New Machine Learning System Can Automatically Identify Shapes Of Red Blood Cells
Using a computational approach known as deep learning, scientists have developed a new system to classify the shapes of red blood cells in a patient's blood. The findings, published in PLOS Computational Biology, could potentially help doctors monitor people with sickle cell disease.
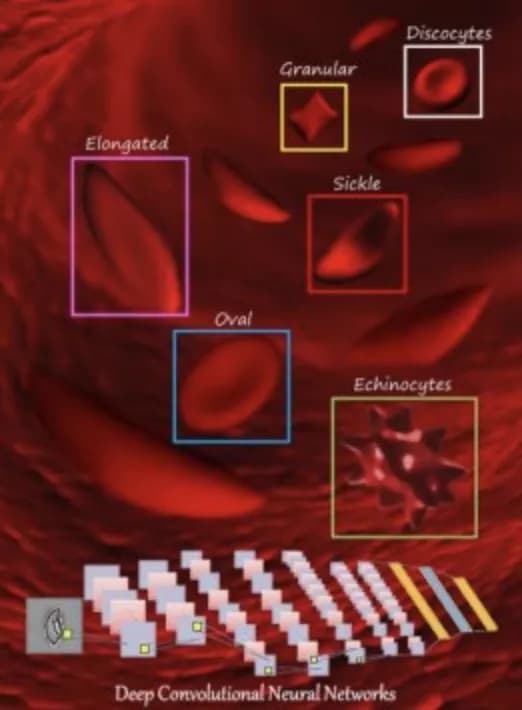
A person with sickle cell disease produces abnormally shaped, stiff red blood cells that can build up and block blood vessels, causing pain and sometimes death. The disease is named after sickle-shaped (crescent-like) red blood cells, but it also results in many other shapes, such as oval or elongated red blood cells. The particular shapes found in a given patient can hold clues to the severity of their disease, but it is difficult to manually classify these shapes.
To automate the process of identifying red blood cell shape, Mengjia Xu of Northeastern University, China, and colleagues developed a computational framework that employs a machine-learning tool known as a deep convolutional neural network (CNN).
The new framework uses three steps to classify the shapes of red blood cells in microscopic images of blood. First, it distinguishes red blood cells from the background of each image and from each other. Then, for each cell detected, it zooms in or out until all cell images are a uniform size. Finally, it uses deep CNNs to categorize the cells by shape.
The researchers validated their new tool using 7,000 microscopy images from eight sickle cell disease patients. They found that the automated method successfully classified red blood cell shape for both oxygenated and deoxygenated cells (red blood cells transport oxygen to tissues throughout the body).
"We have developed the first deep learning tool that can automatically identify and classify red blood cell alteration, hence providing direct quantitative evidence of the severity of the disease," says study co-author George Karniadakis.
The research team plans to further improve their deep CNN tool and test it in other blood diseases that alter the shape and size of red blood cells, such as diabetes and HIV. They also plan to explore its usefulness in characterizing cancer cells.
Materials provided by PLOS. Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Disclaimer: DoveMed is not responsible for the accuracy of the adapted version of news releases posted to DoveMed by contributing universities and institutions.
References:
Mengjia Xu, Dimitrios P. Papageorgiou, Sabia Z. Abidi, Ming Dao, Hong Zhao, George Em Karniadakis. (2017). A deep convolutional neural network for classification of red blood cells in sickle cell anemia. PLOS Computational Biology. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005746
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.