Future Brain Therapies For Parkinson's Possible With Stem Cell Bioengineering Innovation
Scientists at Rutgers and Stanford universities have created a new technology that could someday help treat Parkinson's disease and other devastating brain-related conditions that affect millions of people.
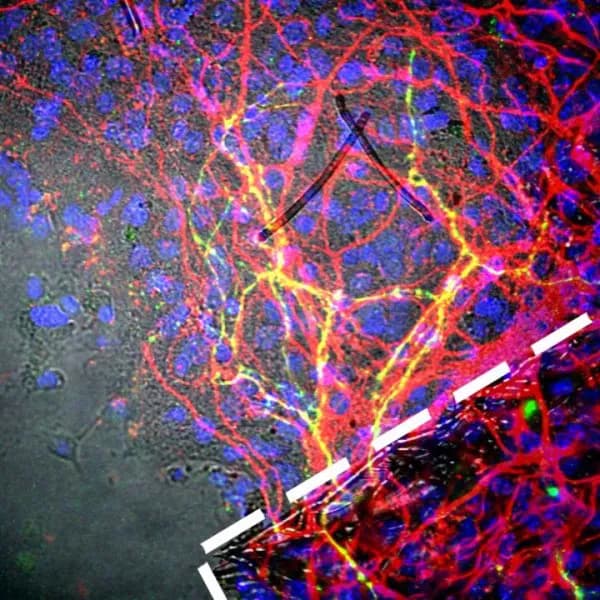
The technology -- a major innovation -- involves converting adult tissue-derived stem cells into human neurons on 3-D "scaffolds," or tiny islands, of fibers, said Prabhas V. Moghe, a distinguished professor in the departments of Biomedical Engineering and Chemical and Biochemical Engineering at Rutgers University.
The scaffolds, loaded with healthy, beneficial neurons that can replace diseased cells, were injected into mouse brains.
"If you can transplant cells in a way that mimics how these cells are already configured in the brain, then you're one step closer to getting the brain to communicate with the cells that you're now transplanting," said Moghe, research director for the School of Engineering/Health Sciences Partnerships at Rutgers. "In this work, we've done that by providing cues for neurons to rapidly network in 3-D."
In their multidisciplinary study, published online today in Nature Communications, a dozen scientists from several Rutgers teams and Stanford discuss the 3-D scaffolds and their potentially widespread benefits.
Neurons, or nerve cells, are critical for human health and functioning. Human brains have about 100 billion neurons, which serve as messengers that transmit signals from the body to the brain and vice versa.
Moghe said a 3-D scaffold, developed by the scientists, consists of tiny polymer fibers. Hundreds of neurons attach to the fibers and branch out, sending their signals. Scaffolds are about 100 micrometers wide -- roughly the width of a human hair.
"We take a whole bunch of these islands and then we inject them into the brain of the mouse," he said. "These neurons that are transplanted into the brain actually survived quite miraculously well. In fact, they survived so much better than the gold standard in the field."
Indeed, the scaffold technology results in a 100-fold increase in cell survival over other methods, Moghe said.
And that may eventually help people suffering from Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), or Lou Gehrig's disease, Alzheimer's disease, spinal cord and traumatic brain injuries, and concussions, he said.
These diseases and conditions often arise from the loss of brain cells. Parkinson's disease, for example, is caused by the loss of brain cells that produce dopamine, a key neurotransmitter. Brain cell loss can lead to trembling in the hands, arms, legs, jaw and face; rigidity, or stiffness of the limbs and trunk; slowness of movement; and impaired balance and coordination, according to the National Institutes of Health.
The next step would be to further improve the scaffold biomaterials, allowing scientists to increase the number of implanted neurons in the brain. "The more neurons we can transplant, the more therapeutic benefits you can bring to the disease," Moghe said. "We want to try to stuff as many neurons as we can in as little space as we can."
The idea is to "create a very dense circuitry of neurons that is not only highly functioning but also better controlled," he said, adding that testing of mice with Parkinson's disease is underway to see if they improve or recover from the illness.
Eventually, with continued progress, the researchers could perform studies in people. Moghe estimated that it would take 10 to 20 years to test the technology in humans.
Developing the scaffold technology and reprogramming the stem cells in the scaffolds was "very hard team work," he said. "It took many years to get here, so there was a lot of sweat and toil."
The above post is reprinted from materials provided by Rutgers University. Note: Materials may be edited for content and length.
Disclaimer: DoveMed is not responsible for the adapted accuracy of news releases posted to DoveMed by contributing universities and institutions.
Primary Resource:
Carlson, A. L., Bennett, N. K., Francis, N. L., Halikere, A., Clarke, S., Moore, J. C., ... & Pang, Z. P. (2016). Generation and transplantation of reprogrammed human neurons in the brain using 3D microtopographic scaffolds. Nature Communications, 7.
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.