What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Direct Inguinal Hernia
- Groin Hernia
- Indirect Inguinal Hernia
What is Inguinal Hernia? (Definition/Background Information)
- When a part or whole of an internal organ protrudes through weak areas of the adjoining abdominal wall muscles, the condition is termed as a hernia
- Medically, there are various types of hernia, and these are called:
- Inguinal hernia
- Incisional hernia
- Femoral hernia
- Umbilical hernia
- Hiatal hernia
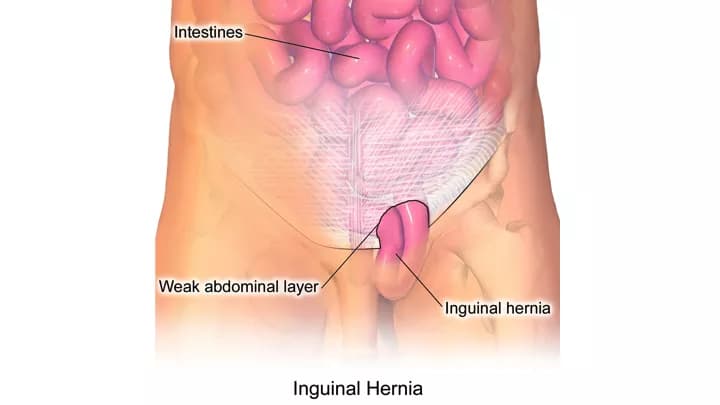
- An Inguinal Hernia is a bulge or lump made-up of soft tissue, typically located in the scrotum or groin region. It usually occurs, if there is a weak area on the groin muscle, or due to a congenital defect
- There are two main types of Inguinal Hernias:
- Direct Inguinal Hernia: It starts in adulthood
- Indirect Inguinal Hernia: It is a type of congenital hernia
- Apart from a bulge in the pubis, other signs and symptoms may include groin pain (particularly during coughing, lifting heavy objects), weakness, numbness in the region, severe discomfort, and even strangulation of the hernia, which is an emergency medical condition
- Severe Inguinal Hernias require surgical correction, though all hernias do not require to be repaired immediately
- The prognosis for Inguinal Hernia is generally good with proper surgical treatment
Who gets Inguinal Hernia? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Both males and females are affected by Inguinal Hernia
- However, both indirect and direct Inguinal Hernias are much more common in males than in females
- Pregnant women are more prone to Inguinal Hernias, due to the immense pressure on the abdominal wall, caused by the pregnancy
- A majority of the congenital Inguinal Hernias are of the indirect type
What are the Risk Factors for Inguinal Hernia? (Predisposing Factors)
There are many risk factors for Inguinal Hernia. The most common predisposing factor for an Indirect Inguinal Hernia is having a congenital defect, wherein a canal or opening in the groin region, does not close the way it should, following birth.
The following risk factors have all shown to contribute to both direct and indirect Inguinal Hernias:
- Having a job that requires a lot of heavy lifting, straining, and/or bending
- Genetics: An Inguinal Hernia is much more likely, if a parent or sibling has the condition
- Older age due to decreased muscle strength
- Being overweight
- Being a smoker
- If one has had a hernia in the past
- Multiple pregnancies, twin pregnancies, large babies
- Premature infants increase the risk for indirect hernias, due to the presence of abnormal congenital opening in the inguinal area
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Inguinal Hernia? (Etiology)
In many cases, there are no proven causes of Inguinal Hernias. However, the following are believed to be potential causes:
- A congenital defect in which the opening in the groin region does not close after birth
- Sudden fast movements that may strain the muscles
- Sudden, intense dieting
- Smoking
- Having a chronic cough
- Not enough exercise, causing weak abdominal muscles
- Excess abdominal fluid
- Straining while lifting heavy objects
- Trouble with urination, causing stress and pressure on abdominal muscles
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Inguinal Hernia?
Most Inguinal Hernias show no signs or symptoms. In some, if symptoms are present, the following may be observed:
- Bulge or lump on the side of the pubic bone, especially if the bulge disappears, while lying flat on one’s back
- Weakness, numbness, pressure or tingling sensation in the groin
- Groin pain when coughing, lifting heavy objects, and/or bending
- Men may have swelling, discomfort, and/or pain, within their testicles or scrotum
- Children and infants may have weakness in their abdomen
- Nausea and/or vomiting may occur, if the intestines become strangulated within the hernia. This can be a medical emergency
How is Inguinal Hernia Diagnosed?
An Inguinal Hernia may be diagnosed through:
- A physical examination and evaluation of medical history by the physician, is normally sufficient to diagnose the condition
- During the exam a physician usually feels the groin area, while having the patient stand and cough, in order to detect any movement or strain in the area
- Imaging modalities, like ultrasound of the groin and CT scan of abdomen, may also be used to diagnose Inguinal Hernias
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Inguinal Hernia?
The possible complications of an Inguinal Hernia may include:
- In certain cases, an Inguinal Hernia may become strangulated, which means part of the intestine gets trapped within the abdominal wall. It can cause intestinal tissue to lose blood supply causing tissue death. Strangulated hernia is a medical emergency and may require an immediate emergency surgery
- If part of the intestine becomes trapped but the blood supply is not necessarily totally cut-off, it is known as incarcerated inguinal hernia. Although this situation does not always require surgery, it may cause immense pain, constipation, nausea or even vomiting, if not corrected promptly
The possible and rare complications that an Inguinal Hernia surgical repair could lead to include:
- The hernia can recur
- Excessive bleeding or loss of blood
- Painful scarring or infection at wound site
- Damage to internal organs
- Complications from anesthesia
How is Inguinal Hernia Treated?
A hernia cannot be repaired or treated using medications. Surgery is the only option for repairing an Inguinal Hernia.
- In many cases, having surgery to correct an Inguinal Hernia is considered an “elective surgery,” as opposed to surgery in emergency situation
- Like other hernias, if strangulation occurs and the hernia causes lack of blood flow to the intestine, immediate surgical intervention is usually deemed necessary
There are two main types of surgeries performed in this situation:
- Herniorrhaphy, or open repair, is when the surgeon makes a cut and physically pushes the intestine that is bulging out, back into the abdomen, and then stitches the damaged tissue or muscle back together. In elective surgeries, most of the surgeons place a synthetic mesh in the weak area, as placing a mesh has shown to decrease hernia recurrence
- Laparoscopy is performed with several small cuts rather than one large one, and a fiber optic tube with a camera is inserted into the abdomen. This enables the surgeon to use special instruments to repair the hernia (synthetic mesh is usually used with these surgery types)
How can Inguinal Hernia be Prevented?
The following measures may be adopted to prevent Incisional Hernias:
- Smoking should be completely stopped or avoided
- Avoid straining, or exerting too much tension, during bowel movements and while urinating
- Individuals suffering from obesity should try and bring down their body weight to reduce the risk
- Avoid losing weight too suddenly, as inadequate nutrition will lead to weakened abdominal muscles, making it more prone to developing a hernia
- When lifting heavy objects, use proper body posture and technique
- Avoid lifting objects that are too heavy (if it is avoidable)
- Eat plenty of foods that are high in fiber, especially if you suffer from chronic constipation
What is the Prognosis of Inguinal Hernia? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- The outcomes of Inguinal Hernias vary, depending on the size of the hernia and how early it is diagnosed. Typically, the longer an individual has a hernia, the more severe it will become
- Many individuals typically have a hernia that never totally goes away or disappears
- Many have hernias that are not severe enough to require a surgical correction (especially, if it never becomes strangulated)
The outcome for patients, who undergo surgery, is usually much more promising, based on the following statistics:
- The chance of getting another hernia after having surgery is only between 1-10 out of every 100 surgeries performed
- If a mesh is used to repair the weak abdominal muscle, the chance of recurrence is reduced by about 50%
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Inguinal Hernia:
- Surgeries are usually performed as an outpatient procedure
- The recovery period for surgery depends on many factors, including the size and duration of the initial Inguinal Hernia, and the health of the patient undergoing surgery
- If hernia is medial to epigastric artery, then most likely it is a direct hernia
- If hernia is lateral to epigastric artery, then most likely it is an indirect hernia
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.