What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Brain Haemangioma
- Central Nervous System Angioma
- Intracranial Hemangioma
What is Brain Hemangioma? (Definition/Background Information)
- Hemangiomas are benign malformation of blood vessels that can occur in a number of tissues such as the brain, kidney, liver, lung, skin (called cherry hemangioma), and nasal cavity. Brain Hemangiomas are often observed in individuals over the age of 40 years
- There are two types of hemangiomas - familial and sporadic. Familial conditions are linked to genetic mutations usually inherited from a parent. The sporadic condition is not linked to a family history of hemangioma and occurs as isolated events
- There are no known risk factors for Brain Hemangiomas; however, individuals who have experienced cranial irradiation may be more likely to develop this condition
- Brain Hemangiomas may present with headaches, poor muscle control, impaired sensations, and hemorrhage. Complications could include bleeding in the tumor, secondary infections, and neurological complications
- 25% of Brain Hemangiomas are asymptomatic; nevertheless, certain complications, such as bleeding, can call for immediate treatment
- Surgical removal of the hemangioma is typically the best treatment for this condition. In some cases, radiation therapy is also performed
- Presently, there are no available measures to prevent the development of Brain Hemangiomas
Who gets Brain Hemangioma? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Brain Hemangiomas are relatively rare, benign brain tumors affecting roughly 0.4% of the population
- They can occur in individuals of any age, but are most often diagnosed in individuals at the age of 40 or older
- Brain Hemangiomas is observed to occur around the world, in individuals of any race, ethnicity, or gender. However, studies show a higher rate of occurrence in women
What are the Risk Factors for Brain Hemangioma? (Predisposing Factors)
Risk factors associated with Brain Hemangioma include:
- Individuals who have undergone cranial irradiation (for various health conditions) during childhood are more likely to develop Brain Hemangiomas later in life
- Studies also suggest that 12.5% of cases occurred following instances of intracerebral hemorrhage
- Individuals with a family history of Brain Hemangiomas are at a high risk for developing familial form of the condition
- Most cases of Brain Hemangiomas are of the sporadic form and occur as isolated events
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Brain Hemangioma? (Etiology)
Brain Hemangiomas are classified as familial and sporadic (majority of the cases).
- Familial Brain Hemangiomas are generally linked to at least 3 genetic mutations, thought to be the cause of the condition. They are associated with mutations in the KRIT1 (CCM1), CCM2, and PDCD10 genes; 85-95% of all familial cases experience mutations in these three genes
- Other Familial Brain Hemangiomas may be caused by mutations in unidentified genes
- There is currently no known cause for Sporadic Brain Hemangiomas. They are not caused by mutations in these 3 genes (KRIT1, CCM2, and PDCD10 genes)
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Brain Hemangioma?
Many of the symptoms associated with Brain Hemangiomas are dependent on the location of individual tumors. The common signs and symptoms include:
- Headaches
- Nausea and vomiting
- Gait abnormalities
- Poor muscle control and coordination
- Numbness or loss of sensations
- Vision or speech abnormalities
- Difficulty swallowing
- Seizures
- Hemorrhage (bleeding within the tumor): Pregnant women and children are at an increased risk of hemorrhage of Brain Hemangioma
Most patients experience symptoms for less than 1 year before being diagnosed.
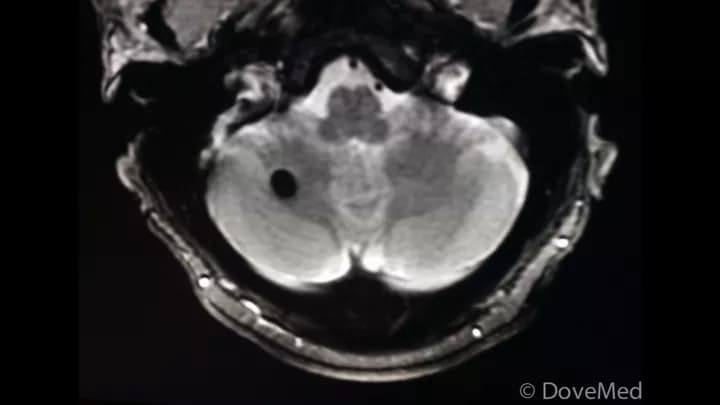
How is Brain Hemangioma Diagnosed?
A diagnosis for Brain Hemangioma includes evaluating the clinical history (physical exam) and a thorough family history. Other tools to help diagnose the condition may include:
- MRI scan of the brain searching for characteristic “popcorn” shape
- CT scans (generally for larger hemangiomas) in addition to a contrast agent
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Brain Hemangioma?
Complications associated with Brain Hemangiomas are mostly related to bleeding in the tumor. These include:
- Accumulation of blood in the hemangioma can cause both generalized and focal seizures. Most often these seizures can be treated with medicine; however, in some cases, the entire removal of the hemangioma is required
- Bleeding of the hemangioma can be lethal if it is near the brainstem
- Bleeding of Brain Hemangiomas may also cause strokes, due to decreased blood flow to other areas of the brain
How is Brain Hemangioma Treated?
Surgical resection is the most common form of treatment for Brain Hemangiomas.
- Microsurgery can be performed through an open-skull incision to remove the tumor and this is recommended for most cases of Brain Hemangiomas
- Tumors in hard-to-reach places, including around the brainstem, are often treated with focused radiation using stereotactic radiosurgery
Currently, radiological methods have not undergone extensive long-term testing, so its efficacy is yet to be well-established.
How can Brain Hemangioma be Prevented?
- Currently, there are no specific methods or preventative techniques for the formation of Brain Hemangiomas. The condition may be caused by genetic factors
- If there is a family history of the condition, then genetic counseling will help assess risks, before planning for a child
- There is a likelihood that Brain Hemangioma risk may be reduced, if cranial irradiation is avoided at a young age
- Active research is currently being performed to explore the possibilities for treatment and prevention of inherited and acquired genetic disorders
What is the Prognosis of Brain Hemangioma? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
The prognosis of Brain Hemangioma depends on the severity of the signs and symptoms. Generally, the affected individuals are either asymptomatic or able to manage and cope with their symptoms on a day-to-day basis.
- Although some Brain Hemangiomas may grow over time, others may stop growing altogether
- If hemangiomas are associated with seizures or repeated hemorrhages, resection of the tumor through surgery is generally performed
- Resection of Brain Hemangiomas are often curative
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Brain Hemangioma:
The following DoveMed website link is a useful resource for additional information:
https://www.dovemed.com/health-topics/neurological-institute/
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.