What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Infestation by Sarcoptes Scabiei
- Sarcoptic Itch
- Sarcoptic Mange (Animal Scabies)
What is Scabies? (Definition/Background Information)
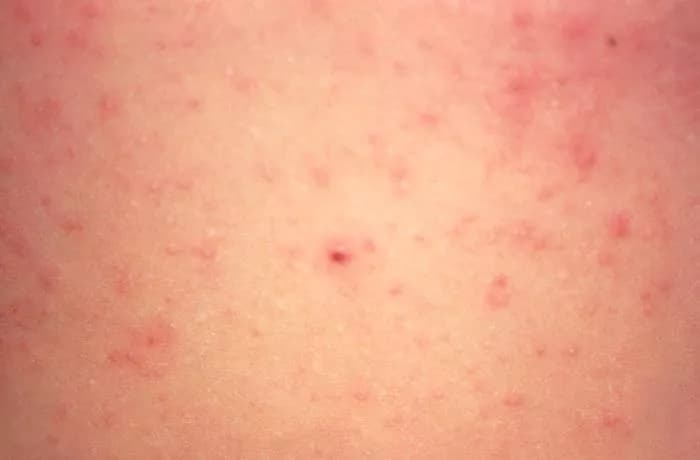
- Scabies is a highly-contagious skin infection caused by a tiny parasitic mite Sarcoptes scabiei. It causes intense itching and small, raised, red spots on the affected skin area. The mites are also known as "itch mites"
- The infection commonly affects children less than 15 years of age and adults over 65 years of age. It is spread by direct contact with the infected person such as by sharing towels, clothes and bedding, and through sexual contact with an infected individual
- Rashes due to Scabies most commonly occur between the fingers, in the armpits, around the breasts and genitalia, and on the inside of the elbow and knees. The most common complication of Scabies is a secondary bacterial infection of the skin
- A diagnosis of the condition requires careful examination of the skin for the appearance and location of the rashes
- The treatment of Scabies involves the use of medications, such as permthrin 5% and lindane, which are commonly used and applied all over the body in the form of creams and lotions
- Individuals with Scabies and even family members (who are in close contact with the affected individuals) who do not show any signs and symptoms should also be treated as a precautionary measure
- The prognosis of Scabies is excellent with appropriate treatment
Who gets Scabies? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Scabies can affect individuals of any age group, but it is more common in children (under 15 years) and older adults (above 65 years)
- Women are affected more commonly than men
- The condition is found worldwide (more common in tropical climates); all racial and ethnic groups may be affected
What are the Risk Factors for Scabies? (Predisposing Factors)
The following are the common risk factors for Scabies:
- Age: Children and older adults seem to have a higher risk
- Sexual contact with the affected individuals
- Sharing clothes, towels, and bedding with the infected individuals
- Living in crowded places such as nursing homes, military barracks, and prisons
- Individuals with weak immune system such as AIDS patients
- Having a pet (cat or dog) that is diagnosed with Animal Scabies
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Scabies? (Etiology)
Scabies is caused by a tiny eight-legged parasitic mite called Sarcoptes Scabiei.
- It mainly spreads because of skin-to-skin contact with the infected individual
- Scabies is not a sexually-transmitted disease, even though it is transmitted from one individual to another through close contact that occurs during sex
- Sharing the bed and clothing with infected individuals also helps in the spread of Scabies
- Despite popular belief, humans cannot get Scabies from animals or pets. However, if humans come in close contact with pet dogs and cats having Animal Scabies (called Sarcoptic Mange), they may be infected
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Scabies?
The signs and symptoms of Scabies mostly occur due to the itching caused by the bite of the mite, infection caused by frequent scratching, and allergic reaction due to the tick bite. Scabies exhibit the following signs and symptoms:
- Intense itching: The itching is severe and intense particularly during the night time, which results in many sleepless nights
- Rashes: Tiny bite-like rashes appear in a variety of parts of the body
- In between the fingers
- Around the armpits
- Around the waist region
- On the inner aspects of the wrists and elbow
- On the soles of the hand and feet
- Around the breasts and back of the shoulder
- Around genital area and buttocks
- Around the knee joints
- In children the Scabies, rashes may appear all over the body, mainly on the palms, soles, and the scalp. In babies, the rashes may be found on the palms and soles
- When babies and children are infected with Scabies, they appear very restless and irritable due to the itching, loss of appetite, and loss of proper sleep
- Blisters on the palms and soles is a common symptom in infants with Scabies (this is called acropustulosis)
- Thick crusts on the skin: This occurs frequently, only when an individual is affected by a severe form of scabies called Crusted Scabies or Norwegian Scabies
- The intense itching can cause extreme psychological discomfort
How is Scabies Diagnosed?
Scabies is most often diagnosed by a physical examination of the skin rashes on the infected individual.
- The healthcare provider may pay special attention to the:
- Location of the rashes
- Its appearances
- Other symptoms exhibited by the patient
- A diagnosis can also be made by taking a skin scraping and examining it under a microscope to confirm the presence of the mites
- Differential diagnosis should include other conditions causing similar signs and symptoms that include contact dermatitis, syphilis of the skin, allergic reactions, and infection with other parasites such as fleas
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Scabies?
The possible complications associated with Scabies include:
- Secondary bacterial infection: Continuous and vigorous scratching of the rashes may lead to secondary bacterial infection, such as impetigo, which is an infection of the skin caused by Staphylococcus or Streptococcus bacteria
- Blood poisoning or sepsis: This occurs when an individual intensely scratches the skin, which leads to the bacterium from the skin entering blood and causing sepsis, Non-stop scratching may also lead to sepsis, which is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the infection reaches the blood
- Crusted Scabies (also called Norwegian Scabies) is a severe form that can affect all parts of the body
- Renal function may be affected in some individuals with chronic Scabies. This occurs more frequently in individuals with longstanding, untreated Scabies
How is Scabies Treated?
Since the signs and symptoms of Scabies infection are related to the following factors such as:
- Itching caused by the bite of the mite,
- Infection caused by frequent scratching, and
- Allergic reaction due to the tick bite
The treatment should address the itching, the scratching side effects, and allergic reaction to the bite of the mites.
- Medications to reduce itching, antibiotics for skin infections, and anti-allergic medications may be necessary, depending on the individual’s combination of signs and symptoms
- Scabies can be treated with medications: Medications are usually available in the form of creams and lotions, which can be applied all over the body and left for 8 hours to be effective. It is generally advised that all members of the household should undergo treatment simultaneously, to check the spread of Scabies
- If a school-going child is diagnosed with Scabies, then all the other children who came in contact with the child should also be screened for Scabies
- In certain situations, the co-workers of the infected individuals may also need screening at the workplace
Medications suggested for Scabies include:
- Permethrin 5 percent (Elimite). It is a cream that contains chemicals to kill the Scabies germs. The physician usually recommends that this cream be applied all over the body, left overnight, and then washed. To be even more effective, it can be applied again after a week. This cream can be used by all individuals above the age of 2 months
- Lindane: This medicine also contains chemicals to kill germs and is available in the form of creams, lotions, and shampoos. It should also be applied from head to foot and reapplied after a period of 7 days. This medication is not recommended for children below 2 years of age, pregnant women, and those with weak immune system
- Crotamiton (Eurax): This medicine is applied once a day for 5 days, as prescribed by the physician
- Ivermectin: An oral medication that is used for treating Crusted Scabies. It cannot be used on infants and children below 6 years of age
- Other medications include benzyl benzoate, malathion, and sulfur preparations
Other points to note include:
- Individuals, who have been diagnosed with Scabies infection, should have their nails clipped
- If individuals have been diagnosed with Animal Scabies, then both the individual and animal should be treated
- Regular follow-up after a treatment course is necessary to detect early recurrence of infection
How can Scabies be Prevented?
Spread of Scabies can be minimized by practicing the following safety measures:
- Avoiding direct skin-to-skin contact with infected individuals
- Sharing of clothes and bed with the infected individuals should be discouraged
- All household members should be treated simultaneously, along with those infected to avoid the spread of Scabies
- The clothes and bed used by the infected person should be machine-washed with hot water and dried or dry cleaned. Items that cannot be washed should be sealed in a plastic bag and kept away for a couple of weeks to kill the mites
- Rooms used by the infected individual should be cleaned thoroughly to remove all germs
- Cats and dogs should be routinely screened by the vet for Animal Scabies
What is the Prognosis of Scabies? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- The prognosis of Scabies depends upon the severity of the infection. Generally, Crusted Scabies has a worse prognosis than milder forms of Scabies infection
- The prognosis also depends upon the underlying health status of the infected individual. Individuals who have poor immune system (such as those with HIV/AIDS) have a worse prognosis
- Scabies is easily curable, if the physician’s advice regarding the medication is followed properly. Within a couple of days, one must be able to see improvement in the health condition and the symptoms
- However, a severe case of Crusted Scabies with lot of scaling and complications would suggest that the individual may be infected with the HIV virus
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Scabies:
- Contrary to popular belief, the Scabies mites cannot jump or fly
- Scabies mites cannot live outside the human body for more than 3 days
- Approximate estimates indicate that over 100 million people are infected with Scabies worldwide annually
- Itch mites are not classified as insects; they belong to the class of Arachnida
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.