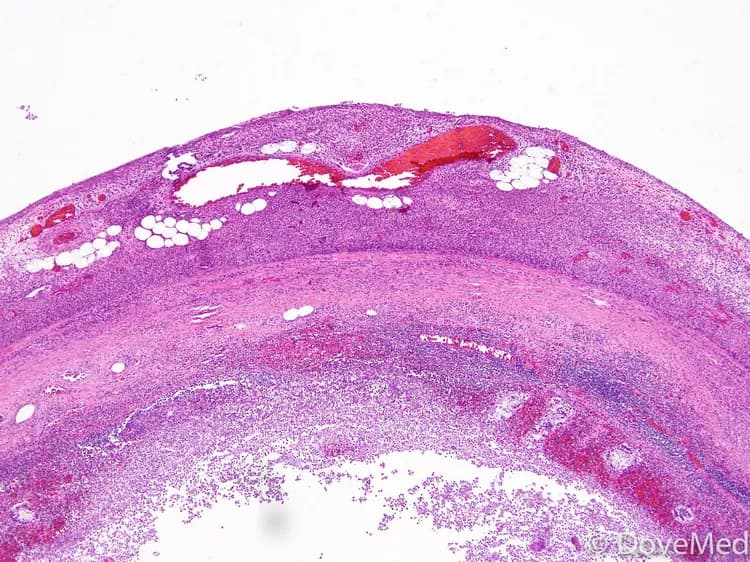
Acute Appendicitis
What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Epityphlitis
What is Acute Appendicitis? (Definition/Background Information)
- Appendicitis is inflammation of the small blind pouch of the bowel called appendix, located at the beginning of the large bowel. The condition can be acute or chronic. Acute Appendicitis is more common in individuals between the ages of 10 and 30 years
- The inflammation is commonly caused by obstruction of the appendix. The obstruction can be due to various reasons, such as infection, the presence of hardened stool (fecalith), foreign bodies, or due to tumor formation
- The obstruction of the appendix in Acute Appendicitis causes increased secretion of fluid and mucous from the inner lining of the appendix, which builds pressure inside the appendix. The fluid attracts bacteria, which in turn multiply and build more pressure
- This causes weakening of the appendix wall and reduces blood supply to the appendix. When blood supply is totally deprived, the wall of the appendix dies and may perforate. Perforation causes flow of bacteria into the abdominal cavity, which is dangerous and can result in a serious illness
- A low fiber intake and chronic constipation are some risk factors for developing Acute Appendicitis. Additionally, ingestion of foreign objects could potentially cause the condition; children are at a high risk of developing Acute Appendicitis owing to this cause
- The presence of foreign bodies, inflammatory bowel diseases, infections, tumors/cancers, and hard stools are some known causes of Acute Appendicitis
- The most typical symptom of the condition is abdominal pain, which becomes more intense on the lower right side of the abdomen. Additionally, there can be nausea, vomiting, fever, constipation or diarrhea, and pain in the general abdominal area. Acute Appendicitis can lead to rupture of the appendix, abscess formation, intestinal blockage, and spread of infection to areas outside the appendix
- Acute Appendicitis is typically diagnosed by a physical examination, wherein a patient might report tenderness in the region of his/her lower right abdomen, known as the McBurney’s point
- The treatment options for Acute Appendicitis are determined on the basis of the signs and symptoms and the presence of any complications. For uncomplicated cases, the appendix may be surgically removed by an open appendectomy or laparoscopic procedure
- Complications might require additional or special treatment, which are determined by a healthcare provider/surgeon on a case-by-case basis. However, when diagnosed properly and treated promptly, the prognosis for Acute Appendicitis is reported to be good
Who gets Acute Appendicitis? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Irrespective of gender, age group, ethnicity or race, any individual is prone to Acute Appendicitis; although, the cause(s) for the condition might vary depending on the age group
- Generally, the condition is rare in children under the age of 2 years. It is most common in the age group 10-30 years
What are the Risk Factors for Acute Appendicitis? (Predisposing Factors)
Some known risk factors for developing Acute Appendicitis are:
- Chronic constipation
- Low fiber intake
- Swallowing small foreign objects (when children are at high risk)
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases one's chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Acute Appendicitis? (Etiology)
Acute Appendicitis occurs as a result of an obstructed appendix. The various causal factors for this condition include:
- Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs) that includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis
- Infections (more common during childhood and in young adulthood)
- Fecal stasis and fecalith or hardened stool; more common among the elderly
- Parasites (especially observed in certain Eastern countries)
- Ingestion of foreign bodies/materials
- The presence of cancer or benign tumors
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Acute Appendicitis?
The following are some common symptoms associated with Acute Appendicitis:
- Abdominal pain that first originates around the umbilicus and then gradually moves towards a point on the right lower quadrant of the abdomen, called the McBurney’s point
- Sometimes, the pain can occur anywhere in the upper or lower abdomen, back, or rectum
- The pain is then followed by nausea and vomiting
- Fever, shivering, chills
- Loss of appetite
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Occasionally, painful urination and severe cramps can occur
How is Acute Appendicitis Diagnosed?
Most cases of Acute Appendicitis can be diagnosed by simple physical examination of the abdomen, which elicits tenderness upon touch over the Mc Burney’s point. Additionally, recording the individual’s medical history can be helpful in the diagnosis.
Based on the condition of the patient and their symptoms, a healthcare provider may request any or all of the following tests and exams:
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Basic metabolic panel
- X-ray of abdomen
- Ultrasound or CT scan of abdomen
Note: In women of child-bearing age, it is important to exclude pregnancy, since ectopic pregnancies and appendicitis present similar symptoms. If the symptoms are due to an ectopic pregnancy, then misdiagnosing the condition may lead to serious consequences.
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Acute Appendicitis?
The following are some potential complications of Acute Appendicitis:
- Rupture/perforation of the appendix
- Peritonitis (spread of infection to areas outside of appendix) secondary to rupture/perforation of the appendix
- Abscess formation
- Blockage of the intestine secondary to an inflammatory mass
- If left untreated, Acute Appendicitis can lead to sepsis. Sepsis is a condition in which infecting bacteria enters the bloodstream and travels to other parts of the body. This is a very serious and potentially life-threatening complication
- Infection of the surgical wound after operating upon the infected appendix
How is Acute Appendicitis Treated?
In some rare cases, mild cases of appendicitis may get better with antibiotic therapy. This decision is taken based on the evaluation of a healthcare provider.
In most cases of Acute Appendicitis, a surgery may be recommended by the healthcare provider. A surgical removal of the appendix (called appendectomy) in uncomplicated appendicitis may be done either laparoscopically or by surgically opening the abdomen.
- Open appendectomy involves making a deep incision on the lower abdomen and removing the appendix from the surrounding abdominal organs
- In laparoscopic approach, a surgeon makes 3 or 4 small incisions for insertion of the camera and the laparoscopic instruments and the appendix is cut and removed
In case of complications, such as perforation or abscess formation, the treatment varies according to the type of complication and is determined by the surgeon on an individual basis.
How is Acute Appendicitis be Prevented?
According to current research, it is not possible to prevent the development of Acute Appendicitis. However, the risk for the condition may be reduced by ensuring the following:
- Having a fiber-rich diet regularly
- Early and complete treatment of infections, especially those that affect the digestive system
- Prompt management of any disorders or health conditions (including cancers and benign tumors) affecting the GI tract
- Some study reports indicate that prolonged or extended breastfeeding can reduce the risk of Acute Appendicitis
What is the Prognosis of Acute Appendicitis? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- The prognosis is typically good, if Acute Appendicitis is diagnosed early and treated immediately
- The recovery is slower when there are complications including perforation, abscess formation, or infection of the inner lining of abdomen (peritonitis)
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Acute Appendicitis:
Open appendectomy is a surgical procedure for removing the appendix. The following link will provide more information about this surgical procedure:
http://www.dovemed.com/common-procedures/procedures-surgical/open-appendectomy/
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.