What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Diabetic Glomerulosclerosis
- Diabetic Kidney Disease
- Nephropathy due to Diabetes
What is Diabetic Nephropathy? (Definition/Background Information)
- Diabetic Nephropathy causes kidney damage and this could be caused by both type-1 and type-2 diabetes. It is also known as Diabetic Kidney Disease
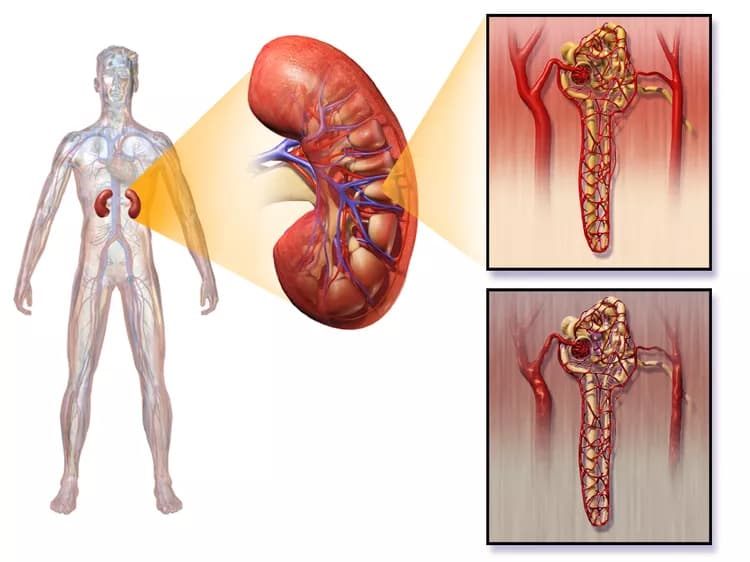
- The kidney comprises thousands of units known as nephrons. The nephrons filter blood, help remove waste from the body, and control fluid balance
- In individuals with high blood sugar, the nephrons slowly thicken and become scarred over time. The kidneys begin to leak and protein (albumin) passes into the urine
- The development of nephropathy in diabetics is dependent on how well controlled the condition is. About 40% of the individuals affected by diabetes are likely to develop Diabetic Nephropathy
- Diabetic Nephropathy is mostly asymptomatic in the initial periods and it may take many years before symptoms, such as fatigue, nausea and vomiting, swelling of the feet and face, and itchy skin, manifest in the affected individuals, due to kidney disease. The condition could lead to chronic kidney disease if treatment is delayed
- The treatment of Nephropathy due to Diabetes includes medications and lifestyle modifications that involve dietary changes and exercise. However, the prognosis depends on many factors and is better with early treatment
Who gets Diabetic Nephropathy? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Diabetic Kidney Disease occurs in 15-40% of patients with type-1 diabetes, with a peak incidence around 15-20 years of diabetes
- In patients with type-2 diabetes, the prevalence is highly variable, ranging from 5-20%
- The disorder is slightly more frequent in men
- In the USA, the development of kidney disease is reported to be greatest among non-Hispanic African-American men and lowest among white females. Native-Americans are reported to have a high incidence of Diabetic Nephropathy as well. Among Asians in the USA, Indian-Americans are reported to have the highest occurrence of Diabetic Kidney Disease
- In Europe, the cumulative incidence of microalbuminuria in patients with type-1 diabetes is reported to be 12.6% over 7.3 years
What are the Risk Factors for Diabetic Nephropathy? (Predisposing Factors)
Kidney damage due to Diabetic Nephropathy is more likely in individuals who:
- Smoke
- Consume alcohol
- Are overweight or obese
- Have elevated blood pressure
- Have uncontrolled blood sugar levels
- Have type 1 diabetes that began before the age of 20 years
- Have family history of diabetes and kidney disorders
- Have higher cholesterol levels
- Pregnant women have a risk of rise in the glomerular filtration rate (GFR), which returns to normalcy after delivery. But hypertensive women with renal disease prior to conception have a higher risk of progression of kidney disease
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Diabetic Nephropathy? (Etiology)
The causal factors of Diabetic Nephropathy may include:
- An individual’s genetic make-up, as Kidney Disease due to Diabetes could run in families
- Poor blood sugar control
- High blood pressure as a co-morbid condition
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Diabetic Nephropathy?
The early stages of Kidney Disease due to Diabetes (or Diabetic Nephropathy) could be without symptoms. Usually, the progression of the condition is gradual and could take up to 5-10 years before an individual starts showing symptoms of kidney distress.
Individuals with long-term (chronic) kidney disease may have the following signs and symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Swelling of legs, feet and face
- Itchy skin
- Headache
- Feeling ill
- Vomiting and nausea
- Poor appetite
- If early-stage kidney disease or microalbuminuria is not diagnosed or controlled, it could lead to macroalbuminuria or end-stage kidney disease (ESKD).
How is Diabetic Nephropathy Diagnosed?
When an individual presents with the above-mentioned signs and symptoms, a physician or specialist will order tests to detect signs of kidney abnormalities caused by diabetes. These may include:
- Check kidneys by using blood tests to detect blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and serum creatinine every year
- Urine analysis to check if albumin (a protein) is leaking into urine
- Albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR)
- Glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
- If these tests are positive, a kidney biopsy may be ordered to confirm or rule out the diagnosis of Diabetic Nephropathy
- The healthcare provider might also check blood pressure, since a correlation has been observed between Diabetic Nephropathy and high blood pressure
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Diabetic Nephropathy?
The following complications may take place due to Diabetic Nephropathy:
- If left undiagnosed or untreated, Diabetic Kidney Disease could develop into chronic kidney disease
- Chronic kidney disease can, in turn, progress even further, eventually leading to total kidney failure and the need for dialysis or kidney transplantation
How is Diabetic Nephropathy Treated?
The treatment measures for Diabetic Nephropathy may include the following:
- It is important to control blood sugar in order to reduce stress on the kidneys. An equally important factor for treatment of nephropathy is blood pressure. It has been reported that blood pressure plays a direct role in progression of Diabetic Nephropathy. It is well-established that a slight increase in blood pressure could worsen kidney disease substantially. Blood pressure may be lowered by:
- Losing weight
- Eating less salt
- Avoiding alcohol and tobacco
- Getting regular exercise
- There are medications available for lowering blood pressure. However, caution must be exercised when such medicines are used, especially when an individual is diabetic. While a few blood pressure medications could increase blood sugar, still others might mask the usual symptoms associated with hypoglycemia or a fall in blood sugar
- Usually ACE inhibitors are prescribed, for those individuals who have from diabetes with associated kidney disease and high blood pressure. Medications, such as Enalapril, which belong to the class of ACE inhibitors, are known to slow kidney damage while also reducing blood pressure
- A low-protein diet to decrease protein loss in the urine and increase protein levels in blood may be recommended
How can Diabetic Nephropathy be Prevented?
The preventive measures for Diabetic Nephropathy may include:
- Keeping the blood pressure under control (below 130/80) is one of the best ways to slow kidney damage. A physician may prescribe medicines to lower blood pressure and protect the kidneys from more damage. These medications can help slow the damage to kidneys, even when the blood pressure is within a healthy range
- One could also slow kidney damage by controlling the blood sugar level by:
- Healthy eating, regular exercise, taking medicine or insulin as instructed by the healthcare provider
- Knowing the signs of urinary tract infections and getting them treated promptly
- Checking blood sugar levels as often as instructed and keeping a record of the same, so that one knows how meals and activities affect the blood sugar levels
Individuals with diabetes and Diabetic Nephropathy should take cognizance of the following:
- Before having an MRI or CT scan, or other imaging test in which a contrast dye may be used, the healthcare provider needs to be informed. Contrast dyes can potentially damage the kidneys in such individuals
- One should check for alternative medication to NSAID pain medicine, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, since NSAIDs are reported to cause damage to the kidneys
What is the Prognosis of Diabetic Nephropathy? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
Diabetic Kidney Disease is a major cause of illness and death in individuals with diabetes. It could lead to the need for dialysis or a kidney transplant, if an early diagnosis and treatment is lacking.
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Diabetic Nephropathy:
- Type 2 diabetes is a chronic disease in which the blood contains high levels of glucose (sugar), the body’s main source of fuel
The following article link will help you understand type 2 diabetes:
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.