What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Blocked Nasolacrimal Duct
- Dacryostenosis
- Tear Duct Obstruction
What is Blocked Tear Duct? (Definition/Background Information)
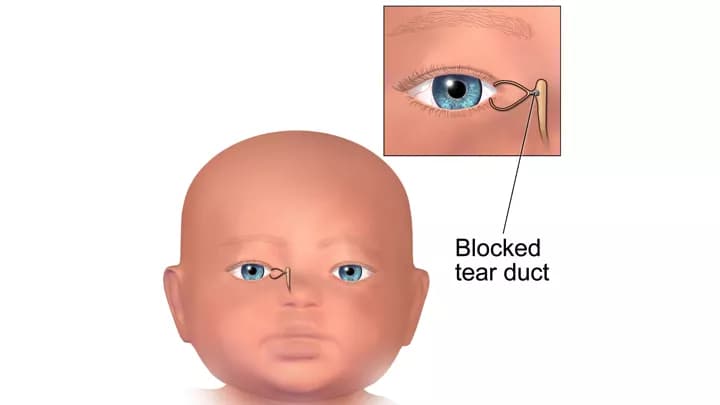
- Blocked Tear Duct is a condition in which there is either a partial or complete obstruction in the tear drainage system. The condition is also known as a Blocked Nasolacrimal Duct
- The pathway, through which tears from the eyes travel to the nose, is blocked completely or partially, causing problems in draining the tears. The tears from the eyes cannot drain through the normal pathway and this leads to watery and irritated eye
- Blocked Tear Duct is common in newborn children, though adults may also be affected. Some contributing factors for the condition include inflammation of the eye, previous history of eye surgery, or glaucoma treatment using topical applications
- The common signs and symptoms of Blocked Tear Duct include excess production of tears and watery eyes. The condition is diagnosed thorough a physical exam and fluorescein dye disappearance test
- Generally, in newborns, the condition improves on its own; but in adults, the treatment of Blocked Tear Duct depends upon the cause of the condition
- It is typically not possible to prevent Blocked Tear Ducts, but the associated prognosis is very good with proper treatment
Who gets Blocked Tear Duct? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Blocked Tear Duct is typically observed in newborns, though it may occur at any age
- The condition can be congenital in presentation and occurs because of failure of canalization in inferior part of the nasolacrimal (or tear) duct
- Both males and females are susceptible, but this condition is more often seen in females
- Blocked Tear Duct condition is seen worldwide and all races and ethnic groups are at risk
What are the Risk Factors for Blocked Tear Duct? (Predisposing Factors)
The risk factors that are likely to increase the incidence of Blocked Tear Duct include:
- Age: Newborns and older adults have a high risk for this condition
- Gender: Females are more likely to be affected than males
- Eye inflammation due to autoimmune disorders such as Sjögren’s syndrome
- History of surgery: Any previous surgery to the eyes, nose, or sinus may cause scarring in the duct, which can increase the risk
- Glaucoma: Topical medicines used to treat glaucoma may increase the risk of acquiring Blocked Tear Duct
- Cancer treatment: Chemotherapy or radiation therapy administered to treat cancer
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases one's chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Blocked Tear Duct? (Etiology)
Tears are produced by the lacrimal glands that are located inside the upper eyelid, on each eye. Tears from these glands flow over the surface of the eye and drain into tiny holes, called puncta, which are situated in the corner of the upper and lower eyelids. The canaculi canals in the eyelids move these tears to the lacrimal sac, from where it travels down a passage to the nose, through a duct called the nasolacrimal (tear) duct, where it is reabsorbed. A blockage in the duct, through which the tears travel (from the puncta to the nose), can result in Blocked Tear Ducts.
These blockages may be due to the following factors:
- Congenital blockage: The tear drainage system is either not developed fully or an abnormality may have occurred
- Age-related changes: With advancing age, the holes (puncta) may get narrowed, slowing down the flow of tears
- Eye infections and inflammations can block the tear ducts resulting in improper tear drainage
- Facial injuries and trauma: Injuries to the face can damage the bones near the drainage system creating obstruction to the normal flow of tears
- Tumors: Tumors of the nose, sinus, or lacrimal sac may form very near to the drainage system blocking the flow of tears
- Topical medications: Certain topical medicines that are used for a long period, can lead to Blocked Tear Ducts
- Cancer treatment: Treatment of certain cancers using chemotherapy or radiation therapy
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Blocked Tear Duct?
The common signs and symptoms of Blocked Tear Duct include:
- Excess production of tears
- Watery eyes
- Conjunctivitis, or continuous and repeated eye inflammation
- Recurrence of eye infection
- The inside corner of the eye (near the nose) may get swollen resulting in pain
- Mucus or pus discharge from the eye
- Blurring of vision
How is Blocked Tear Duct Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of a Blocked Tear Duct may involve the following tests and exams:
- Physical examination and detailed evaluation of medical history
- An eye examination may be performed by an eye specialist, to check how the tears are draining
- A physical examination of the inside of the nose is performed, to see if any obstruction is present in the nasal passages
- Tear drainage test:
- Also known as fluorescein dye disappearance test, it helps in measuring the rate at which the tears are drained
- A special dye is used for this purpose, and one drop of the dye is applied to each eye
- In case a substantial amount of the dye still remains in the eye after 5 minutes, a case of Blocked Tear Duct is confirmed
- Irrigation and probing
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Blocked Tear Duct?
Blocked Tear Ducts can lead to tear stagnation in the eye. This can cause bacterial, viral, or fungal infections resulting in inflammation.
How is Blocked Tear Duct Treated?
A treatment of Blocked Tear Duct is undertaken based on the cause of the condition and age of onset. Combined treatment options may be necessary to cure the condition.
- Antibiotic eye drops are prescribed in case of an eye infection
- If Blocked Tear Ducts are caused by a tumor, a surgical removal of the tumor may be advised
Conservative methods of treating Blocked Tear Ducts may include:
- Generally, Blocked Tear Ducts in babies improve with time as the draining system of the baby develops
- When the disorder is not cured easily, a massage technique may be taught to open the membrane that blocks the flow of tears. The technique involves gentle pressing of the lacrimal sac repeatedly, twice daily, for at least a month, or till the draining problem resolves. The massage opens up the distal end of the nasolacrimal duct that is occluded by a membranous tissue
- Minimally-invasive treatments may be necessary for adults with narrow puncta (a small opening along the eyelid margin through which tears drain), and for those who have a partially-blocked duct
These methods include dilation, probing, and irrigation:
- Young babies and infants with Blocked Tear Ducts are treated using this method
- The punctal openings are made bigger with the help of a dilation instrument; a thin tube is inserted through the puncta, into the tear draining system, all the way through the nasal opening
- The drainage system is flushed using a saline solution which helps to remove any obstructions
- For elderly adults with narrowed puncta, a similar procedure as stated above is performed, which can help provide a temporary relief
When all the above methods do not produce satisfactory results and when the infection becomes severe, surgery may be recommended to widen the narrowed puncta.
- Balloon catheter dilation: When Blocked Tear Ducts are caused by scars, inflammation, and other medical conditions, the balloon catheter dilation method is used
- A tube with contracted balloon at its tip is inserted through the nasolacrimal duct in the nose
- A pump to inflate and deflate the balloon is used, and the balloon is moved to different locations so that all obstructions can be removed
- This method is a very useful procedure for infants and toddlers
- Stenting or intubation:
- A thin tube made up of silicon or polyurethane is inserted through one or both the puncta
- This passes through the tear drainage system into the nose
- These tubes are left in the eye for about three months
Surgical procedures:
- Dacryocystorhinostomy: This is a minimally-invasive surgical procedure used to reconstruct the passage way for the tears to pass through easily. The various types of this procedure include:
- External dacryocystorhinostomy: It is the most commonly used surgical method. A hole is made on the side of the nose, somewhere near the lacrimal sac. The lacrimal sac and nasal cavity are connected; a stent is placed in the new passage way, and the hole is closed with the help of sutures
- Endoscopic or endonasal dacryocystorhinostomy: A microscopic camera is inserted through the nasal opening to the duct system. In rare occasions, a fiber optic light is also inserted into the puncta to brighten the surgical area. There is no scar as a result of the procedure, because no surgical incision is made (scarless surgery)
- Conjunctivodacryocystorhinostomy (CDCR): It is a procedure to bypass the entire lacrimal system
- In this procedure, the entire tear drainage system is reconstructed
- A new route from the conjunctiva to the nose is created and the original tear drainage system bypassed
- As a follow-up action after surgery and to prevent infection, the use of nasal decongestant spray and topical eye drops are recommended
How can Blocked Tear Duct be Prevented?
Blocked Tear Ducts are conditions that cannot be usually prevented. However, the following measures may be considered to reduce one's risk for the same:
- Avail early treatment of conditions causing eye inflammation
- Athletes may avoid trauma to the face by using suitable protective gear and helmets while participating in sports
- Wear seatbelts while driving or travelling so as to minimize risk of injury to the face
If the eyes are protected from infection, the chances of acquiring Blocked Tear Ducts may be minimized. This can be achieved by:
- Avoiding contact with individuals with infectious forms of conjunctivitis
- Frequent and regular washing of the hands is a good practice; avoid frequently touching the face or eyes, especially when in public places
- Rubbing the eyes excessively must be avoided
- Avoid using old or expired eye wear or eye-related cosmetic items; also avoid sharing eye cosmetics with others to reduce the risk of infection
- Wear suitable contact lenses and ensure that they are kept clean
What is the Prognosis of Blocked Tear Duct? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
Overall, the prognosis of Blocked Tear Duct is very good with appropriate therapy.
- In infants, usually the blocked ducts get better on its own; otherwise, it may be corrected with the help of suitable treatment
- In adults, generally the prognosis depends upon the cause, but is typically good with appropriate treatment
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Blocked Tear Duct:
- The opening of a tear (nasolacrimal) duct is a surgical procedure to open the tear ducts, in order to allow the tears to drain properly
The following article link will help you understand the opening of a tear duct surgical procedure:
http://www.dovemed.com/common-procedures/procedures-surgical/opening-of-tear-duct/
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals


0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.