What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Degenerative Joint Disease of the Hip
- Degenerative Osteoarthritis of Hip
- Hip Arthritis
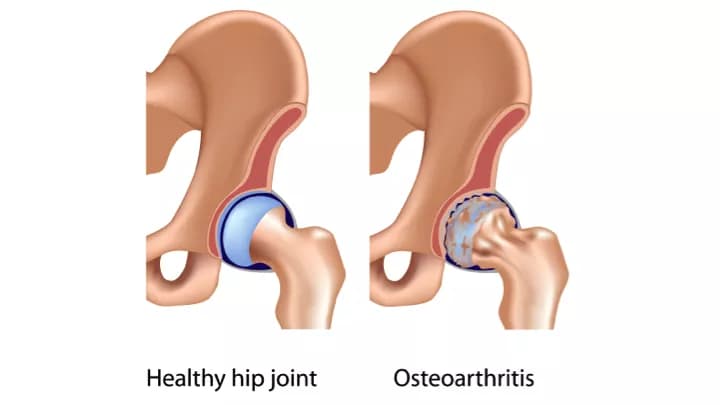
What is Osteoarthritis of the Hip? (Definition/Background Information)
- Osteoarthritis is a painful joint disorder characterized by the progressive degeneration of the articular cartilage that covers the bone surface of joints. Over time, the cartilage wears down.Studies have indicated that Osteoarthritis has a genetic component to it
- Osteoarthritis of the Hip is a gradual progressive degenerative disorder that affects one or more joints of the hip
- Individuals, who develop the condition, begin to experience pain and stiffness within the hip that usually increase with age
- Treatment associated with Osteoarthritis of the Hip includes nonsurgical and surgical methods
Who gets Osteoarthritis of the Hip? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Osteoarthritis of the Hip may occur in individuals of all age, race, ethnic group, and belonging to any gender
- A high percentage of individuals, who develop the condition, are middle-aged to elderly women
- Middle-aged men and young athletes, who sustain traumatic joint injuries, are higher prone to develop osteoarthritis
- Women (especially after menopause), are more likely to develop the degenerative condition, than men
What are the Risk Factors for Osteoarthritis of the Hip? (Predisposing Factors)
Common risk factors associated with Osteoarthritis of the Hip include:
- Osteoarthritis in the Hip is rarely diagnosed in individuals under 40 years old. However, since it is a gradually progressing disorder, the risk of developing this condition usually increases with age
- Women are higher susceptible to the condition than men, especially after menopause
- Individuals, who sustain a joint injury, while participating in a rough/high impact sports, such as football and basketball
- Abnormal pressure on the joints, due to excess body weight (obesity)
- Repetitive stress on the hip associated with certain occupations, such as with farming, can increase the risk
- Gout: A medical condition caused by a high level uric acid within the blood
- Paget’s disease of bone: A rare bone disorder characterized by abnormal growth and deformity of bones
- Hypothyroidism: A medical condition characterized by the body’s inability to produce enough thyroid hormone
- Diabetes type I: High blood glucose levels that result from insulin secretion deficiency
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Osteoarthritis of the Hip? (Etiology)
Causes associated with Osteoarthritis of the Hip include:
- An injury to the hip joint, while participating in sports, such as football and basketball
- Repetitive stress on the hip due to certain occupations, such as farming or construction
- Studies have indicated that Osteoarthritis has a genetic component to it
- Obesity, causing abnormal pressure on the joints
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Osteoarthritis of the Hip?
Osteoarthritis is a gradual and progressive disorder that usually worsens over time. Common signs and symptoms associated with Osteoarthritis within the Hip include:
- Noticeable pain, tenderness
- Swelling
- Stiffness, reduced mobility of the hip joint
- Formation of bone spurs around the hip joint
How is Osteoarthritis of the Hip Diagnosed?
Diagnostic methods that a physician may use to help diagnose Osteoarthritis in the Hip include:
- Physical examination: The physician will perform a thorough physical examination to determine, if the individual has Osteoarthritis. In addition to this, a complete medical history may aid in arriving at a definitive diagnosis
- X-ray of hip joint: X-rays are utilized to visualize images of the soft tissues and bones of the hip. A physician may discover evidence of Osteoarthritis in the Hip, before the individual experiences any noticeable symptoms
- Blood test: A blood test is routinely used to diagnose various disease and conditions. During this test, a blood sample is drawn from an artery or vein using a needle and taken to a laboratory for analysis. Blood tests help the healthcare provider evaluate other causes of arthritis
- Joint fluid analysis of hip joint: Occasionally, fluid may accumulate around a joint. Analysis of this fluid will give clues regarding the cause of the joint fluid accumulation, which causes pain and disability. A needle is inserted into the joint space and the accumulated fluid aspirated with a syringe. It is then sent to a laboratory for analysis to determine:
- The type of cells present in the fluid
- Chemical composition of the fluid
- The presence of crystals (examination of fluid under a microscope)
- If an infection is suspected as a cause accumulation of the joint fluid, then a joint fluid culture may be performed. The culture of joint fluid will confirm an infection of the hip joint, as the cause of arthritis(termed infective arthritis)
- Ultrasound imaging of hip joint: The use of high-frequency sound waves to generate a thorough image of the hip
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Osteoarthritis of the Hip?
Osteoarthritis is a progressive condition that gradually worsens over time. The complications of Osteoarthritis of the Hip could include:
- Chronic pain and stiffness within the hip joint, which may prevent individuals from performing their routine daily activities
- Permanent disability
- Due to a lack of mobility, the incidence of obesity, heart disease, and hypertension could increase
How is Osteoarthritis of the Hip Treated?
The treatment of Osteoarthritis of the Hip includes nonsurgical and surgical methods. A healthcare provider may start with non-surgical treatment methods before adopting surgical procedures and techniques. These include:
- Rest: Any activity that aggravates the hip condition further should be avoided. The physician usually advises to refrain from all such activities, until the symptoms stop
- Heat and ice: Applying a damp heated towel or ice to the hip joint, can help reduce pain and swelling
- Assistive device: Occasionally, specific assistive devices, such as a cane or walker, are recommended. This may help the individual in performing some of their everyday activities
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication: Oral medications, such as ibuprofen and naproxen, can help decrease the hip pain and swelling
- Topical non-steroidal medications have been shown to improve osteoarthritis at specific locations. Application twice a day is required for a month, then daily, to attain relief
- Corticosteroid injections help provide temporary relief of symptoms, and in improving the range of motion. It is important to note that corticosteroid injections only give temporary relief. Prolonged episodes of such injections, may injure the joints in the long-run
- Normal fluid within a joint contains a material called hyaluronic acid. When a joint is affected by osteoarthritis, the hyaluronic acid levels within the joint reduces, which reduces the joints ability to lubricate. Visco supplementation is a minimally invasive technique commonly used in treating osteoarthritis. During this procedure, a small dose of hyaluronic acid is injected into the hip, which helps relieve pain
- After the symptoms have decreased, it is important to begin some light motion exercises. Physical therapy may help restore strength, as well as provide flexibility, in the muscles
Surgical treatment measures include:
- Joint fusion: Joint fusion is a surgical technique that involves the removal of the arthritic part within the joint and fusing two surrounding bones together. The purpose of this procedure is to relieve pain, stabilize the joint, and regain some range of motion of the hip
- Total hip arthroplasty: Total arthroplasty involves the complete removal of cartilage within the hip joint. The hip joint (acetabulum and femoral head) is then removed and replaced by a metal and plastic prosthetic implant. A physician will recommend this surgical procedure, if the disorder affects the entire hip joint
How can Osteoarthritis of the Hip be Prevented?
A few recommendations to help prevent Osteoarthritis of the Hip include:
- Estrogen replacement therapy can decrease the incidence of Osteoarthritis of the Hip after menopause, in women
- Using correct posture and tools that decrease stress on hip joints in the work place can decrease incidence of the hip disorder, due to occupational causes
- Proper treatment of gout
- Prompt and adequate treatment of individuals with Paget’s disease
- In individuals with hypothyroidism, prompt treatment of the thyroidal condition
- Proper treatment of type I diabetes
- Maintaining a healthy body weight can help prevent abnormal pressure on the joints
- Individuals, who participate in any high-risk sports, such as football, should wear appropriate safety equipment to help prevent serious injuries to their joints
What is the Prognosis of Osteoarthritis of the Hip? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- The long term prognosis of osteoarthritis depends on the severity of the degenerative disorder
- If Osteoarthritis of the Hip is detected early, and proper, aggressive treatment provided; then, the prognosis is good in a majority of individuals
- In general, without treatment measures a high percentage of individuals, who develop this condition, may experience a lifetime of gradual degeneration associated with this debilitating disorder
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Osteoarthritis of the Hip:
- Research is being conducted to understand the processes involved in the development of Osteoarthritis of the Hip
- Studies are being performed to understand, why some individuals continue to have severe Osteoarthritis of the Hip despite treatment
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.