Key Discoveries Offer Significant Hope Of Reversing Antibiotic Resistance
Resistance to antibiotics is becoming increasingly prevalent and threatens to undermine healthcare systems across the globe. Antibiotics including penicillins, cephalosporins and carbapenems are known as β-lactams and are the most commonly prescribed worldwide.
In the first paper, University of Bristol researchers defined the relative importance of two mechanisms associated with β-lactam antibiotic resistance. In one, bacteria restrict the entry of antibiotics into the cell; in the other, bacteria produce an enzyme (a β-lactamase), which destroys any antibiotic that gets into the cell. The latter was found to be the more important of the two mechanisms. These findings imply that if chemicals could be developed to inhibit β-lactamase enzymes, a significant proportion of antibiotic resistance could successfully be reversed.
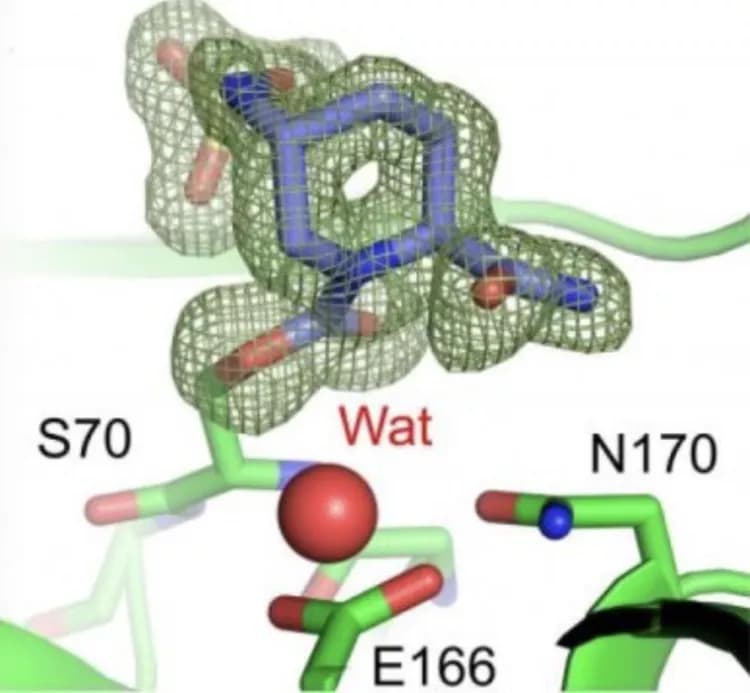
Building on these findings, and working in partnership with chemists at the University of Oxford and the University of Leeds, in the second paper, Bristol researchers studied the effectiveness of two types of β-lactamase enzyme inhibitor in a bacterium known to be highly resistant to common antibiotics.
Using a variety of approaches, the authors studied avibactam, an inhibitor that has recently been introduced into clinical practice, and a "bicyclic boronate" inhibitor, which was first reported by the Oxford/Leeds/Bristol team in 2016.
They found both inhibitors failed to consistently protect the β-lactam antibiotic, ceftazidime, from attack by the β-lactamase enzyme. However, when paired with a different β-lactam antibiotic =, aztreonam, the inhibitors worked extremely well and killed some of the most resistant bacteria ever seen in the clinic.
Dr Matthew Avison, Reader in Molecular Bacteriology from the University of Bristol's School of Cellular & Molecular Medicine, and senior author for both studies said:
"Our bacteriology research has further demonstrated that β-lactamases are the real "Achilles heel" of antibiotic resistance in bacteria that kill thousands of people in the UK every year.
"Structural/mechanistic work on β-lactamase enzymes, including that led by my colleague Dr Jim Spencer, is helping to drive the discovery of wave after wave of β-lactamase inhibitors, including the potentially game-changing bicyclic boronate class, shown to be effective in our research, and recently successful in phase one clinical trials.
"Two β-lactamase inhibitors have recently been licenced for clinical use: avibactam and vaborbactam. Our work shows that avibactam might more successfully be deployed with aztreonam instead of ceftazidime as its antibiotic partner. We are delighted to see that this combination has entered clinical trials, and has recently saved the life of a patient in the USA who was suffering from a previously untreatable infection."
"This is an exciting time for researchers studying β-lactamase inhibitors. At the risk of sounding like King Canute, it is the first time for a decade that there is some genuine positivity about our ability to turn back the rising tide of β-lactam antibiotic resistance."
Materials provided by University of Bristol. Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Disclaimer: DoveMed is not responsible for the accuracy of the adapted version of news releases posted to DoveMed by contributing universities and institutions.
References:
- Juan-Carlos Jiménez-Castellanos, Wan Ahmad Kamil Wan Nur Ismah, Yuiko Takebayashi, Jacqueline Findlay, Thamarai Schneiders, Kate J Heesom, Matthew B Avison. (2017). Envelope proteome changes driven by RamA overproduction in Klebsiella pneumoniae that enhance acquired β-lactam resistance. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkx345
- Karina Calvopiña, Philip Hinchliffe, Jürgen Brem, Kate J. Heesom, Samar Johnson, Ricky Cain, Christopher T. Lohans, Colin W. G. Fishwick, Christopher J. Schofield, James Spencer, Matthew B. Avison. (2017). Structural/mechanistic insights into the efficacy of nonclassical β-lactamase inhibitors against extensively drug resistant Stenotrophomonas maltophilia clinical isolates. Molecular Microbiology. DOI: 10.1111/mmi.13831
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.