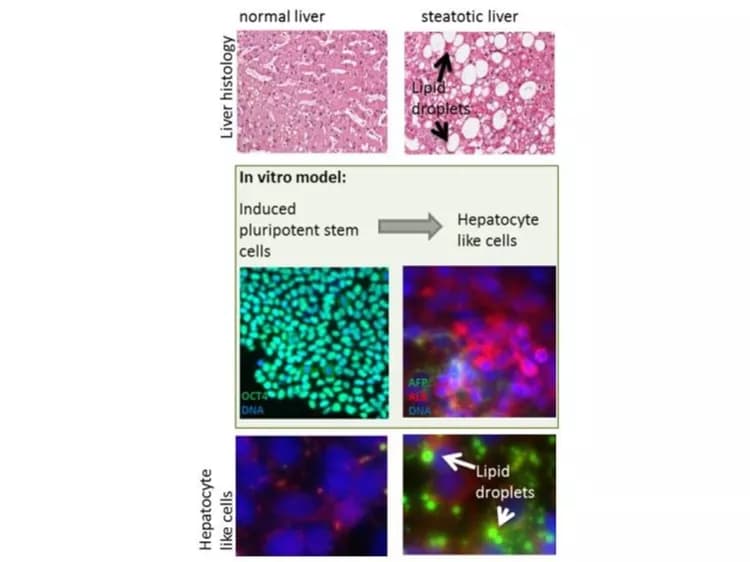
Modeling NAFLD With Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Derived Immature Hepatocyte Like Cells
Researchers from the Institute for Stem Cell Research and Regenerative Medicine at the University Clinic of Düsseldorf have established an in vitro model system for investigating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). The study led by Prof. James Adjaye has now been published in the journal Stem Cells and Development.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), also called steatosis, is a dramatically under-estimated liver disease, with increasing incidences throughout the world. It is frequently associated with obesity and type-2 diabetes. Approximately one third of the general population in Western countries are affected, often without even having symptoms. It is a result of a high caloric diet in combination with a lack of exercise, where the liver starts incorporating fat as lipid droplets. Initially, this is a benign state, which can, however, develop into NASH /steatohepatitis, an inflammatory disease of the liver. Then many patients develop fibrosis, cirrhosis or even liver cancer. However, in many cases patients die of heart failure before they develop severe liver damage.
A major obstacle for NAFLD research was, up to now, that biopsies of patients and healthy individuals were required. The Düsseldorf researchers elegantly solved this problem by reprogramming skin cells into so called induced pluripotent stem cells which they differentiated into hepatocyte like cells. "Although our hepatocyte-like cells are not fully mature, they are already an excellent model system for the analysis of such a complex disease", explains Dr. Nina Graffmann, first author of the study. The researchers recapitulated important steps of the disease in vitro. For example they demonstrated up-regulation of PLIN2, a protein that covers lipid droplets. Mice without PLIN2 do not become obese, even when overfed with a high fat diet. Also the key role of PPARα, a transcription factor involved in controlling glucose and lipid metabolism, was reproduced in the in vitro system. "In our system, we can efficiently induce lipid storage in hepatocyte-like cells and manipulate associated proteins or microRNAs by adding various factors into the culture. Thus, our in vitro model offers the opportunity to analyse drugs which might reduce the stored fat in hepatocytes" says Dr. Graffmann.
The team now expands the model using induced pluripotent stem cells derived from NAFLD patients, hoping to discover differences which might explain the course of the disease. "Using as reference the data and biomarkers obtained from our initial analyses on patient liver biopsies and matching serum samples (1), we hope to better understand the etiology of NAFLD and the development of NASH at the level of the individual, with the ultimate aim of developing targeted therapy options," states Professor James Adjaye, senior author of the current study.
The above post is reprinted from materials provided by Heinrich-Heine University Duesseldorf. Note: Materials may be edited for content and length.
Disclaimer: DoveMed is not responsible for the adapted accuracy of news releases posted to DoveMed by contributing universities and institutions.
Primary Resource:
Graffmann, N., Ring, S., Kawala, M. A., Wruck, W., Ncube, A., Trompeter, H. I., & Adjaye, J. (2016). Modeling Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Immature Hepatocyte-Like Cells Reveals Activation of PLIN2 and Confirms Regulatory Functions of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Alpha. Stem Cells and Development.
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.