What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Knee Injury - Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL)
- MCL Injury
- MCL Sprain
What is Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Injury? (Definition/Background Information)
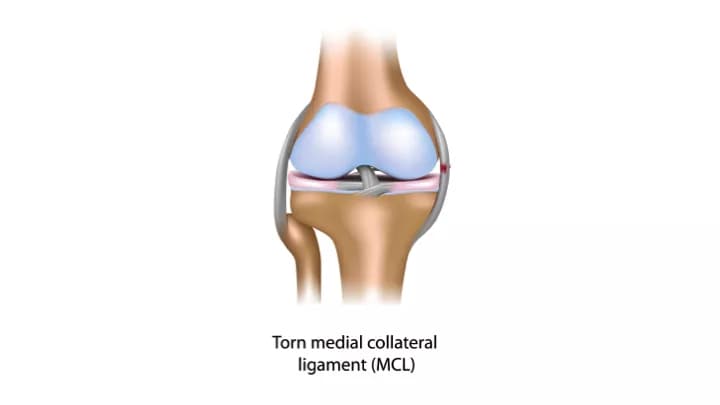
- The medial collateral is a ligament located on the inner part of the knee joint. A Medial Collateral Ligament Injury is a sprain or tear to the medial collateral ligament (MCL) in the knee
- Individuals who participate in athletic sports, such as football or basketball, have a higher risk of injuring their medial collateral ligament
- Treatment for this condition depends on the type and severity of injury and involves both surgical and nonsurgical treatment methods
- The prognoses of a Medial Collateral Ligament Injuries are usually excellent with appropriate treatment
Depending on the severity of the injury, physicians usually classify a Medial Collateral Ligament Injury into three different grades. These grades include:
- Grade I Medial Collateral Ligament Injury: Grade I occurs when only a small number of ligament fibers have been stretched, but not torn
- Grade II Medial Collateral Ligament Injury: Grade II occurs when the ligament fibers have been partially torn
- Grade III Medial Collateral Ligament Injury: Grade III is a complete rupture of the ligament fibers in the knee
Who gets Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Injury? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Individuals of any age, gender, race, or ethnic group, may sustain a Medial Collateral Ligament Injury
- Adults between the ages of 20-34 and 55-65 years old have the highest rate of incidence of the condition
- Medial Collateral Ligament injuries occur equally in men and women
What are the Risk Factors for Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Injury? (Predisposing Factors)
Risk factors of a Medial Collateral Ligament Injury include:
- Participation in any sports that involves a violent change of direction such as with American football, soccer, cricket, or basketball
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Injury? (Etiology)
The following factors may lead to a Medial Collateral Ligament Injury.
- Participation in any sports that cause the knee to twist forcefully or rotate
- Squatting or lifting of heavy objects
- Sudden directional change causing abnormal pressure on the knee
- Direct trauma to the outside part of the knee
- Hyperextension of the knee
- Landing awkwardly on one’s knee
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Injury?
The signs and symptoms of a Medial Collateral Ligament Injury may include:
- Decreased range of motion in the knee, difficulty walking
- Pain and tenderness on the inside part of the knee
- Noticeable swelling in the knee
- A loud popping sound noticed at the time of injury
How is Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Injury Diagnosed?
A Medial Collateral Ligament Injury is diagnosed using the following methods:
- Physical examination: During a physical examination, the physician may check for any signs of tenderness and swelling in the knee. A physician may also test the range of motion in the knee. In addition to this, a complete medical history can aid in arriving at a definitive diagnosis
- X-ray of the knee: Although MCL Injuries do not show up on x-rays, they can help rule out other causes of knee injuries and help confirm the diagnosis
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the knee: An MRI is a more detailed scan that uses a magnetic field to produce images, which allows a physician to view any damage to the bones and soft tissue to confirm the diagnosis
- Ultrasound imaging of the knee: High-frequency sound waves are used to generate a more detailed image of the knee. This can help determine if any loose cartilage is caught in the knee
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Injury?
Complications of a Medial Collateral Ligament Injury include:
- Chronic knee instability
- Prolonged and chronic pain
- Degenerative joint disease, such as osteoarthritis
How is Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Injury Treated?
Both nonsurgical and surgical methods may be used to treat a Medial Collateral Ligament Injury. However, treatment depends on the severity of the injury.
Nonsurgical treatment for Medial Collateral Ligament Injury may include:
The RICE method is effective for a high percentage of sports-related injuries. RICE is an acronym for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation.
- Rest: Any activity that aggravates the knee condition should be avoided. The physician usually advises individuals to refrain from activities, until the symptoms get better
- Ice: Applying ice to the knee may help decrease pain and reduce swelling
- Compression: Wearing an elastic compression bandage can help stop additional swelling and loss of blood
- Elevation: Elevating the knee helps to decrease swelling
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication, such as ibuprofen and naproxen, can help decrease the pain in the knee
- Physical therapy may help restore strength, as well as flexibility in the muscles
Surgical treatment for Medial Collateral Ligament Injury may include:
- Knee arthroscopy: Arthroscopic surgery is a minimally-invasive surgical procedure that is used to visualize, diagnose, and repair the medial collateral ligament using small instruments. During this procedure, a surgeon inserts a thin tube attached to a camera (a fibro-optic camera) into the joint via a small incision on the skin of the joint. Visualizing the joint via a camera helps the physician view the inside of the knee and to determine the treatment
- Knee ligament repair: Knee ligament repair is a procedure to repair or replace the medial collateral ligament with surgery
How can Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Injury be Prevented?
A few recommendations to help prevent a Medial Collateral Ligament Injury include:
- Improve conditioning and strengthen the hamstrings. It has been proven that exercising regularly to strengthen the hamstrings and surrounding structures around the knee is very effective in decreasing the risk of a MCL Injury
- Wear appropriate safety equipment, such as a knee brace, while participating in certain high impact sports, like American football, soccer, cricket, or basketball. Individuals, who participate in such sports, should ensure that any safety equipment worn is properly adjusted and correctly fitted to provide support for the knee
- Warming-up prior to exercising
- Use proper technique when exercising so that there is a decreased stress on the knee
What is the Prognosis of Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Injury? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- When Medial Collateral Ligament Injuries are properly diagnosed and treated, individuals usually make a complete recovery and usually regain full strength and range of motion in the injured knee
- However, complications, such as osteoarthritis in the knee, may develop in some individuals with a Grade III MCL Injury
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Injury:
The following DoveMed website link is a useful resource for additional information:
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.