What are the other Names for this Test? (Equivalent Terms)
- H. pylori Tissue Test
- Rapid Urease Test (RUT) for Helicobacter Pylori
- RUT for Helicobacter Pylori
What is Helicobacter Pylori Tissue Test? (Background Information)
- Helicobacter pylori, or H. pylori, is a bacteria responsible for causing stomach and intestinal ulcers. Upon ingestion, H. pylori migrate to the edge of the stomach wall. There, it is protected from the acidic environment by mucus. The bacterium releases several toxins that damages tissues and causes ulcers
- H. pylorus is very commonly found in humans. It is present in up to 80% of individuals with ulcers, where it causes infection. It is also present in up to 50% of individuals, who do not exhibit any symptoms
The Helicobacter Pylori Tissue Test detects the presence of H. pylori in the stomach or intestinal tissues. It can do this in four different ways:
- Detection of specific antibodies created by the immune system upon exposure to H. pylori: The presence of H. pylori-specific IgM antibodies indicates recent or current exposure; H. pylori-specific IgG antibodies indicate past exposure
- Detection of genetic material belonging to H. pylori: A technique called PCR is used to detect traces of specific DNA that H. pylori is known to possess, but that which is absent in humans
- Detection of urease produced by H. pylori: Urease, an enzyme made by H. pylori to help it survive in the acidic stomach, is identified and used to indicate the presence of H. pylori
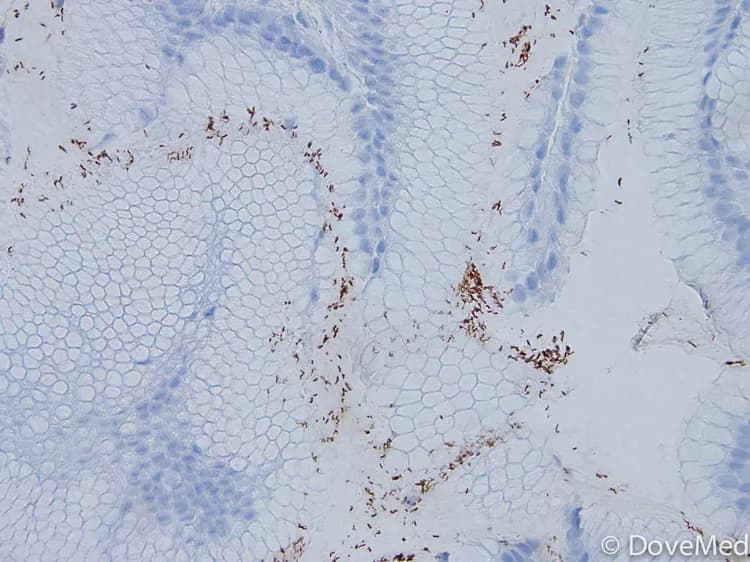
- Helicobacter Pylori can be detected on a stomach or intestinal biopsy using special studies when examined by a pathologist under a microscope. The special studies may include immunohistochemical stains for H. pylori or histochemical stains for H. pylori
What are the Clinical Indications for performing the Helicobacter Pylori Tissue Test?
Following are the clinical indications for performing the Helicobacter Pylori Tissue Test:
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Gas
- Unexplained weight loss
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Bloating
- Discolored stool
How is the Specimen Collected for Helicobacter Pylori Tissue Test?
Following is the specimen collection process for Helicobacter Pylori Tissue Test:
Sample required: Tissue
Process: Insertion of a thin, flexible tube with a camera through the throat, into the stomach and small intestine (upper GI endoscopy).
Preparation required: No special preparation is needed prior to the test.
What is the Significance of the Helicobacter Pylori Tissue Test Result?
- A positive Helicobacter Pylori Tissue Test may indicate infection or colonization by H. pylori
The laboratory test results are NOT to be interpreted as results of a "stand-alone" test. The test results have to be interpreted after correlating with suitable clinical findings and additional supplemental tests/information. Your healthcare providers will explain the meaning of your tests results, based on the overall clinical scenario.
Additional and Relevant Useful Information:
- Recent evidence indicates that Helicobacter pylori have the ability to transmit between household pets and humans
- There are many different types of stains to detect H. pylori. Some of these include Warthin-Starry stain, modified Giemsa stain, Genta stain, Gimenez stain, and modified McCullen stain.
Certain medications that you may be currently taking may influence the outcome of the test. Hence, it is important to inform your healthcare provider, the complete list of medications (including any herbal supplements) you are currently taking. This will help the healthcare provider interpret your test results more accurately and avoid unnecessary chances of a misdiagnosis.
Please visit our Laboratory Procedures Center for more physician-approved health information:
http://www.dovemed.com/common-procedures/procedures-laboratory/
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.