What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Pitcher’s Shoulder
- Shoulder Impingement Syndrome
- Tennis Shoulder
What is Rotator Cuff Tendinitis? (Definition/Background Information)
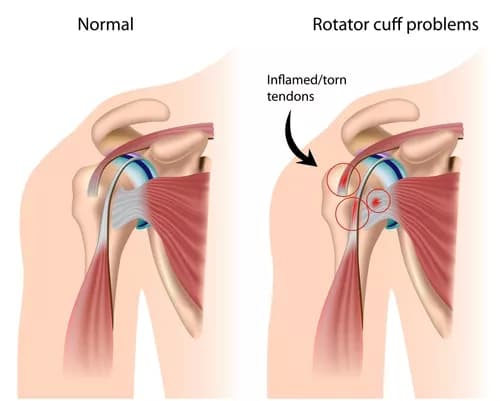
- A Rotator Cuff Tendinitis is a common and very painful injury that occurs, when the muscles or tendons within the shoulder joint, are overworked and become inflamed
- The condition is usually caused by any physical activity, such as an athletic sport, or a normal daily activity that may require repetitive use of the shoulder joint.
- Overall, there is a high rate of occurrence of this condition, among young athletes
- Rest, physical therapy, and over-the-counter medications, are usually the initial recommended measures to treat Rotator Cuff Tendinitis. However, surgery is an option, if these aforementioned treatment methods are unsuccessful, to manage impingement of the shoulder joint
Who gets Rotator Cuff Tendinitis? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Rotator Cuff Tendinitis can occur in individuals of any gender, race, or ethnic group
- Young athletes, who participate in any sport that require a set of repetitive shoulder muscle or shoulder joint movements, have a higher incidence rate
What are the Risk Factors of Rotator Cuff Tendinitis? (Predisposing Factors)
Common risk factors associated with Rotator Cuff Tendinitis include:
- An advancing age increases the risk for development of impingement of the shoulder joint, due to tendinitis
- Individuals with certain occupations (like carpenters and painters), which require a set of repetitive physical movement/motion for prolonged periods, have an increased risk
- Any sport that requires repetitive overuse of the shoulder
- Poor throwing or overhead techniques, while participating in sports, such as baseball or tennis, increases the risk of an individual developing Rotator Cuff Tendinitis
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Rotator Cuff Tendinitis? (Etiology)
- There are 4 main muscles that connect the upper arm bone (humerus) to the shoulder blade (scapula), which constitute the rotator cuff. These muscles include the subscapularis, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and teres minor
- Shoulder injuries involving the rotator cuff muscles are quite common; they also include any irritation to the muscles/tendons of the rotator cuff
- Constant damage to the rotator cuff leads to impingement of shoulder joint movement. Hence, Rotator Cuff Tendinitis is also known as Shoulder Impingement Syndrome
A few causal factors associated with Rotator Cuff Tendinitis include:
- Individuals participating in certain sports activities that require a set of repetitive movements for prolonged periods, such as baseball or tennis
- Certain occupations that require repetitive overuse of the shoulder muscles, such as with carpentry and painting
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Rotator Cuff Tendinitis?
The symptoms are usually mild at the beginning and do not warrant immediate medical attention. There could be a noticeable pain associated with any activities that involve lifting the arms above one’s head/shoulder. The signs and symptoms of a Rotator Cuff Tendinitis include:
- Relentless pain in the shoulder, especially while performing any overhead activities, such as overhead lifting
- Radiating pain from the shoulder to the arm
How is Rotator Cuff Tendinitis Diagnosed?
Some of the tests a physician may use to help diagnose a Rotator Cuff Tendinitis include:
- Physical examination: A thorough physical examination is important in examining the range of motion, strength, and stability, of the shoulder. Individuals are also expected to provide an explanation of the circumstances that caused the injury. In addition to this, a complete medical history can aid in arriving at a definitive diagnosis
- X-ray of the shoulder: X-rays use radiation to produce images of the shoulder. This can help your physician rule-out other possible causes for discomfort, such as a fracture
- Magnetic imaging (MRI): An MRI is a more detailed scan that uses a magnetic field to produce images that allow a physician to view any damage to the bones and soft tissue that surrounds the rotator cuff
- Ultrasound imaging of the shoulder joint: The use of high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the shoulder
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Rotator Cuff Tendinitis?
Complications due to a Rotator Cuff Tendinitis may include:
- Recurrence of the injury or tendon rupture, without adequate treatment
- Limited range of motion in the shoulder, severely affecting one’s work
How is Rotator Cuff Tendinitis Treated?
The treatment of Rotator Cuff Tendinitis includes both nonsurgical and surgical treatment methods.
Nonsurgical treatment:
- Any activity that aggravates the shoulder condition should be avoided. The physician may advise the individual to refrain from participating in any physical activities, till the pain or symptoms get better
- Applying ice to the shoulder/arm can help reduce pain and swelling
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory oral medications, such as Ibuprofen and naproxen, can help reduce the pain and swelling, within the shoulder
- Corticosteroid injections help provide temporary relief of symptoms, and in improving the range of motion. It is important to note that corticosteroid injections only give temporary relief. Prolonged episodes of such injections, may injure the joints in the long-run
- Individuals are likely to need physical therapy exercises. The goals of these exercises are to strengthen the shoulder muscles, improve flexibility, and decrease any stiffness
Surgical treatment: If nonsurgical treatments are unhelpful, surgical treatment may be recommended. Common surgical procedures may include:
- Arthroscopy: Arthroscopic surgery is a moderately invasive surgical intervention that is used to repair the shoulder joint using small surgical instruments (through a fiber-optic scope connected to a television camera). These instruments are inserted through a small incision within the shoulder and guided using a video monitor
- Open surgery: Open surgery is an invasive procedure in which, an incision is made in the shoulder, to allow the physician to repair the damaged muscles or tendons
How can Rotator Cuff Tendinitis be Prevented?
In individuals with a history of Rotator Cuff Tendinitis, a daily stretching exercise program may help reduce the chances of its recurrence. It is also important to incorporate exercises (into one’s activities) to help strengthen the shoulder. A few other ways would include:
- Avoid any repetitive lifting or pulling (especially overhead) of objects that are heavy
- In sports, learn the correct techniques and avoid poor (overhead) throwing techniques
What is the Prognosis of Rotator Cuff Tendinitis? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- In the majority of the individuals, the long-term prognosis of Rotator Cuff Tendinitis is usually good. The individuals can regain their full strength and range of shoulder motion
- However, those with a more severe condition may experience recurrence of the symptoms, even after physical therapy has been completed. The duration for a complete recovery may be prolonged
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Rotator Cuff Tendinitis:
A rotator cuff tear is an injury that occurs, when one or more muscles and the tendons that help, to secure the shoulder joint, tear. Such tears are very painful and they result from any physical activity, such as an athletic sport, or a normal daily activity that may require repetitive use of the shoulder muscles.
The following article links will help you understand a rotator cuff tear.
http://www.dovemed.com/diseases-conditions/rotator-cuff-tear-rct/
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.