Mutations In FTO, Dopamine Receptor Genes Increase Risk Of Obesity, Diabetes
In the development of obesity and diabetes, signals from the brain play an important role. Here an important neurotransmitter is dopamine. DZD scientists from Tübingen and Munich, together with Swedish and American colleagues, have investigated how mutations in the obesity risk gene FTO and variants of the dopamine D2 receptor gene interact. Their results suggest that people in whom both genes are altered have a higher risk of developing obesity and diabetes.
More and more people throughout the world suffer from obesity. Currently about 500 million people are obese, including about 15 million in Germany. The causes of obesity are often an unhealthy diet, too little physical activity and a genetic predisposition. In particular, people with an altered obesity risk gene called FTO (FTO is the abbreviation for "fat mass and obesity-associate) are more often obese.
But how do the gene variants work? Why can they cause people to become overweight? "FTO is strongly expressed in the central nervous system," said PD Dr. Martin Heni of the Institute for Diabetes Research and Metabolic Diseases (IDM) of Helmholtz Zentrum München at the University of Tübingen. "Studies on rodents show that altered FTO influences dopamine signaling in the brain and thus leads to higher food intake." The "reward hormone" dopamine plays an important role in the regulation of appetite. If the information that you have already eaten is not transmitted correctly, then your desire for food increases. One of the causes for this may be an insufficient number of dopamine D2 receptors to which the neurotransmitter binds.
Researchers of the German Center for Diabetes Research have now investigated the effects when both the FTO gene and the gene for the dopamine D2 receptor, ANKK1/Taq1A, are mutated. For this purpose, they examined samples from the Tübingen Family Study (n = 2245) and the Malmo Diet and Cancer Study (n = 2921). They found that about 20 percent of the participants were carriers of both mutations.
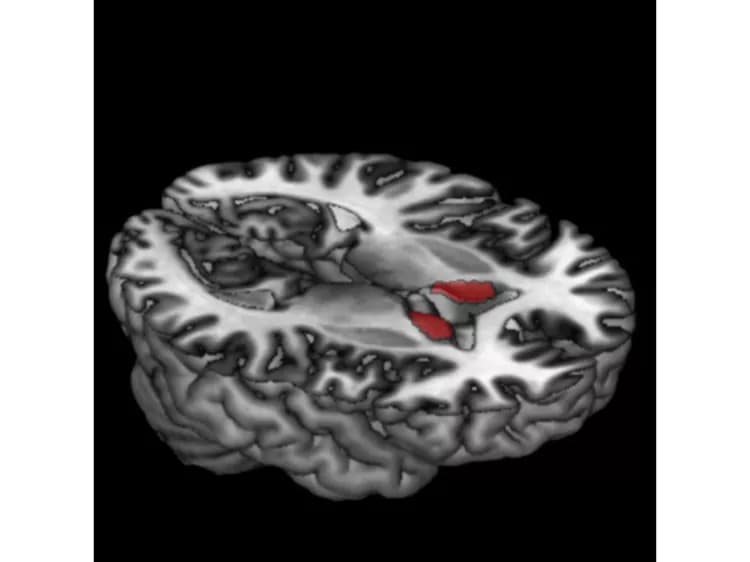
"Our studies show that when both genes are mutated, this can have a far-reaching effect on health. If due to the ANKK1 polymorphism there are fewer dopamine D2 receptors, those affected with mutated FTO have a higher percentage of body fat, more abdominal fat and low sensitivity to insulin in the body. In addition, in the caudate nucleus, the brain region that is important for dopamine metabolism, insulin sensitivity was altered," said Heni, summarizing the results. "From this we conclude that the effects of a mutated FTO gene depend on the number of dopamine D2 receptors," added his IDM colleague Professor Hubert Preissl. If an affected individual is a carrier of both mutated genes, his or her risk of diabetes and obesity is increased. "Unfortunately, this unfavorable combination of both gene mutations is present in about one-fifth of the population," said Heni.
The findings suggest that FTO influences dopamine signaling not only in rodents, but also in humans. This interaction not only appears to be important for body weight, but also for the metabolism in the entire body. FTO gene mutations are important risk factors for overweight and diabetes. However, the effects are less critical if there are sufficient dopamine D2 receptors.
Materials provided by Deutsches Zentrum fuer Diabetesforschung DZD. Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Disclaimer: DoveMed is not responsible for the adapted accuracy of news releases posted to DoveMed by contributing universities and institutions.
Primary Resource:
Heni, M., Kullmann, S., Ahlqvist, E., Wagner, R., Machicao, F., Staiger, H., ... & Fritsche, A. (2016). Interaction between the obesity-risk gene FTO and the dopamine D2 receptor gene ANKK1/TaqIA on insulin sensitivity. Diabetologia, 1-10.
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.