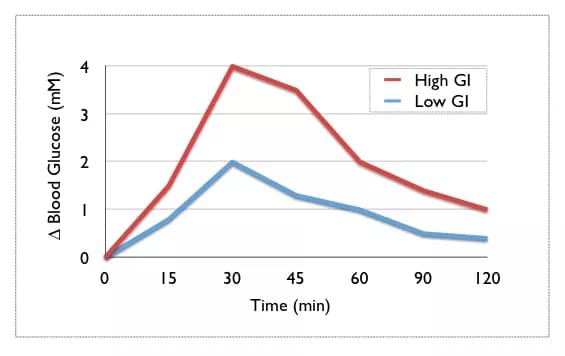
The Glycemic Index, known as GI, is the measurement of the degree in which certain carbohydrate-containing foods raise your blood glucose level. This term is synonymous with diabetes and blood sugar monitoring on a daily basis. The lower a food’s glycemic index, the less it will have an impact on your blood sugar or insulin levels.
The glycemic index transmits the potential of foods that contain the same amount of carbohydrates to raise blood sugar. This measurement, however, does not take into account that the amount of carbohydrates you intake, which also has an affect on blood glucose. Due to this, the glycemic load was created to better describe the quality and quantity of the carbohydrates in your diet. The glycemic load is calculated by the glycemic index multiplied by the carbohydrates, in grams, that the food contains, and this value is then divided by 100.
Individuals with diabetes who need to monitor their glucose levels at regular intervals often use this tracking system. There are many Glycemic Index charts exist on the Internet that allows the user to look up the value of various carbohydrates in their diets. The foods are ranked either as low, medium, or high. This system allows the user to choose low and medium GI foods and balance of the high GI foods with low GI options.
Low GI foods include pasta, oatmeal, sweet potatoes, most fruits, corn, peas, and carrots.
Medium GI foods include whole wheat, rye, and pita bread, brown, wild, or basmati rice, and quick oats. Examples of high GI foods are white bread, popcorn, pretzels, rice cakes, white rice, and corn or bran flakes.
The American Diabetes Association claims that fat and fiber can lower the glycemic index of certain foods. Oftentimes, the more cooked or processed a food is, the higher its glycemic index will be. However, foods with higher nutritional value tend to have a higher GI than those with little nutritional value. This indicates the necessity to use the glycemic index to balance out high GI foods with lower ones.
A nutritional expert can better help you to understand how to incorporate the glycemic index into your daily routine and whether or not it is right for you.
References and Information Sources used for the Article:
http://www.glycemicindex.com/ (accessed on 04/02/2016)
http://www.whfoods.com/genpage.php?tname=faq&dbid=32 (accessed on 04/02/2016)
http://www.diabetes.org/food-and-fitness/food/what-can-i-eat/understanding-carbohydrates/glycemic-index-and-diabetes.html?referrer=https://www.google.co.in/ (accessed on 04/02/2016)
Glycemic Index and Diabetes [Internet]. American Diabetes Association [updated 2014 May 14; cited 2015 Jan 2]. Available from: http://www.diabetes.org/food-and-fitness/food/what-can-i-eat/understanding-carbohydrates/glycemic-index-and-diabetes.html
Ludwig DS. The glycemic index: physiological mechanisms relating to obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. JAMA. 2002;287(18):2414-23.
Higdon J. Oregon State University Linus Pauling Institute, 2005 Dec [updated 2009 Feb; cited 2015 Jan 2]. Available from: http://lpi.oregonstate.edu/infocenter/foods/grains/gigl.html
Riccardi G, Rivellese AA, Giacco R. Role of glycemic index and glycemic load in the healthy state, in prediabetes, and in diabetes. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008;87(1):269-274.
Wolever, T. M. (1989). The glycemic index. World review of nutrition and dietetics, 62, 120-185.
Kim, I. J. (2009). Glycemic index revisited. Korean Diabetes Journal, 33(4), 261-266.
Jenkins, D. J., Wolever, T. M., Taylor, R. H., Barker, H., Fielden, H., Baldwin, J. M., ... & Goff, D. V. (1981). Glycemic index of foods: a physiological basis for carbohydrate exchange. The American journal of clinical nutrition, 34(3), 362-366.
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.