Regulatory T Cells' Involvement In The Progress Of Colon Cancer
Researchers at Osaka University, clarified that T-lymphocytes expressing FOXP3 at a low level found in colorectal cancers (CRCs) facilitated cancer immunity. FOXP3 is a master gene of Regulatory T (Treg) cells that suppress various immune responses including cancer immuity. They found that a certain intestinal bacteria species was involved in the induction of such FOXP3-low T cells enhancing tumor immunity. These findings suggest new potentials in the treatment of CRCs via regulation of intestinal bacteria.
Treg cells have been drawing attention in cancer immunotherapy. Since Treg cells suppress the immune cells that attack tumors, they are thought to be disadvantageous for antitumor immunity. Indeed tumor-infiltrating Treg cells have been reported as a factor for poor prognosis in many cancers. However, results running counter to the notion have been found with CRCs, leaving the roles of Treg cells in CRCs unclear.
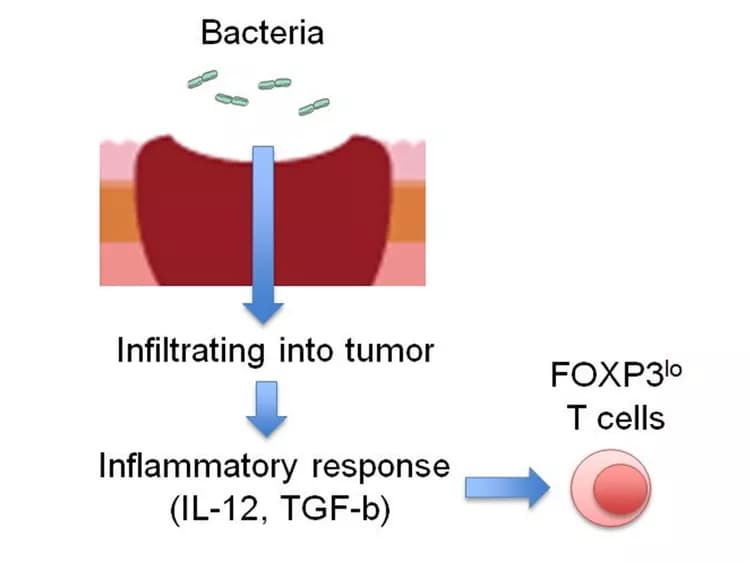
A research group led by Professor Shimon Sakaguchi at the Immunology Frontier Research Center, Osaka University now discovered that among the FOXP3+ cells that had infiltrated deeply into CRCs, a group of T-cells with low FOXP3 expression were facilitating cancer immunity. Although the majority of FOXP3+ T-cells are thought to be immunosuppressive Treg cells, this research showed that a group of FOXP3-low (FOXP3lo) cells did not possess immune-suppressing functions but rather augment immune responses and that they were induced by inflammatory cytokines such as IL-12, which was induced by intestinal bacteria attaching to CRCs. CRCs with abundant infiltration of such inflammatory FOXP3lo Treg cells showed good prognosis, while those with predominant FOXP3hi Treg cell infiltration like other cancers showed poor prognosis.
Detailed analysis of the lymphocytes invading CRCs allowed the researchers to clarify the roles of Treg cells and FOXP3+ cells as well as the influence of intestinal bacteria in inducing these cells. Intestinal bacteria attaching to CRCs cause tumor-internal inflammation by invading the tumor, thereby inducing FOXP3lo Treg cells facilitating tumor immunity. In addition, the researchers found that FOXP3hi Treg cells, unlike FOXP3lo T-cells, suppressed antitumor immunity response as seen with other cancers.
In this research, the researchers were able to conduct an accurate assessment of FOXP3+cells in CRCs. Precise identification of these cell groups will become a useful marker for assessing immune status in cancer tissues. Since cancer immunotherapy is effective for only some types of tumors, the research results suggest new potentials for cancer immunotherapy targeting Treg cells while also defining new patient groups. Furthermore, new preventive potentials for intestinal cancers can be expected by controlling intestinal bacteria as it was demonstrated that these bacteria can increase cancer immunity via inflammation in tumors.
The above post is reprinted from materials provided by Osaka University. Note: Materials may be edited for content and length.
Disclaimer: DoveMed is not responsible for the adapted accuracy of news releases posted to DoveMed by contributing universities and institutions.
Primary Resource:
Saito, T., Nishikawa, H., Wada, H., Nagano, Y., Sugiyama, D., Atarashi, K., ... & Nagase, H. (2016). Two FOXP3+ CD4+ T cell subpopulations distinctly control the prognosis of colorectal cancers. Nature medicine, 22(6), 679-684.
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.