What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- BD (Boutonnière Deformity)
- Boutonnière Deformity of Finger
- Central Slip Disruption
What is Boutonnière Deformity? (Definition/Background Information)
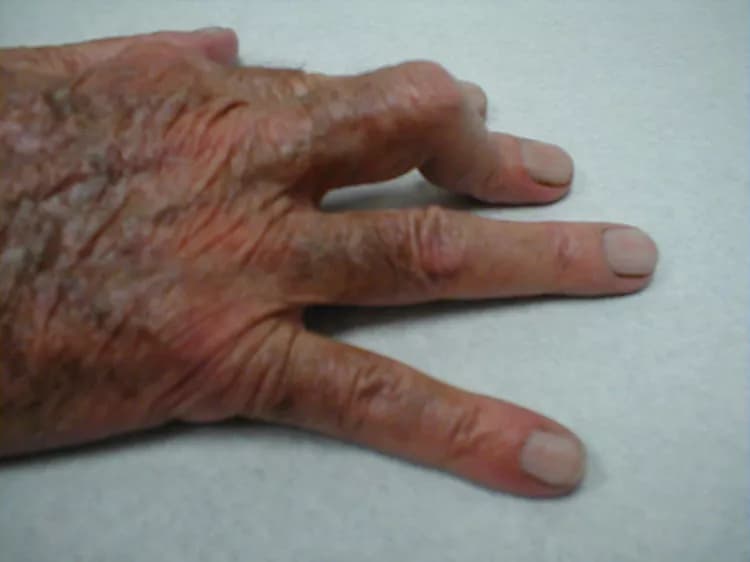
- Boutonnière Deformity (BD) is a common injury to the tendons of the finger, which usually prevents the finger from completely straightening out
- Extensor tendons are tendons in the fingers and hand that allow the fingers to straighten. If the injury site is in the middle joint tendon that is located over the back of the finger, then it is called a central slip injury
- BD occurs, when there is a disturbance to the central slip of the extensor tendon, causing an abnormal finger deformity
- Without immediate treatment and rehabilitation, this deformity may continue to progress resulting in permanent disability and diminished functionality of the extremity (finger)
Who gets Boutonnière Deformity? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Boutonnière Deformity may occur in individuals of all age, gender, race/ethnic groups
- However, it is more prevalent in young men, due to a greater frequency of participation in high-impact sports
What are the Risk Factors for Boutonnière Deformity? (Predisposing Factors)
Common risk factors associated with Boutonnière Deformity include:
- Participating in sports that require catching or throwing a ball, such as baseball, basketball
- Chronic inflammatory disorder (rheumatoid arthritis)
- Excess connective tissue formation (painless) beneath the skin of the fingers and palm (Dupuytren’scontracture)
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Boutonnière Deformity? (Etiology)
Boutonnière Deformity of Finger causal factors include:
- Direct trauma to a bent finger
- Taking part in any rough or high-impact sport
- Individuals, who have rheumatoid arthritis
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Boutonnière Deformity?
Signs and symptoms of Boutonnière Deformity include:
- Inability to straighten finger middle joint and bend the fingertip joint; a noticeable deformity of the finger is observed
- Swelling and pain in the middle joint of the finger
How is Boutonnière Deformity Diagnosed?
Diagnostic methods that a physician may use to help diagnose Boutonnière Deformity include:
- Physical examination: During a physical examination, the physician will also ask the individual to perform a few tasks, like straightening the injured finger, bending it at the fingertip, etc.
- The individuals are also expected to provide an explanation of the circumstances that led to the injury. In addition to this, a complete medical history will also be evaluated, which may aid in a definitive diagnosis
- X-ray: X-rays are occasionally recommended. This may help the physician identify, if any fractured bones are connected to the central slip of the extensor tendon
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Boutonnière Deformity?
A complication associated with Boutonnière Deformity is severe injury to the tendons surrounding the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) and distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints. This may cause an abnormal finger deformity.
How is Boutonnière Deformity Treated?
Nonsurgical treatment measures for Boutonnière Deformity are:
- Complete immobilization of the finger with a splint or cast, is required to restrict its movement
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory oral medications may be used to treat BD, which help decrease pain and swelling
- Some individuals may require physical therapyto restore strength and flexibility of the finger muscles. It is important that you begin with only some light motion exercises
Surgical treatment measures for Boutonnière Deformity are:
- Joint fixation: Joint fixation is a surgical procedure to repair the damaged PIP joint. Surgical hardware (such as plates, screws, or rods) is then used to stabilize the joint, while it heals
- Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF): For displaced bone fragments, open reduction technique is used to realign the fractured bone, to its original position. Surgical hardware (such as plates, screws, or rods) is then used to stabilize the fractured bones, below the skin
- Finger joint fusion: Finger joint fusion is a surgical procedure in which a physician fuses two joint surfaces of the finger together, restricting finger movement. The purpose of this procedure is to relieve pain, immobilize the joint, and prevent reoccurrence of this deformity
How can Boutonnière Deformity be Prevented?
Although there are no methods to prevent some of the factors that contribute to Boutonnière Deformity, certain steps that may be taken include:
- Individuals, who participate in any high-risk sports, such as basketball/baseball, should wear appropriate safety gear, to help prevent the possibility of injuries to the finger (particularly to the extensor tendon)
- Aggressive treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
What is the Prognosis of Boutonnière Deformity? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- A majority of Boutonnière injuries heal without any serious complications; though, some may require surgical interventions
- When immediate treatment and rehabilitation measures are provided, a high percentage of individuals regain full strength and range of motion in their injured finger
- Some Boutonnière Deformity cases may result in permanent deformity and disability of the finger
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Boutonnière Deformity:
A PIP (proximal interphalangeal) joint sprain or a PIP joint dislocation, is a very painful injury affecting the middle joint of a finger. In this, the middle joint may get sprained (ligaments are torn) or dislodged, due to an external injury/trauma.
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.