What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Human Babesiosis
- Redwater Fever
- Malaria of the Northeast
What is Babesiosis? (Definition/Background Information)
- Babesiosis is a rare and severe tick-borne disease, caused by a parasite. The ticks (blacklegged ticks, deer ticks, or bear ticks) are carriers (host) to parasites of the genus babesia
- The condition is most commonly found in certain European regions and United States (particularly in the northeast and north of the Midwest region). The peak seasons are the summer months, when the conditions are warm
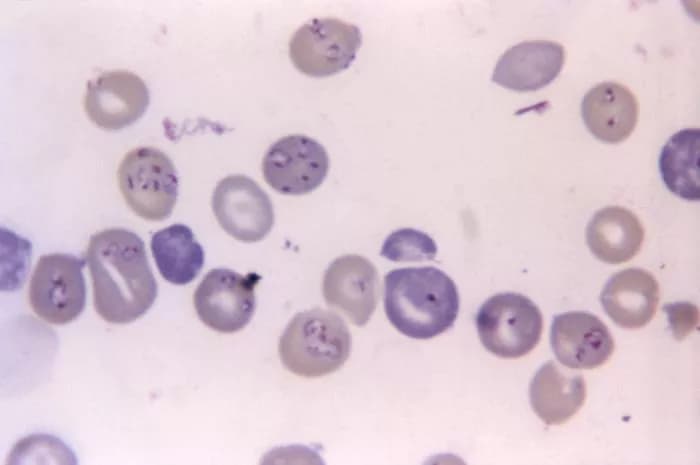
- Most human infections are caused by the parasites Babesia microti (in the US) or Babesia divergens (in Europe), which infect the red blood cells. The infection causes malaria-like symptoms in humans, including muscle aches, nausea, and enlargement of spleen (splenomegaly)
- A treatment for Babesiosis would involve the use of anti-microbial drugs. Generally, healthy individuals who are infected by the parasite, make a complete recovery without any major complications. Hence, the prognosis of Babesiosis is generally excellent
- The infection may be fatal in immunocompromised individuals, or in whom a surgical removal of the spleen is performed
Who gets Babesiosis? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Babesiosis is caused by a parasite, through infected tick bites; no specific age or sex distribution is observed
- The infected tick bites are generally confined to individuals residing or travelling to certain regions of Europe and USA
- All racial and ethnic groups are prone to this infection
What are the Risk Factors for Babesiosis? (Predisposing Factors)
The following are the risk factors for Babesiosis:
- Exposure to infected ticks during any outdoor activities, such as camping, trekking through tick-infested regions
- Residing in an area endemic to the blacklegged, deer, or bear ticks, is a high risk factor in contracting Babesiosis
- Individuals with weak immune system, or whose immune system has been suppressed by the continuous use of immune suppressing medications and treatment for other diseases
- Those who have undergone a splenectomy (surgery to remove spleen). Spleen helps in removing infected blood cells. When the spleen is removed, the defense against Babesiosis infection is lost. Hence, there is an increased risk of Babesiosis in a patient, who has undergone a splenectomy
- Babesiosis infection can be transmitted through blood transfusion, from an infected blood donor
- Congenital transmission can occur from an infected mother to the baby during pregnancy and delivery
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Babesiosis? (Etiology)
- Babesiosis is caused by the parasite babesia
- The babesia microorganisms are transmitted by Ixodes scapularis ticks, also called by various names, such as blacklegged ticks, deer ticks, or bear ticks
- Animals (such as cattle, white-tailed deer, mouse) are the normal hosts to these ticks; infections to human beings are typically uncommon
- When an individual is bitten by an infected tick, usually while being outdoors, babesia infects the human red blood cells and causes Babesiosis illness. Multiplication of the parasites in human blood, causes the clinical manifestations of Babesiosis
- Babesiosis can also spread through contaminated blood transfusions; from the infected blood of a donor to another receiving the blood (recipient)
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Babesiosis?
Most individuals infected with Babesiosis, feel fine and are asymptomatic. Some may develop flu-like symptoms that include:
- High fever, chills, fatigue
- Muscle aches and headache
- Drenching sweats
- Loss of appetite
- Anemia
- Nausea and vomiting
Since the signs and symptoms of Babesiosis can be confused with flu, any (recent) travel history should always be mentioned to the healthcare providers.
How is Babesiosis Diagnosed?
A diagnosis of Babesiosis is made by the following tests:
- Physical examination with evaluation of medical history, which also includes a recent history of travel, places visited, etc.
- Multiple peripheral blood smears are examined to test for Babesiosis. But, this test is effective, only when performed within the first 2 weeks of the infection
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Blood tests are also done to test for the level of antibodies against Babesiosis
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction) Test: It is done to detect babesia DNA in blood
- Liver function blood test
- Kidney function tests
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Babesiosis?
In a majority of the individuals, Babesiosis does not cause any complications. However, it may lead to the following complications in elderly adults, individuals in whom the spleen has been surgically removed, or in patients, whose immunity has been suppressed using medications, for various reasons:
- Very low blood pressure (hypotension)
- Severe hemolytic anemia (breakdown of red blood cells)
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
- A low platelet count (thrombocytopenia)
- Intravascular coagulation leading to blood clot and bleeding (DIC)
- Kidney and liver damage
How is Babesiosis Treated?
Individuals, in whom Babesiosis is asymptomatic, may not require any treatment. In others, the treatment is started only after confirming a diagnosis of this tick-borne infection. The treatment measures may include:
- Administering antimicrobial drug is the best treatment for Babesiosis
- Combination of two types of anti-parasitic drugs, such as atovaquone (Mepron) and azithromycin, or quinine and clindamycin combination, may be recommended
- The drug quinine must be avoided during pregnancy, since the drug can affect the unborn child
- The patient may be advised plenty of rest
- Plenty of fluids are recommended to avoid dehydration
How can Babesiosis be Prevented?
Currently, there are no vaccines available for the prevention of Babesiosis. Some preventive steps and control measures may include the following:
- Avoiding exposure to ticks that cause Babesiosis is the best form of prevention. Ticks are usually found in bushes and overgrown grasses. Avoiding such places may prevent individuals from being exposed to the ticks
- While going for an outdoor trip, walk on cleared trails, or in the center of the trail to avoid bushes and overgrown grasses, where ticks carrying Babesiosis are found in plenty
- Wearing socks, long pants, and long sleeved shirts, are advised to protect the skin from being exposed to the ticks. A light-colored clothing is recommended, so that if ticks get attached to the skin, they can be easily identified and quickly removed before they infect the individual
- Use of repellents on skin and clothing is recommended. However, the instructions in the product label should be carefully followed, prior to usage of such products
- In areas where tick-infestation for Babesiosis has been established (or is known) - after returning from any outdoor activities, ‘tick checks’ should be conducted on the body, with sufficient lighting and using a large mirror. If any ticks are found, these have to be removed with the help of a pair of pointed tweezers
What is the Prognosis of Babesiosis? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- Healthy patients usually recover completely from Babesiosis; in such individuals, the infection may not cause any symptoms too
- The disease may last several months, if no proper treatment is administered
- Babesiosis could be severe and fatal in individuals, who have undergone a spleen removal surgery (splenectomy) and in those who have a suppressed immune system (due to other medical conditions)
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Babesiosis:
- The backlegged tick or deer tick also transmits a variety of other diseases, such as Lyme disease, ehrlichiosis, and human granulocytic anaplasmosis
- Individuals affected by Babesiosis, may also be simultaneously infected by other tick-borne diseases (at the endemic locations)
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.