What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Ball of Foot Pain
What is Sesamoiditis? (Definition/Background Information)
- Sesamoiditis is a common and painful condition that is characterized by inflammation of the sesamoid bones. Sesamoids are bones that are embedded in a tendon or muscle and located in many joints
- Sesamoiditis is predominantly caused by any physical activity, such as an athletic sport, causing repetitive stress. There is a high incidence rate of this condition among young athletes and sportspersons
- The condition is usually treated non-surgically. However, surgery is an option if the symptoms and pain does not improve. The prognosis of Sesamoiditis is usually excellent with appropriate treatment
Who gets Sesamoiditis? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Sesamoiditis may occur in individuals of all ages, races, ethnic groups, and genders
- However, it is commonly seen in young individuals who participate in certain physical activities such as running or dancing
- Individuals over the age of 60 years also have an increased risk of Sesamoiditis
What are the Risk Factors for Sesamoiditis? (Predisposing Factors)
A few risk factors for Sesamoiditis include:
- Advancing age
- Participating in certain sports that causes one to use the balls of the feet more often, such as with tennis and basketball
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases one's chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Sesamoiditis? (Etiology)
The common causes of Sesamoiditis include:
- Repetitive stress on the forefoot due to certain physical or sports activities
- Direct trauma to the sesamoid bones
- Osteoarthritis of the sesamoid bones
- Excessive pronation (inward movement) of the foot
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Sesamoiditis?
The signs and symptoms of Sesamoiditis may include:
- Gradual onset of pain under the joint of the big toe
- Difficulty bending and straightening the big toe
- Difficulty walking
How is Sesamoiditis Diagnosed?
Diagnostic methods that a physician may use to help diagnose Sesamoiditis include:
- Physical examination: During a physical examination, the physician will examine for tenderness at the sesamoid bones. The physician may also ask the individual to bend and straighten the big toe. In addition to this, a complete medical history can aid in arriving at a definitive diagnosis
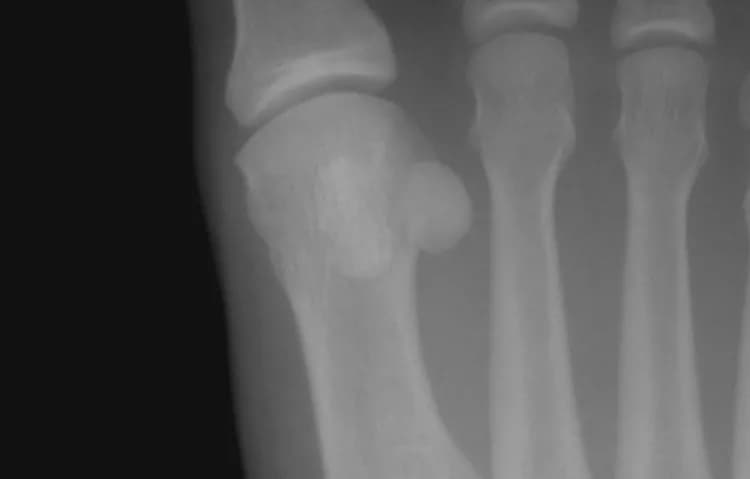
- X-ray of the foot: X-rays use radiation to produce images of the foot. In many individuals, the sesamoid bone close to the center of the foot (the medial sesamoid) has two parts, called bipartite. Given that the edges of the bipartite sesamoid are usually smooth, and the edges of fractured sesamoids are usually jagged, x-rays are very important in assuring a correct diagnosis. A physician may also order an x-ray of the other foot to compare the bone structures
- Additionally, a bone scan may be ordered if the x-rays appear normal
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Sesamoiditis?
The complications of Sesamoiditis include:
- Prolonged and chronic pain, if left untreated
- Weakness and deformity of the toe
- Fracture of the sesamoid bone
How is Sesamoiditis Treated?
Sesamoiditis is mostly treated with conservative and nonsurgical interventions. However, surgery is an option, if the pain or other symptoms show no improvement.
Nonsurgical treatment for Sesamoiditis may include:
- Any activity that further aggravates the condition should be avoided. The physician usually recommends refraining from all such activities until the symptoms improve
- Applying ice to the affected area can help reduce pain
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory oral medications, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, may be used to treat Sesamoiditis. These medications can help decrease the pain
- Corticosteroid injections help provide temporary relief of symptoms and in improving the range of motion. It is important to note that corticosteroid injections only give temporary relief. Prolonged episodes of such injections may injure the joints in the long run
- Use of a well-padded custom-made shoe with soft soles and low heels
- Physical therapy may help to restore strength, as well as flexibility in the muscles
Surgical treatment for Sesamoiditis may include:
- Bone removal: A bone removal procedure is the surgical removal of an affected sesamoid bone
- Scraping: Scraping is a surgical procedure used to scrape off the affected part of the tissue on the sesamoid bone. This procedure is performed when individuals are diagnosed with plantar keratosis
- Bone graft: A bone graft is a surgical procedure that involves repairing and replacing damaged bones. This is performed in case a fracture results from Sesamoiditis
How can Sesamoiditis be Prevented?
Some of the common recommendations to help prevent Sesamoiditis include:
- Wear appropriate footwear
- Joggers and runners should use orthotic insoles to help with overpronation (higher susceptibility to sports injuries)
What is the Prognosis of Sesamoiditis? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- The majority of Sesamoiditis cases are successfully treated without surgery. The long-term prognosis is usually good after treatment
- When properly treated, a high percentage of individuals regain their full strength and range of motion in their foot
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Sesamoiditis:
The patella (kneecap) is the largest sesamoid bone.
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.