What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Fallot's Tetralogy
- Subpulmonic Stenosis, Ventricular Septal Defect, Overriding Aorta, and Right Ventricular Hypertrophy
- TOF (Tetralogy of Fallot)
What is Tetralogy of Fallot? (Definition/Background Information)
- Congenital heart defects are relatively common birth defects involving the heart, and these may be of several types. Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is an uncommon, complex, and critical congenital heart defect. A congenital condition indicates that the condition is present at birth
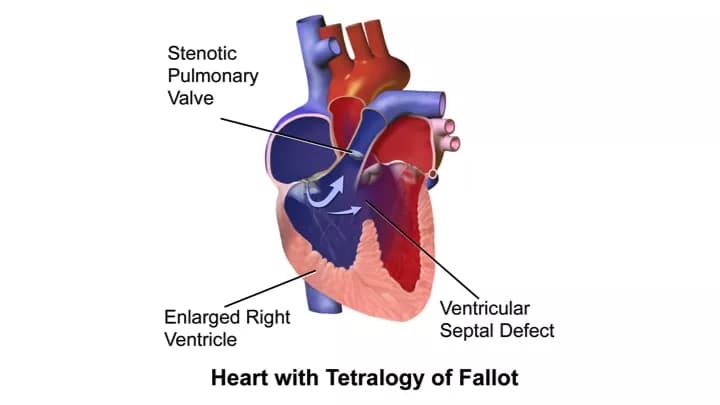
- Tetralogy of Fallot consists of four heart defects, namely subpulmonic stenosis, ventricular septal defect, overriding aorta, and right ventricular hypertrophy. TOF causes low oxygen levels in blood leading to cyanosis, which is a bluish-purple discoloration of the skin
- The combination of four congenital heart defects present at birth, affect the structural integrity of the heart, cause ‘oxygen-poor’ blood to flow from the heart to the rest of the body. Tetralogy of Fallot signs and symptoms include failure to thrive, poor feeding habits, heart murmurs, and complications such as heart arrhythmias and endocarditis
- It is diagnosed by evaluation of medical history, physical examination and specific tests that include chest X-ray and fetal echocardiogram. The condition is fatal if there is a delay in the diagnosis and/or if it remains untreated. With suitable surgical treatment of Tetralogy of Fallot at a young age, the prognosis may be improved
Who gets Tetralogy of Fallot? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is a rare congenital heart condition; children are born with this condition
- The incidence of the condition is around 1 in 2,500-3,000; about 1 in 10 children with congenital heart disease (CHD) present TOF
- Generally, male babies are affected more than female babies
- TOF is observed worldwide and no predilection towards any particular race or ethnic group is observed
What are the Risk Factors for Tetralogy of Fallot? (Predisposing Factors)
There may be several factors that increase the risk for Tetralogy of Fallot during pregnancy. These include:
- Alcoholism (during pregnancy)
- Genetic factors
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- The expectant mother is over 40 years of age
- Lack of adequate nutrition during pregnancy
- Babies who are born with Down syndrome or DiGeorge syndrome
- Having rubella or other viral illnesses during pregnancy
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases one’s chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Tetralogy of Fallot? (Etiology)
- Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is a congenital heart defect of unknown cause. The condition occurs during fetal development of the heart
- The four abnormalities of the heart that encompass TOF are:
- Pulmonary valve stenosis: A narrow pulmonary valve that hinders the flow of blood from the heart to the lungs
- Ventricular septal defect: A hole between the two lower chambers (ventricles) of the heart
- Overriding aorta: The aorta (blood vessel) lies over the hole in the lower chambers
- Right ventricular hypertrophy: The muscle that surrounds the right lower chamber becomes overly thickened
- TOF may develop from a combination of factors that may be genetic and environmental. It is also believed that what the expectant mother consumes, such as food, drink, or even some medications, may be contributive
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Tetralogy of Fallot?
The signs and symptoms of Tetralogy of Fallot may vary, depending on the extent of obstruction of blood flow out of the right ventricle into the lungs. These may include:
- Blue discoloration of the skin (cyanosis) that can worsen when the baby cries, known as ‘blue baby syndrome’
- Clubbing of fingers, thickening of the fingertip resembling a drumstick
- Poor feeding habits
- Failure to gain weight and poor development
- Passing-out or fainting
- The child assumes a squatting position during episodes of cyanosis that make him/her feel better
Tet spells: These are episodes in infants characterized by the skin color turning deep blue after crying, feeding, having a bowel movement, or kicking legs upon awakening. These spells occur from a rapid drop in oxygen levels in blood and are more common in young infants between the ages of 2 and 4 months.
How is Tetralogy of Fallot Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of Tetralogy of Fallot may involve the following tests and exams:
- A detailed physical examination with medical history evaluation. A physical examination using a stethoscope may reveal a heart murmur
- Chest X-ray that may indicate a boot-shaped heart
- Complete blood count (CBC) test
- Fetal echocardiogram; which is a very important diagnostic tool may reveal structural and functional heart abnormalities
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) to provide details about the electrical activity of the heart
- Prenatal screening tests
- Newborn pulse oximetry screening may help the healthcare suspect the condition prior to symptom presentation
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Tetralogy of Fallot?
Several complications may arise due to Tetralogy of Fallot. These include:
- Delayed growth and development
- Irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias)
- Fainting and seizures during periods with lack of oxygen (low blood oxygen)
- Increased risk of infective endocarditis, an inflammation of the inner lining of the heart due to a bacterial infection
- Treatment and post (surgical) treatment complications
How is Tetralogy of Fallot Treated?
The treatment of Tetralogy of Fallot may involve the following:
- A surgical procedure to repair Tetralogy of Fallot is performed when the infant is young (usually soon after birth). The procedure may include intracardiac repair, a type of open heart surgery
- More than one surgery is sometimes needed to correct the condition. In such cases, the first surgery is generally performed to increase blood flow to the lungs
- Surgery to widen a portion of the narrowed pulmonary tract and close the ventricular septal defect may be done at a later time
- Use of medication to control high blood pressure, prior to and after surgery. The individual is requested to avoid stressful physical exercises during this period
- Post-operative care with control of blood pressure is important. A minimum activity level is to be ensured until complete healing takes place
- Regular health check-ups with the heart specialist are essential
How can Tetralogy of Fallot be Prevented?
- Currently, there are no known definitive preventive methods available for Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF)
- However, measures, such as avoiding alcohol during pregnancy, good control of diabetes, genetic counseling of expectant mothers over 40 years of age, and adequate immunization of women prior to pregnancy, can help reduce the incidence of TOF
Regular medical screening at periodic intervals with tests, scans, and physical examinations are mandatory for those who have already undergone surgical correction of the defect.
What is the Prognosis of Tetralogy of Fallot? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- In most cases, Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) can be treated with surgery. If surgeries are performed during infancy, then more than 90% survive to adulthood and lead healthy lives
- Without surgery, death usually occurs before the individual is 20 years old. Nearly 50% of children with TOF may die before the age of 6 years from a lack of proper treatment
- Patients with continued defects of ‘leakiness’ of the pulmonary valve may need to have the valve replaced
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Tetralogy of Fallot:
Children with repaired Tetralogy of Fallot need regular medical follow-up with their pediatric cardiologist. As an adult, they would need lifelong follow-up with a cardiologist, who has special training in congenital heart defects.
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.