What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Vulvar Lipoma
What is Lipoma of Vulva? (Definition/Background Information)
- Lipoma of Vulva is an uncommon benign tumor of fat tissues (adipose tissues) occurring in the vulva (area around the external opening of the vagina)
- In general, lipomas can occur in almost every part of the body. In less than 5% of the individuals, lipomas can occur as multiple masses in different parts of the body
- Lipomas of Vulva are usually observed in young and middle-aged adult women; although, they may occur at any age. Significant signs and symptoms or complications are generally not observed
- Vulvar Lipoma usually occurs just below the skin (subcutaneous location) and is normally painless. In some cases, they can cause pain and difficulty in walking
- The treatment of choice is a complete surgical excision and removal of the tumor. The prognosis of Lipoma of Vulva is excellent with suitable treatment
Who gets Lipoma of Vulva? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Adult women between 20-45 years of age are generally affected by Vulvar Lipomas, though they can occur at any age. In rare cases, even infant children and very old women may present with this tumor type
- No racial or ethnic preference is noted
- Even though lipomas are generally very common, a Lipoma of Vulva is not a common occurrence
What are the Risk Factors for Lipoma of Vulva? (Predisposing Factors)
No risk factors are evident for Lipoma of Vulva in a majority of the cases.
- However, certain types of lipomatous tumors are linked to certain preexisting genetic conditions
- Rarely, in some individuals, having a family history of lipoma can increase the risk. This can result in the presence of multiple lipomas at various locations in the body
- Trauma has been implicated as a risk factor occasionally
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Lipoma of Vulva? (Etiology)
The exact cause and mechanism of Lipoma of Vulva formation is unknown.
- Chromosomal abnormalities, such as rearrangements and deletion of chromosomes, have been noted in some subtypes of lipomas
- An autosomal dominant inheritance pattern is proposed by research scientists for rare, familial cases; a condition that is termed as familial multiple lipomatosis
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Lipoma of Vulva?
The signs and symptoms of Lipoma of Vulva include:
- Individuals frequently have a slow-growing lump under the skin/mucosal surface of the vulva
- The lump is typically painless, but can be occasionally painful too
- The skin over the mass is intact; the soft mass is usually moveable under the skin
- Usually the mass is small (less than 3 cm), but if it grows in size, the mass may give rise to cosmetic issues
- Even though there may not be any pain in most cases, the location and large size of the tumor can result in walking difficulties and in maintaining certain postures (such as sitting)
- There may be pain during sexual intercourse
- Large tumors may cause significant signs and symptoms such as abdominal/pelvic pain and discomfort, urination difficulties, and even lower back pain
- The anterolateral aspect of vulva is the most common location for Vulvar Lipoma in children
- Variants of lipoma observed on the vulva are the spindle cell variant and lipoblastoma-like tumor
How is Lipoma of Vulva Diagnosed?
Lipomas of Vulva are diagnosed using the following tools:
- Evaluation of the individual’s medical history and a thorough physical (pelvic) examination
- Ultrasound scan of the abdomen
- CT or CAT scan with contrast of the abdomen and pelvis may show a well-defined mass. This radiological procedure creates detailed 3-dimensional images of structures inside the body
- MRI scans of the abdomen and pelvis: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a magnetic field to create high-quality pictures of certain parts of the body, such as tissues, muscles, nerves, and bones. These high-quality pictures may reveal the presence of the tumor
- Colposcopy:
- The cervix (including the vagina and vulva) is examined with an instrument, called a colposcope. This helps the physician get a magnified view of the cervix
- In order for this procedure to be performed, the individual has to lie on a table, as for a pelvic exam. An instrument, called the speculum, is placed in the vagina to keep the opening apart, in order to help the physician visualize the cervix. The colposcope is then used to get a magnified view of the inside
Although the above modalities can be used to make an initial diagnosis, a tissue biopsy of the tumor is necessary to make a definitive diagnosis to begin treatment. The tissue for diagnosis can be procured in multiple different ways which include:
- Fine needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy of the tumor: A FNA biopsy may not be helpful, because one may not be able to visualize the different morphological areas of the tumor. Hence, a FNA biopsy as a diagnostic tool has certain limitations, and an open surgical biopsy is preferred
- Core biopsy of the tumor
- Open biopsy of the tumor
Tissue biopsy:
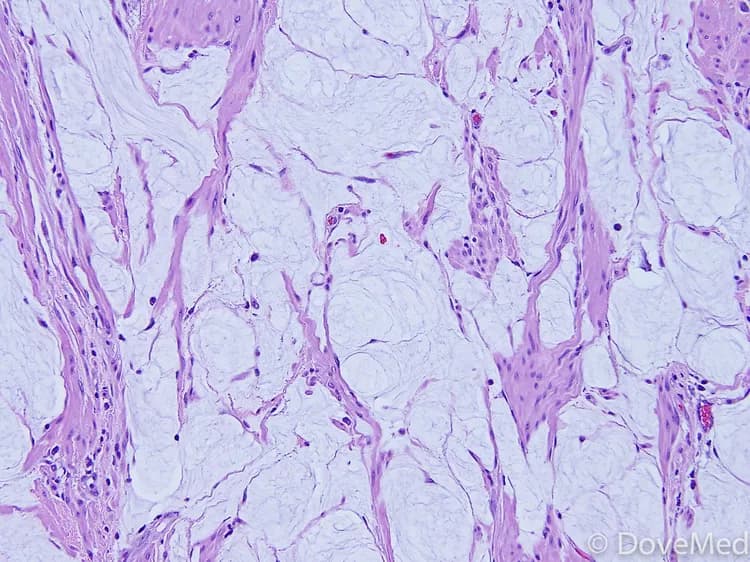
- A tissue biopsy of the tumor is performed and sent to a laboratory for a pathological examination. A pathologist examines the biopsy under a microscope. After putting together clinical findings, special studies on tissues (if needed) and with microscope findings, the pathologist arrives at a definitive diagnosis. Examination of the biopsy under a microscope by a pathologist is considered to be gold standard in arriving at a conclusive diagnosis
- Biopsy specimens are studied initially using Hematoxylin and Eosin staining. The pathologist then decides on additional studies depending on the clinical situation
- Sometimes, the pathologist may perform special studies, which may include immunohistochemical stains, molecular testing, and very rarely, electron microscopic studies to assist in the diagnosis
Note:
- It is extremely important to rule out the presence of a liposarcoma, which is a malignant tumor, since it can have presentations similar to a lipoma, which is a common and benign tumor
- Rarely, lipomas can show foci of calcification that can be detected on radiological studies
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Lipoma of Vulva?
Complications due to Lipoma of Vulva could include:
- Recurrence of the tumor after surgery (if surgery does not entirely remove the tumor)
- The presence of the tumor can lead to painful sexual intercourse
- Emotional stress due to a concern for cancer
- If the tumor is large and has infiltrated deep into adjoining regions, it may lead to significant risks during surgical operations, which could include damage of vital nerves, blood vessels, and other adjoining organs
- Post-surgical infection at the wound site is a potential complication
How is Lipoma of Vulva Treated?
The treatment measures for Lipoma of Vulva may include the following:
- The healthcare provider may recommend a ‘wait and watch’ approach for small-sized tumors that do not cause any significant signs and symptoms, following a diagnosis of a lipoma is established
- In general, even though lipomas may be treated using steroids and liposuction techniques, healthcare providers may advise the surgical removal of Vulvar Lipomas in most cases
- Surgical intervention with complete excision can result in a complete cure. It can also help reduce the chances of tumor recurrence
- Radiation therapy and chemotherapy are not usually required
- Post-operative care is important: Minimum activity level is to be ensured until the surgical wound heals
- Follow-up care with regular screening and check-ups are important
How can Lipoma of Vulva be Prevented?
- Current medical research has not established a way of preventing Lipoma of Vulva formation
- Medical screening at regular intervals with scans and physical examinations are advised to detect any early recurrences
What is the Prognosis of Lipoma of Vulva? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
The prognosis of Vulvar Lipoma is excellent through a complete excision and removal, since it is a benign fat tissue tumor.
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Lipoma of Vulva:
There are many histological subtypes of lipomas and all subtypes are benign tumors. The lipoma subtype is usually diagnosed on a microscopic examination of the tumor sample by a pathologist and is mentioned on the pathology report.
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.