What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Adenoma of Anogenital Mammary-Like Glands of Vulva
- Ectopic Breast Fibroadenoma - Vulva
- Vulvar Fibroadenoma
What is Fibroadenoma of Vulva? (Definition/Background Information)
- Fibroadenoma of Vulva is an extremely rare, benign mesenchymal tumor that resembles a breast fibroadenoma. It is mostly observed in young and middle-aged women
- Vulvar Fibroadenomas are thought to originate from anogenital tissue (similar to breast gland tissue) or from ectopic breast tissue. The tumors are believed to form due to increased sensitivity to estrogen
- Vulvar Fibroadenomas are generally small and painless; they may be found anywhere around the vulva (the area around the external vaginal opening). Some are known to grow to large sizes and cause pain and compression of the adjoining genital organs
- The treatment of choice is a surgical removal of the entire tumor. The prognosis of Fibroadenoma of Vulva is excellent with appropriate treatment and the rate of recurrence is also minimal
Who gets Fibroadenoma of Vulva? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Fibroadenoma of Vulva is generally present in young and middle-aged adult women, typically in the active reproductive phase
- However, these tumors may also be present in postmenopausal women, and occasionally, in prepubertal young girls.
- There is no geographical, racial, or ethnic preference noticed
What are the Risk Factors for Fibroadenoma of Vulva? (Predisposing Factors)
Currently, no specific risk factors are evident for Fibroadenoma of Vulva. However, the common risk factors for fibroadenoma of the breast (which it resembles) include:
- Estrogen therapy or other hormone therapies
- Pregnancy
- Breastfeeding
- Presence of ectopic (abnormally located) breast tissue
- Use of birth control pills: A link has been found between the use of birth control pills and the development of fibroadenomas. Women, who began using birth control pills, before the age of 20 years, have a higher risk of developing fibroadenomas
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Fibroadenoma of Vulva? (Etiology)
The exact cause of Fibroadenoma of Vulva development is unknown. However, a few proposals have been put forth by the research scientists:
- Some believe that the tumor arises from ectopic breast (mammary) tissue which originates from the primitive embryological milk line. The primitive milk line extends from the armpits (axilla) to the groin (inguinal) region
- Others believe that the origin of the tumor may be from specialized structures known as mammary-like anogenital glands
- It is believed that fibroadenoma development is linked to reproductive hormone levels, in the body. This is because the highest incidence of fibroadenoma occurrence is typically during a woman’s reproductive years
- The fact that fibroadenomas grow in size during pregnancy and breastfeeding, and shrink when menopause occurs, provides further evidence that links them to reproductive hormone levels
Note: Vulvar Fibroadenoma does not occur due to a sexually-transmitted infection.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Fibroadenoma of Vulva?
The signs and symptoms of Fibroadenoma of Vulva include:
- The presence of a solitary, firm and solid lump in the vulvar region; the tumors are externally visible in most cases
- This well-defined tumor is noted below the skin (subcutaneous location) and may be present at any site around the vaginal opening, including in the perineum
- Increased tumor size during pregnancy, in breastfeeding mothers, or in individuals undergoing hormone therapy may be noted
- In a few cases, a bilateral presentation of the fibroadenoma has been observed (present on both sides of the vulva)
- Rarely, other fibroadenomas may be present in the body (concurrence), such as in the breast, which is the most common location for this tumor type
- Vulvar Fibroadenomas can range in size from a few mm to as large as 6 cm; the average size is about 3-4 cm
- Most of the tumors appear as painless masses, while large-sized tumors may cause pain and compress surrounding structures and organs
How is Fibroadenoma of Vulva Diagnosed?
Fibroadenoma of Vulva diagnosis may involve the following tools:
- Evaluation of the individual’s medical history and a thorough physical (pelvic) examination
- Ultrasound scan of the abdomen
- CT or CAT scan with contrast of the abdomen and pelvis may show a well-defined mass. This radiological procedure creates detailed 3-dimensional images of structures inside the body
- MRI scans of the abdomen and pelvis: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a magnetic field to create high-quality pictures of certain parts of the body, such as tissues, muscles, nerves, and bones. These high-quality pictures may reveal the presence of the tumor
- Colposcopy:
- The cervix (including the vulva and vagina) is examined with an instrument, called a colposcope. This helps the physician get a magnified view of the cervix
- In order for this procedure to be performed, the individual has to lie on a table, as for a pelvic exam. An instrument, called the speculum, is placed in the vagina to keep the opening apart, in order to help the physician visualize the cervix. The colposcope is then used to get a magnified view of the inside
Although the above modalities can be used to make an initial diagnosis, a tissue biopsy of the tumor is necessary to make a definitive diagnosis to begin treatment. The tissue for diagnosis can be procured in multiple different ways which include:
- Fine needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy of the tumor: A FNA biopsy may not be helpful, because one may not be able to visualize the different morphological areas of the tumor. Hence, a FNA biopsy as a diagnostic tool has certain limitations, and an open surgical biopsy is preferred
- Core biopsy of the tumor
- Open biopsy of the tumor
Tissue biopsy:
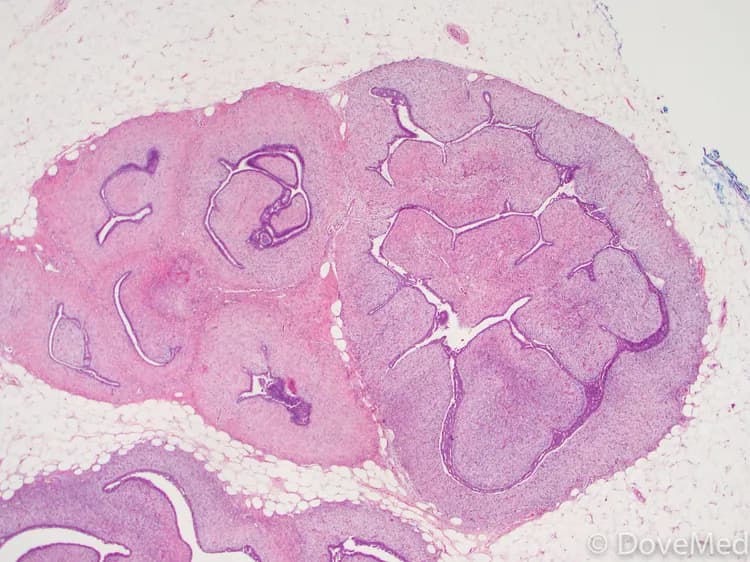
- A tissue biopsy of the tumor is performed and sent to a laboratory for a pathological examination. A pathologist examines the biopsy under a microscope. After putting together clinical findings, special studies on tissues (if needed) and with microscope findings, the pathologist arrives at a definitive diagnosis. Examination of the biopsy under a microscope by a pathologist is considered to be gold standard in arriving at a conclusive diagnosis
- Biopsy specimens are studied initially using Hematoxylin and Eosin staining. The pathologist then decides on additional studies depending on the clinical situation
- Sometimes, the pathologist may perform special studies, which may include immunohistochemical stains, molecular testing, and very rarely, electron microscopic studies to assist in the diagnosis
A differential diagnosis may have to be considered to eliminate other tumor types, in order to arrive at a definitive diagnosis. The following tumors may be considered towards the differential diagnosis:
- Apocrine adenoma
- Bartholin’s gland duct cyst
- Epidermal cyst
- Fibrocystic disease
- Follicular cyst
- Hidradenoma papilliferum
- Intraductal papilloma
- Lactating adenoma
- Lipoma
- Phyllodes tumor
- Pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia
- Sclerosing adenosis
- Syringoma
Note: Studies indicate that ectopic breast tissue occurs in 1-6% of the population. However, Vulvar Fibroadenoma is an extremely rare tumor type.
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Fibroadenoma of Vulva?
The possible complications of Fibroadenoma of Vulva include:
- Emotional stress and concern, especially with tumors in the genital region
- Tumor recurrence following surgery is known to take place in rare cases
- Damage of vital nerves, blood vessels, and surrounding structures, during surgery to remove the tumors
- Post-surgical infection at the wound site is a potential complication
How is Fibroadenoma of Vulva Treated?
Following are the treatment methods adopted for Fibroadenoma of Vulva:
- The healthcare provider may recommend a ‘wait and watch’ approach for small-sized tumors presenting mild signs and symptoms, after a diagnosis of fibroadenoma is made
- Pain medications, in case of tumors causing pain
- Surgical intervention with complete excision can result in a complete cure. It can also help reduce the chances of tumor recurrence
- Radiation therapy and chemotherapy are not usually required
- Post-operative care is important: Minimum activity level is to be ensured until the surgical wound heals
- Follow-up care with regular screening and check-ups are important, since the tumor can recur in some cases
How can Fibroadenoma of Vulva be Prevented?
- Current medical research has not established a method of preventing Fibroadenoma of Vulva
- Medical screening at regular intervals with scans and physical examinations are advised
What is the Prognosis of Fibroadenoma of Vulva? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
The prognosis of Fibroadenoma of Vulva is generally excellent on surgical excision and removal of the tumor. It is a benign tumor with very little risk of recurrence.
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Fibroadenoma of Vulva:
Please visit our Cancer & Benign Tumor Health Center for more physician-approved health information:
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.