What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Deep Angiomyxoma of Vulva
- Deep Vulvar Angiomyxoma
- Vulvar Aggressive Angiomyxoma
What is Aggressive Angiomyxoma of Vulva? (Definition/Background Information)
- Aggressive Angiomyxoma of Vulva is a rare, benign, soft tissue tumor with subcutaneous and deep tissue involvement. It has no metastatic potential, but can be locally aggressive with high-infiltrative capacity (spreading to adjacent tissues and structures)
- Aggressive Angiomyxoma of Vulva is mostly found in young and middle-age women (during the active reproductive age). The tumor commonly occurs in the pelvic region and in areas, between the anus and genitals (called the perineum)
- There are no clearly established risk factors for Vulvar Aggressive Angiomyxoma and the cause of tumor formation is also unknown. Current research indicates that the cause may be due to certain genetic abnormalities
- The tumor appears as a vulvar cyst (due to its shiny outer surface) and may be mistaken for a Bartholin gland cyst during examination by a healthcare provider. Small tumors are often asymptomatic, while large tumors occur as a poorly-defined (deep tissue) infiltrative mass or an area of firmness
- The treatment of choice is a surgical removal of the entire tumor. Following surgery to remove the tumor, an aggressive angiomyxoma is generally known to recur. The prognosis of Aggressive Angiomyxoma of Vulva is good with appropriate treatment and adequate follow-up
Who gets Aggressive Angiomyxoma of Vulva? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Aggressive Angiomyxoma of Vulva is generally present in young and slightly middle-aged women. Women in the age category of 30-40 years are affected the most
- Rare occurrences have been noted in children (young girls)
- There is no geographical, racial, or ethnic preference noticed
What are the Risk Factors for Aggressive Angiomyxoma of Vulva? (Predisposing Factors)
- No specific risk factors are evident or identified for Aggressive Angiomyxoma of Vulva
- They are generally found during the reproductive years in women
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Aggressive Angiomyxoma of Vulva? (Etiology)
- The exact cause of Aggressive Angiomyxoma of Vulva development is unknown
- Some studies show that certain chromosomal rearrangements may be involved in the formation of these tumors
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Aggressive Angiomyxoma of Vulva?
The signs and symptoms of Aggressive Angiomyxoma of Vulva include:
- Small aggressive angiomyxomas can remain asymptomatic or present only a set of mild symptoms; they may resemble a benign cyst
- Some tumors may appear outwardly small, but they are known to infiltrate into deep tissue and may be actually larger on imaging studies
- Larger tumors appear as a poorly-circumscribed mass or an area of firmness with no pain; some vulvar tumors may appear pedunculated
- Large tumors are known to reach sizes of 10-16 cm; they can ulcerate and discharge fluid
- There may be discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse
- It may cause pain and compress the surrounding structures and organs
- Large tumors may also cause significant signs and symptoms such as abdominal/pelvic pain and discomfort, urination difficulties, and even lower back pain
How is Aggressive Angiomyxoma of Vulva Diagnosed?
Aggressive Angiomyxoma of Vulva diagnosis may involve the following tools:
- Evaluation of the individual’s medical history and a thorough physical (pelvic) examination
- Ultrasound scan of the abdomen
- CT or CAT scan with contrast of the abdomen and pelvis may show a well-defined mass. This radiological procedure creates detailed 3-dimensional images of structures inside the body
- MRI scans of the abdomen and pelvis: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a magnetic field to create high-quality pictures of certain parts of the body, such as tissues, muscles, nerves, and bones. These high-quality pictures may reveal the presence of the tumor
- Colposcopy:
- The cervix (including the vagina and vulva) is examined with an instrument, called a colposcope. This helps the physician get a magnified view of the cervix
- In order for this procedure to be performed, the individual has to lie on a table, as for a pelvic exam. An instrument, called the speculum, is placed in the vagina to keep the opening apart, in order to help the physician visualize the cervix. The colposcope is then used to get a magnified view of the inside
Although the above modalities can be used to make an initial diagnosis, a tissue biopsy of the tumor is necessary to make a definitive diagnosis to begin treatment. The tissue for diagnosis can be procured in multiple different ways which include:
- Fine needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy of the tumor: A FNA biopsy may not be helpful, because one may not be able to visualize the different morphological areas of the tumor. Hence, a FNA biopsy as a diagnostic tool has certain limitations, and an open surgical biopsy is preferred
- Core biopsy of the tumor
- Open biopsy of the tumor
Tissue biopsy:
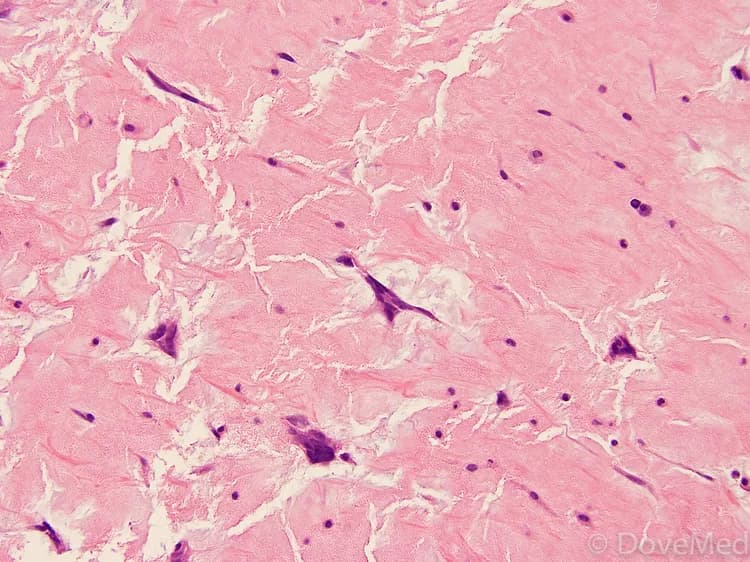
- A tissue biopsy of the tumor is performed and sent to a laboratory for a pathological examination. A pathologist examines the biopsy under a microscope. After putting together clinical findings, special studies on tissues (if needed) and with microscope findings, the pathologist arrives at a definitive diagnosis. Examination of the biopsy under a microscope by a pathologist is considered to be gold standard in arriving at a conclusive diagnosis
- Biopsy specimens are studied initially using Hematoxylin and Eosin staining. The pathologist then decides on additional studies depending on the clinical situation
- Sometimes, the pathologist may perform special studies, which may include immunohistochemical stains, molecular testing, and very rarely, electron microscopic studies to assist in the diagnosis
Note: During the initial stages, a Vulvar Aggressive Angiomyxoma may be misdiagnosed as a Bartholin’s cyst or other vulvar cysts.
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Aggressive Angiomyxoma of Vulva?
The possible complications of Aggressive Angiomyxoma of Vulva may include:
- Emotional stress and concern for vulvar cancer
- Frequently, tumor recurrence following surgery is known to take place
- Tumor metastasis has been noted in a few isolated cases; but, this is exceedingly rare
- If the tumor is large and has infiltrated deep into adjoining regions, it may lead to significant risks during surgical operations, which could include damage of vital nerves, blood vessels, and other adjoining organs
- Post-surgical infection at the wound site is a potential complication
Aggressive angiomyxoma is an aggressive tumor that can destroy the adjacent tissue structures, unlike a superficial angiomyxoma that is typically indolent.
How is Aggressive Angiomyxoma of Vulva Treated?
Following are the treatment methods adopted for Aggressive Angiomyxoma of Vulva:
- Wide surgical excision, with removal of the entire lesion is the standard treatment method. If the tumor is not fully removed, then there is a high chance of its recurrence
- Tumors that cannot be surgically removed may be treated using gonadotropin releasing hormone agonist therapy. This may be undertaken either prior to surgery to shrink the tumor size, or to treat the tumor in individuals who cannot tolerate surgery
- Tumor embolization is a possible treatment option. Here the blood supply to the tumor is blocked resulting in tumor death or tumor shrinkage
- If there is any pain, it is controlled through pain medications
- Chemotherapy and radiation therapy generally have no therapeutic effect on the tumor
- Post-operative care is important: Minimum activity level is to be ensured until the surgical wound heals
- Follow-up care with regular screening and check-ups are important, since the tumor can recur
How can Aggressive Angiomyxoma of Vulva be Prevented?
- Current medical research has not established a method of preventing Vulvar Aggressive Angiomyxoma
- Medical screening at regular intervals with scans and physical examinations are advised. Due to chances of its recurrence, often several years of active follow-up vigilance is necessary
What is the Prognosis of Aggressive Angiomyxoma of Vulva? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- The prognosis of Aggressive Angiomyxoma of Vulva is generally excellent, when the tumor is small and located in a surgically accessible area, without much local infiltration. In such cases, the tumor recurrence risk can also be minimized
- Surgical excision of deeply infiltrated angiomyxoma is difficult and intricate, if it has generally spread around the region. In such situations, the prognosis may be guarded
- Long-term periodic follow-up check-ups with screening are advised
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Aggressive Angiomyxoma of Vulva:
Please visit our Cancer & Benign Tumor Health Center for more physician-approved health information:
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.