Hypertension
What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Elevated Blood Pressure
- Hyperpiesia
- Hypertensive Disease
What is Hypertension? (Definition/Background Information)
The heart is responsible for pumping fresh, oxygen-rich blood to various organs of the body. The oxygen-rich blood reaches the organs through a system of blood vessels, called the arteries. Blood pressure (BP) refers to the pressure with which blood flows through these vessels. When this pressure exceeds the normal upper limit of flow pressure, it is known as Hypertension (or High Blood Pressure).
There are two components of blood pressure:
- Diastolic blood pressure: It is the pressure with which blood flows in the arteries, when the heart is in a relaxed state
- Systolic blood pressure: The pressure flow in the arteries, measured when blood is pumped into them by the heart
Blood pressure can be classified as follows:
- Normal: Systolic BP less than 120; diastolic BP less than 80
- Prehypertension: Systolic BP between 120-139; diastolic BP between 80-89
- Stage 1 Hypertension: Systolic BP between 140-159; diastolic BP between 90-99
- Stage 2 Hypertension: Systolic BP greater than 160; diastolic BP greater than 100
All the values of blood pressure measurements are expressed in millimetres of mercury (mm Hg).
Who gets Hypertension? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- The risk of developing a High Blood Pressure, increases with age
- The condition is slightly more common in males, than females
- The Afro-American population seems to be more affected than the Caucasian population
What are the Risk Factors for Hypertension? (Predisposing Factors)
Hypertension risk factors may include:
- The condition of High Blood Pressure may run in the family; hence, it is called a familial condition. One is more likely to have high BP, if one of the family members has this condition
- The risk increases in menopausal females
- The African-American population are at an increased risk of developing elevated BP levels, compared to other racial groups
- With advancing age, the arteries become more thickened. This increases the risk of developing such a condition
- Being overweight
- Certain lifestyle habits, like smoking, lack of exercises, regularly eating a high-fat diet and, a consumption of alcohol in excess increases the probability high BP
- Individuals who work in high stress environment, are more likely to develop the condition
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases one's chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Hypertension? (Etiology)
Based on the causes, Hypertension is classified as:
- Primary (essential) Hypertension: When no underlying cause is identified for High Blood Pressure, it is called as a primary or idiopathic Hypertension. This type of Hypertension is responsible for almost 95% of all cases.
- Secondary Hypertension: When an underlying cause is identified, it is labeled as secondary Hypertension. Some of the causes of secondary Hypertension include:
- Diseases affecting the kidneys, such as narrowing of the renal arteries, certain infections of the kidneys, polycystic kidney disease, etc.
- Diseases affecting the adrenal gland, such as tumors of the adrenal gland, which results in high level of circulating hormones responsible for Elevated Blood Pressure
- Medications such as: Oral contraceptive pills, anti-tumor medications (cyclosporine), steroids, illicit drugs(like cocaine and amphetamine)
Defects in the arteries, which are present since birth, like coarctation of aorta, can also predispose one to High Blood Pressure.
There is also a BP type, termed as “white coat Hypertension”. In this type, an individual develops increased BP levels while visiting their healthcare providers, due to anxiety. Normally, such individuals do not have High Blood Pressure. A white coat Hypertension is a transient rise in blood pressure, which is due to the anxiety associated with the visit to a doctor’s office or hospital. It is harmless and resolves on providing the patient with some reassurance.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Hypertension?
- In a majority of the cases, Hypertension is diagnosed incidentally on a routine visit to a doctor’s office,for any other reason
- Symptoms develop when the blood pressure is very high, and is due to a decrease in the supply of blood, to important organs of the body
- Extremely high values of blood pressure in the range of, systolic > 220 mm Hg and diastolic >120 mm Hg, can lead to any one of the following conditions:
- Hypertensive urgency: It is defined as BP in the range of, systolic > 220 and diastolic >120, without damage to any of the body organs
- Hypertensive emergency: It is defined as BP in the range of, systolic > 220 and diastolic >120, with evidence of organ damage
The following signs and symptoms may occur with consistently elevated levels of High Blood Pressure:
- Headache: It may be due to a decreased supply of nutrients, or due to bleeding in the brain
- Lack of energy or altered mental status
- Light-headedness, which may progress to blackouts
- Changes in visual acuity, causing vision problems
- When blood supply to heart decreases, one may experience chest pains
- Urinary symptoms can occur from damage to the kidney vessels,which in turn can lead to spilling of blood in urine (hematuria)
- Some individuals may also complain of a feeling of rapid heartbeats, called palpitations
How is Hypertension Diagnosed?
A diagnosis of Hypertension is made by measuring the blood pressure in the arms, using a device known as a sphygmomanometer. The reading is recorded in terms of systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Once an elevated reading of BP is obtained, repeated measurements (minimum of 3) are needed to classify it as Hypertension.
Some other tests that the physician might order include those that are meant to rule-out any underlying causes of High Blood Pressure:
- Blood test/analysis to determine the levels of sodium and potassium
- Urinary tests to detect any kidney disorders
- Determination of blood sugar levels
- Echocardiogram, to identify any abnormality in the structure of heart
- Ultrasound of the kidneys, to detect any abnormal blood flow and/or changes in the structure of the kidneys
Tests that may be performed to rule out organ damage include:
- Comprehensive eye exam
- Head CT, in cases of hypertensive emergencies
- EKG (electrocardiograph) to determine effects of high BP on heart
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Hypertension?
The complications of Hypertension develop over a long period of time. They are due to an inadequate flow of blood, to various organs of the body. Following are some of the complications:
Effects on the heart:
- With long-standing Hypertension the heart may increase in size, due to a condition known as left ventricular hypertrophy; in which the left chamber of the heart becomes bigger in size
- This leads to an increased burden of work, on the heart. It may progress to heart attack or even heart failure
Effects on the eye:
- If High Blood Pressure is left untreated, a sequence of change occurs in the eye. This leads to damage of the retina, which is responsible for image formation
- This may eventually end-up in blindness, which is often irreversible
Effects on the brain:
- Due to an increased force of blood flow, the vessels supplying blood to the brain may rupture and lead to bleeding in the brain
- This is known as stroke and it may cause permanent neurological defects in the body
Individuals with high BP and those who also smoke, are at an increased risk of developing a condition, known as aneurysm:
- Aneurysm is dilatation (expansion) of a part of blood vessels, due to weakening of the vessel wall
- The blood vessels may rupture and cause uncontrolled bleeding
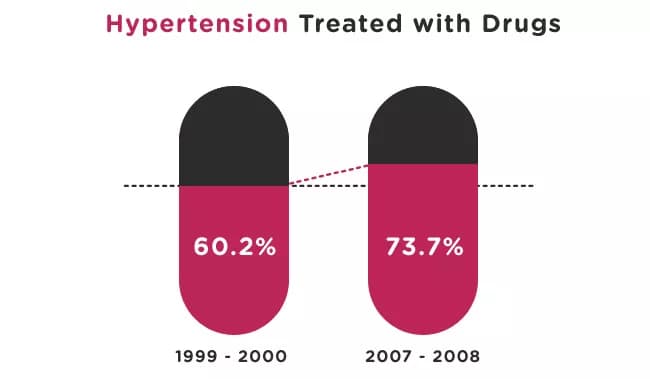
How is Hypertension Treated?
The management of Hypertension consists of the following:
Lifestyle modifications:
- It is the first step in the management of prehypertension and stage 1 Hypertension
- Weight loss: It is the most important factor in management of High Blood Pressure
- Smoking cessation, low alcohol intake
- Regular exercising
- Taking a low-fat, low-salt diet
Medications:
- Once a trial of lifestyle modification fails to achieve the target blood pressure, medications are used to achieve the desired result
- They are selected on the basis of how quickly the physician diagnoses that the BP must be lowered
- The choice of medication also depends on the underlying cause (if any)
- The various medications used to lower blood pressure are: Alpha blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, central alpha agonists, diuretics, vasodilators, etc.
- For stage 1 Hypertension, initially only one medication is prescribed
- For stage 2 Hypertension, two medications might be prescribed, to achieve the target BP
Newer medications to alter the effects of abnormal proteins using RNA interference (RNAi) and other molecular technologies are in various stages of development and commercialization. The medical provider may help with information on advancements in new treatment methods.
How can Hypertension be Prevented?
The various methods to avoid developing a Hypertension may include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Eating a diet low in salt and low in fat
- Exercising regularly
- Smoking cessation, limit the intake of alcohol
- Taking the medications regularly
- Managing stress using certain relaxation techniques
What is the Prognosis of Hypertension? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- Timely diagnosis and management of Hypertension may prevent certain grave complications associated with it. Once the complications develop, they might be irreversible
- If complications develop, then the prognosis is dependent upon the extent of damage to the organs (if any). Greater the duration an individual has increased BP and greater the level of Hypertension, poorer is the prognosis; especially if the condition is not treated adequately
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Hypertension:
Abnormally low blood pressure level is termed as hypotension. This condition can also cause heart attacks, strokes, and renal failures.
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.