develop a thin shell of bone around the tissue, which usually cracks upon touch
- There may be pain associated with the tissue growth, if it spreads to the sinus cavities and floor of the nose
How is Ameloblastoma Diagnosed?
The diagnostic tests may vary, based on the location of the tumor. A diagnosis of Ameloblastoma may involve:
- Physical examination, evaluation of the individual’s medical history
- Radiographic imaging to show the presence of growth and to aid in obtaining a clear image of the tumor. These may include:
- X-ray of the jaw
- CT scan of the head and neck
- MRI of the jaw region
- Tissue biopsy of the tumor - the specimen is examined under a microscope by a pathologist, to arrive at a definitive diagnosis
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Ameloblastoma?
Complications due to Ameloblastoma could include:
- Pain and facial deformity
- Breathing difficulty, if the tumor grows large
- Secondary infection of the tumor
- The tumor can recur after treatment and hence, a close follow-up is needed. The recurrence rate of these tumors is between 25-35%
- World Health Organization (WHO) considers Ameloblastoma a benign tumor. Metastases to the lungs or central nervous system (CNS) have rarely been reported
How is Ameloblastoma Treated?
The treatment of Ameloblastoma is undertaken based on the type of tumor. These may involve:
- Surgery: It is the only effective method for removing the excess tissue growth. A wide surgical excision is often required; in most cases, a part of the bone beneath the growth must be removed as well
- Since, surgery is a highly effective method to treat Ameloblastoma, in most situations, chemotherapy and radiation treatment is not preferred
- Surgical curettage of the bone tumor - though, there is a higher chance of recurrence with this treatment method
- Facial reconstructive surgeries may be required, after removal of the tumor
How can Ameloblastoma be Prevented?
- Current medical research has not established a way of preventing Ameloblastoma
- Regular medical screening at periodic intervals with scans and physical examinations are important
What is the Prognosis of Ameloblastoma? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- Generally, complete surgical excision with wide surgical margins result in a good prognosis for Ameloblastoma
- The tissue growth may be removed, but newer growths could be a frequent occurrence
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Ameloblastoma:
- Ameloblastoma originates from the early English word ‘amel’, meaning enamel and the Greek word ‘blastos’, meaning erm
- This tumor was previously called adamantinoma. But, this term is considered inaccurate now and is not to be used
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.