Percutaneous (through the skin) Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG Procedure)
Background Information:
What are the other Names for the Procedure?
- G-Tube Placement
- PEG Procedure
- Stomach Tube Insertion
What is Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy surgical procedure?
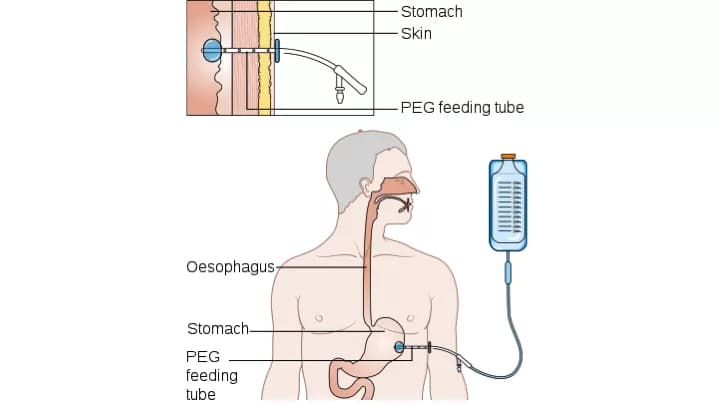
Percutaneous (through the skin) Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG Procedure) is a surgical procedure that involves the placement of a feeding or drainage tube, directly into the stomach.
What part of the Body does the Procedure involve?
The Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy procedure involves the stomach, skin, and underlying structures of the abdominal wall.
Why is the Procedure Performed?
A Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy procedure is performed for the following reasons:
- Prevent pneumonia in patients with swallowing disorders
- Provide nutrition to individuals with inability to swallow
- Obstruction of the esophagus
- Provide an alternate outlet for feeding or drainage of contents, within the stomach
What are some Alternative Choices for the Procedure?
Some of the alternative techniques used include:
- Laparoscopic technique (Janeway gastrostomy) for placement of gastrostomy tube
- Open surgical placement of gastrostomy tube (Stamm gastrostomy)
What are the Recent Advances in the Procedure?
Laparoscopic placement is an advancement to the procedure; however, PEG tube placement remains a gold standard, as it is less invasive than a laparoscopic procedure.
What is the Cost of performing the Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy surgical procedure?
The cost of Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy procedure depends on a variety of factors, such as the type of your health insurance, annual deductibles, co-pay requirements, out-of-network and in-network of your healthcare providers and healthcare facilities.
In many cases, an estimate may be provided before the procedure. The final amount depends upon the findings during the surgery / procedure and post-operative care that is necessary.
When do you need a Second Opinion, prior to the Procedure?
- It is normal for a patient to feel uncomfortable and confused by the information regarding a Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy procedure and on what needs to be done
- If the patient needs further reassurance or a second opinion, a physician will almost always assist and also recommend another physician, if required
- They can also choose to approach another physician independently. Besides, if the procedure has many alternatives, the patient may take a second opinion to understand and choose the best one
What are some Helpful Resources?
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/002937.htm
http://www.cincinnatichildrens.org/health/g/g-tube-care/
Complete Guide to Symptoms, Illness & Surgery; Written by H Winter Griffith, M.D.; Revised and updated by Stephen Moore, M.D. and Kenneth Yoder, M.D.; The Berkley Publishing Group, 5th Edition, New York, 2006
Prior to Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy surgical procedure:
How is the Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy surgical procedure Performed?
PEG Tube (or G-Tube) Placement:
- An endoscope (a thin, flexible tube with a tiny camera and light at the tip) is inserted through the mouth and into the stomach, to guide the physician position the G-tube
- After the endoscopic tube is inserted, the skin over the left side of belly (abdomen) area is cleaned and numbed
- A small surgical cut is made in this area and a small, flexible, hollow tube (the G-tube), with a balloon or special tip, is inserted into the stomach, with guidance from the endoscope
- Surgical incision around the tube is then closed with sutures
Where is the Procedure Performed?
A Gastrostomy is usually performed in an out-patient surgery center facility, a gastrointestinal lab (GI lab), or a hospital. Normally, the individual can go home once the procedure is completed.
Who Performs the Procedure?
A general surgeon or a gastroenterologist performs the Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy procedure.
How long will the Procedure take?
A Gastrostomy procedure usually takes about 30-45 minutes.
What do you need to tell your Physician before the Procedure?
It is very important to provide the following information to your healthcare provider. This enables your healthcare provider in assessing the risks for the surgical procedure and helps avoid unnecessary complications.
- Provide a complete list of medications you are currently taking, to your physician. This information is useful for a variety of reasons. For example, it can help your healthcare provider prevent complications due to a drug interaction
- If you are allergic to any specific medication or food items
- If you are taking blood thinners, such as aspirin, warfarin, herbal supplements, or any other such medications
- If you or your family members, have a history of bleeding disorders, or if there is a tendency to bleed more than normal
- If you have diabetes, high blood pressure, chest pains, or have previously suffered from a heart attack
- If you have ever been diagnosed with blood clots in your leg (deep vein thrombosis) or lung (embolism of lung)
- If you have a history of frequent bone fractures (this may affect bone-healing, if bones are involved as part of your procedure)
- A list of all previous surgical procedures you have undergone, like for example: Removal of appendix, gallbladder, or any other part, of your body; surgical repair of any body part, such as hernia repair, perforation of bowel wall, etc.
What Preparations are needed, prior to the Procedure?
- The physician may evaluate the individual’s medical history to gain a comprehensive knowledge of the overall health status of the patient including information related to the medications that are being currently taken
- Some medications increase a person’s chances of bleeding and it may be recommended to discontinue them for a period of time, before the procedure is performed
- Blood tests may be performed to determine if there is a bleeding tendency or any other medical conditions that prevents the person from undergoing the procedure
- Do inform the physician if you are allergic to any local anesthetics, lidocaine, etc.
- Avoid application of any cosmetics, deodorant, or topical medicines on the area, prior to the procedure
- It is advisable to quit smoking and the use of any nicotine based products, for a while, before the surgery
- Consumption of alcoholic drinks must also be avoided for a period of time, as instructed
- The patient must avoid eating or drinking at least 8 hours prior to the surgical procedure, depending on when the procedure is arranged
- For persons suffering from diabetes, it is important that the blood sugar stays within the normal range; if not their diabetologist may have to control blood sugar by recommending insulin and/or a combination of oral medicines
What is the Consent Process before the Procedure?
A physician will request your consent for the Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy procedure using an Informed Consent Form.
Consent for the Procedure: A “consent” is your approval to undergo a procedure. A consent form is signed after the risks and benefits of the procedure, and alternative treatment options, are discussed. This process is called informed consent.
You must sign the forms only after you are totally satisfied by the answers to your questions. In case of minors and individuals unable to personally give their consent, the individual’s legal guardian or next of kin, shall give their consent for the procedure.
What Tests are needed, before the Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy surgical procedure?
Prior to a Gastrostomy procedure, the individual may need to undergo certain tests, such as:
- Routine blood and urine analysis
- X-ray of the gastrointestinal tract
- Endoscopy
What are some Questions for your Physician?
Some of the basic questions that you might ask your physician are as follows:
- What is a Percutaneous (through the skin) Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG Procedure)?
- Why is this procedure necessary? How will it help?
- How soon should I get it done? Is there an emergency?
- Who are the medical personnel involved in this procedure?
- Where is the procedure performed?
- What are the risks while performing the procedure?
- What are the complications that might take place, during recovery?
- How long will it take to recover? When can I resume normal work?
- How many such procedures have you (the physician) performed?
- Are there any follow-up tests, periodic visits to the healthcare facility required, after the procedure?
- What are the costs involved?
During the Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy surgical procedure:
What kind of Anesthesia is given, during the Procedure?
An injection of local anesthesia or general anesthesia is administered for this procedure. It may also be performed under conscious sedation, or deep sedation.
How much Blood will you lose, during the Procedure?
Since PEG Tube Placement is a less invasive procedure, the amount of blood loss is minimal.
What are the possible Risks and Complications during the Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy surgical procedure?
There are general factors that increase the risk of getting complications during the procedure, which include:
- Obesity: Generally greater the degree of obesity, greater is the surgical risk
- Smoking: Longer the smoking history (in pack years smoked), greater the surgical risk
- Advancing age
- Poorly controlled diabetes, as evidenced by a high hemoglobin A1c and a high fasting glucose
- Poorly functioning kidney, as evidenced by increased BUN (blood urea nitrogen) and blood creatinine
- Poorly functioning liver, as evidenced by increased blood liver function tests
- Hypertension (increased blood pressure), especially if it is poorly controlled
- Poor nutritional status (malnutrition with mineral and vitamin deficiencies)
- Poor lung function, as evidenced by abnormal lung function tests
- History of bleeding disorders
- Longstanding illness, such as autoimmune disorders, chronic infections
- Poor immune system due to a variety of causes
The possible risks or complications that may arise during the surgery are:
- Excessive bleeding
- Infection surrounding the surgical wound
- Obstruction or dislodgement of the feeding tube
- Anesthetic complications
What Post-Operative Care is needed at the Healthcare Facility after the Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy surgical procedure?
At the healthcare facility, generally there is no requirement for any post-procedure care, unless any complications arise.
After the Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy surgical procedure:
What are the possible Risks and Complications after the Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy surgical procedure?
Post Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy procedure, the following complications may arise:
- Excessive bleeding
- Signs of an infection
- Irritation of the skin around the Gastrostomy tube
- Leaking of the feeding tube
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Cramping
- Tube dislodgement
What is the Prognosis after the Surgery?
- The Gastrostomy site can be prone to infection and irritation, so it must be kept clean and dry, and frequent hand washing is a must
- Once the site is healed, patients who have had a gastrostomy have very few, if any, restrictions related to the tube
- After a few months of healing, the doctor may recommend replacing the longer tube with a mic-key "button" - a device that is flatter, shorter, and lies against the skin of the abdomen
- This can often be done without surgery in the doctor's office, unless your doctor advises otherwise
- If and when the doctor decides that the patient is able to take in enough nutrition by mouth, the G-tube or button, may be removed
- Removal takes only minutes and is usually done in the office, by the doctor or nurse
- Once the button or G-tube is out, a small hole will remain, which should be kept clean and covered with gauze until it closes on its own
- In some cases, surgery is necessary to close the hole; either way, the scar that remains will be small
When do you need to call your Physician?
Do contact your physician if you notice any of the following symptoms:
- Worsening pain and swelling surrounding the surgical wound
- Bleeding or fluid drainage around the surgical wound
- Abnormal swelling
- Any symptom that causes uneasiness, such as nausea and vomiting
- Signs of an infection
- Fever
- Dizziness
- Muscle aches
- Fever
- Feeling sick
- Changes in vision
- Complications associated with prescription medications used in treatment
- The tube dislodges
What Post-Operative Care is needed at Home after the Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy surgical procedure?
The individual or his/her family will be taught by the healthcare provider on:
- How to care for the skin around the tube
- How to read any signs and symptoms of infection, of tube blockage
- What is to be done, if the tube is pulled out? This is important because if the tube falls out of place, the hole may begin to close itself
- How to empty the stomach through the tube
- How to hide the tube under one’s clothing
- What normal activities are allowed, or may be continued
- How and what to feed through the tube
Apart from these, the following post-operative care is recommended at home, after a Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy procedure:
- Resume regular/daily activities, as early as possible (under advice by the physician). This aids in a faster recovery
- Prevent accidental dislodgment of the tube when dressing, feeding, and participating in any physical activities
- Avoid obstruction of the Gastrostomy tube, if the tube is used for drainage
- Keep skin around the Gastrostomy tube thoroughly clean
- Resume showering; keep the wound clean and dry. Gently wash the surgical wound with soap
- Replace the surgical wound dressing, as needed
- Elevate legs while resting,in order to prevent formation of blood clots and reduce the possibility of swelling
- Take antibiotic medication to help combat or prevent infection, as advised by the physician
- Complete the course of prescribed medication
- Avoid taking nonprescription medications, like aspirin. However, individuals may take acetaminophen to relieve pain, as necessary
Post-operative cares related to feeding include:
- A nutritionist will help plan a specific diet and schedule based on the individual’s needs
- Feeding should be started slowly with liquids and gradually advanced, as the individual’s tolerance level increases
- You might hear feedings referred to as "bolus" or "continuous”. Bolus feedings are larger and less frequent (more like a regular meal); while continuous feedings, which often take place overnight, are delivered by a pump to patients who need smaller, slower feedings
- It does not mean that individuals,who have a G-tube insertion, are unable to eat by their mouth. Although tube feedings can be used to replace all oral feedings, in some cases the tube supplements what an individual eats by mouth
- If your physician decides that the individual is physically able to eat, the medical team will help teach the skills needed for independent eating
How long does it normally take to fully recover, from the Procedure?
It takes about 1-2 weeks, to recover from the procedure.
Additional Information:
What happens to tissue (if any), taken out during the Procedure?
The procedure does not involve the surgical removal of any tissue.
When should you expect results from the pathologist regarding tissue taken out, during the Procedure?
Since no tissue is removed during the procedure, a pathologist does not get involved in the care of the patient.
Who will you receive a Bill from, after the Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy surgical procedure?
It is important to note that the number of bills that the patient may receive depends on the arrangement the healthcare facility has with the physician and other healthcare providers.
Sometimes, the patient may get a single bill that includes the healthcare facility and the consultant physician charges. Sometimes, the patient might get multiple bills depending on the healthcare provider involved. For instance, the patient may get a bill from:
- The outpatient facility, physician’s office or hospital
- An anesthesiologist (if anesthesia was administered)
- General surgeon or a gastroenterologist
The patient is advised to inquire and confirm the type of billing, before the Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy procedure is performed.
Thanks and Gratitude:
We sincerely acknowledge and thank Dr. Douglas J. Jones for reviewing the article. His valuable input and feedback has helped enrich the contents of this article.
Douglas J. Jones, MD FACS
Board Certified General Surgeon and Faculty Member
University of Illinois, College of Medicine at Urbana-Champaign
506 S. Mathews Ave., Urbana, IL 61801, USA
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.