How To Turn White Fat Brown
A signaling pathway in fat cells may one day provide the key to better treatments for obesity, according to new research by scientists in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. They reported their findings online ahead of print in Genes & Development.
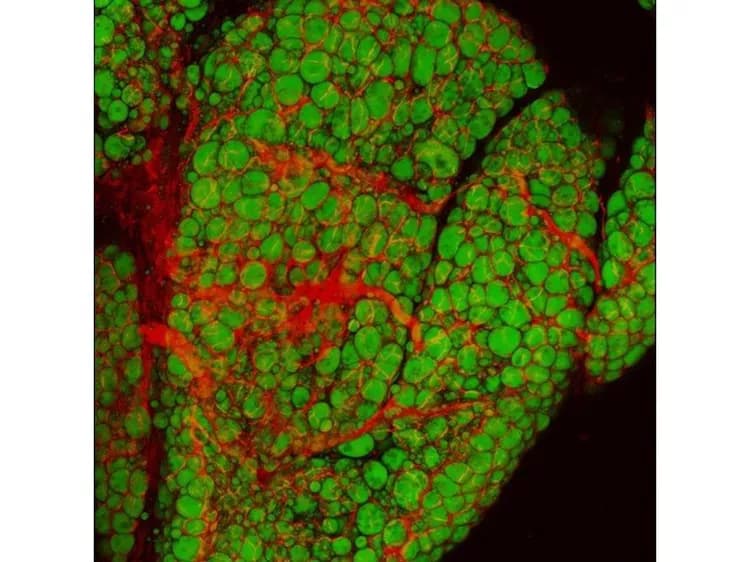
Ordinary fat cells, also called white adipocytes, stuff themselves with fat molecules to store up energy, and their overloading leads to obesity and related conditions, including diabetes. Brown adipocytes, which are prevalent in children as "baby fat," but much less so in adults, do virtually the opposite: they burn energy rapidly to generate heat, and thereby protect the body from cold as well as obesity and diabetes. The signaling pathway discovered by the Penn scientists activates a "browning program" in white adipocytes, making them more like energy-burning brown adipocytes.
"It's conceivable that one would be able to target this pathway with a drug, to push white fat to become brown fat and thereby treat obesity," said the study's senior author Zoltan P. Arany, MD, PhD, an associate professor of Cardiovascular Medicine. About 36 percent of American adults are considered obese and nearly 10 percent have type 2 diabetes.
Arany and colleagues found that the browning program in white adipocytes is normally suppressed by a protein called FLCN. It performs this function in cooperation with a major cellular signaling hub, a protein complex known as mTOR. The FLCN-mTOR interaction keeps the browning program switched off by preventing a protein called TFE3 from entering the cell nucleus.
The scientists showed that deleting the FLCN gene in the white adipocytes of mice allows TFE3 to migrate into the nucleus, where it binds to DNA and activates a key regulator of cellular metabolism called PGC-1β. It then turns on the set of genes for the browning program.
In the mice in which FLCN was deleted, white adipocytes became visibly browner as they produced more mitochondria -- tiny, oxygen reactors that supply chemical energy within cells and convert energy to heat in brown adipocytes. In several other ways too, including their altered cellular structures, mitochondria's higher capacity for consuming oxygen, and their distinctive pattern of gene expression, the cells became more like brown adipocytes.
Arany and his team showed that they could reproduce this browning effect merely by forcing the overexpression of PGC-1β in the white adipocytes of mice. "In principle, a drug that boosts the activity of PGC-1β or some of its target genes might serve as a therapeutic activator of the browning program to curb obesity and treat or prevent diabetes," Arany said.
Aside from its potential medical relevance, the discovery is an important advance in understanding cell biology. "Cellular metabolism is regulated by major signaling pathways and with this study we're linking two of these major pathways, the mTOR and the PGC-1 pathways," Arany said. "The connection between them hasn't been well understood, but here we're clarifying it significantly." Arany and his team plan further studies of the pathway and its relation to other mTOR signaling pathways.
Materials provided by Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Disclaimer: DoveMed is not responsible for the adapted accuracy of news releases posted to DoveMed by contributing universities and institutions.
Primary Resource:
Wada, S., Neinast, M., Jang, C., Ibrahim, Y. H., Lee, G., Babu, A., ... & Martina, J. A. (2016). The tumor suppressor FLCN mediates an alternate mTOR pathway to regulate browning of adipose tissue. Genes & Development. DOI: 10.1101/gad.287953.116
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.