What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Acute Poliomyelitis
- Infantile Paralysis
- Polio
What is Poliomyelitis? (Definition/Background Information)
- Poliomyelitis (Polio) is an acute and infectious disease caused by the poliovirus that affects the nervous system.
- Children are most prone to Polio attacks and the infection spreads on contact with the infected source. Poliomyelitis is a highly contagious disease.
- It causes paralysis, breathing difficulties and even death, if suitable and timely treatment is not administered.
- In the last few decades, there has been an active global campaign to eradicate Polio, especially in certain geographical regions, where it affects the most (Asia, Africa).
Who gets Poliomyelitis? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- All those who are not vaccinated against Poliomyelitis, are prone to contract the disease
- However, children (below the age of 5 years), pregnant women, and those with weak immune systems, are most vulnerable
What are the Risk Factors for Poliomyelitis? (Predisposing Factors)
The risk factors for Poliomyelitis are:
- Children below the age of 5 years
- Those living in unhygienic settings with poor sanitary conditions, and those who are not immunized against Polio have the greatest risk
- Travelers, who visit areas that have had recent Polio outbreaks
- Healthcare individuals - those who handle lab specimens containing the virus
- Living with someone who has the disease
- People who indulge in vigorous physical activities, even though unaware that they are exposed to the poliovirus
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Poliomyelitis? (Etiology)
- Poliovirus is transmitted chiefly through the fecal-oral route by humans. It enters the human body, through the mouth and nose. This usually happens in locations with poor (or absent) sanitary systems
- Poliomyelitis is a highly contagious disease and can spread through water and food contaminated by the virus, or through someone carrying the virus
- The incubation period, before the onset of symptoms, averages 1-2 weeks
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Poliomyelitis?
- Most of the affected victims are unaware that they carry the virus, since no symptoms are generally seen
- Individuals, who develop symptoms due to the virus, may either have Non-Paralytic Polio (most common form of Poliomyelitis), or Paralytic Polio (these are rare, and are of several types; but, are the most serious form of Poliomyelitis)
- Some individuals are disabled by a set of severe signs and symptoms that last for many decades (25-35 years), after they had been initially affected by Polio; this is typical of Post-Polio Syndrome
Non-Paralytic Polio signs and symptoms (lasting for a week) include:
- Typical viral infection symptoms (like flu)
- Fever and headache
- Fatigue and vomiting
- Stiffness and pain in the legs, arms, neck, and back
- Sore throat
- Tenderness of the muscles, muscular spasms
- Meningitis (inflammation of the brain membrane)
Paralytic Polio signs and symptoms (appearing after a week): These are based on the body parts affected and are termed Spinal Polio, Bulbar Polio (affecting the brainstem), Bulbospinal Polio (both spine and brain are affected).
- Initial symptoms that appear for about a week, resemble those of Non-Paralytic Polio
- Specific Paralytic Polio symptoms, which appear suddenly are muscular aches and spasms, loss of reflexes
- Flaccid paralysis (dangling limbs)
Post-Polio Syndrome signs and symptoms: Continuously affecting some for many years (even decades), after Poliomyelitis attack
- Early exhaustion and fatigue after normal, simple physical activities
- Muscular weakness, joint pain, atrophy; worsening progressively
- Difficulty swallowing and breathing (even while sleeping)
- Intolerance to cold conditions
How is Poliomyelitis Diagnosed?
- Physical examination and evaluation of medical history
- Poliomyelitis symptoms are key pointers to the physician
- Pathological studies of throat secretions, cerebrospinal fluid, or the feces, can help confirm the presence of poliovirus
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Poliomyelitis?
- Permanent muscle damage and paralysis may occur with Paralytic Polio, leading to severe disabilities or deformities of the feet and legs
- Other complications of Poliomyelitis include: Pneumonia, kidney stones, high blood pressure, lung/heart problems, shock, etc.
How is Poliomyelitis Treated?
- Once the poliovirus attack sets in, there is no cure. Supportive care and treatment is provided to prevent complications, soothe the patient’s condition, and to hasten recovery from Poliomyelitis
- Administration of antibiotics (to prevent other new conditions from arising) and pain relievers
- Good, nutritious diet and plenty of rest
- Physiotherapy, moderate exercising, to prevent complete loss of muscle function
How can Poliomyelitis be Prevented?
- Vaccination using Polio vaccine, for both children and adults, is the best and proven method to prevent Poliomyelitis. Multiple administration of the vaccine is employed, to ensure complete protection from the virus attack
- Improved hygiene and sanitary conditions, particularly in overcrowded habitats, to prevent spread of this highly infectious disease
What is the Prognosis of Poliomyelitis? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- The prognosis for Poliomyelitis depends primarily on the type of disease condition (Paralytic or Non-Paralytic Polio) and the affected body part. Paralytic Polio has an incidence of 1 in 200
- If the brain or spine is affected (which happens in a small proportion of the cases), then immediate medical attention is required to prevent complete paralysis, or even death
- Complete paralysis of limbs or loss of limb control for severe conditions, is a high possibility
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Poliomyelitis:
- There are two Poliomyelitis vaccine types that offer protection against the virus; inactivated polio vaccine (IPV) and oral polio vaccine (OPV)
- Initiated by the World Health Assembly in 1988 (and under the direction of several national governments and organizations), a worldwide campaign against Poliomyelitis, was launched through the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI). The last 25 years have seen a decrease in Polio incidents, by over 99% (from the 350,000 cases that existed in 1988)
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals
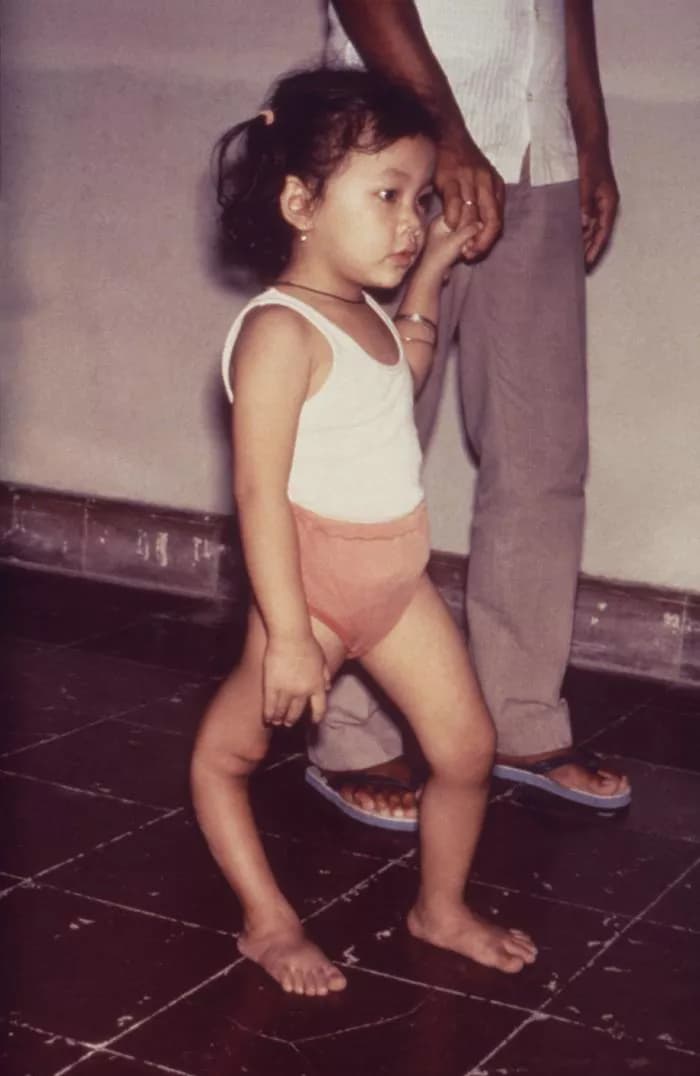

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.