What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Hyalinizing Spindle Cell Tumor with Giant Rosettes
- LGFMS (Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma)
- LGFS (Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma)
What is Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma? (Definition/Background Information)
- Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma (LGFS) is a rare, malignant, soft tissue tumor often seen in young adults. The tumors are mostly present in the extremities (arms and legs), or chest and back region
- There are no identified risk factors for Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma, but the cause is associated with genetic defects. In particular, the presence of FUS and CREB3L2 (or CREB3L1) gene fusion is a characteristic feature of LGFS
- Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma are mostly slow-growing and do not present pain, in most cases. Tumor recurrence and metastasis to the lungs may take place several years after initial treatment (including surgical removal)
- The treatment of choice for Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma is a complete surgical excision. However, long-term follow-up is necessary to ‘watch-out’ for recurrence and/or metastasis
- The prognosis of Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma depends upon several factors including the location, size, and stage of the tumor. Small-sized tumors that are detected early and can be completely removed have a generally good prognosis
Who gets Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma is a rare malignancy with only 350 cases being reported so far. However, scientists believe that many cases are unreported
- It may be present in individuals of any age, but LGFS is mostly seen in young adults. 1 in 5 cases are seen in individuals below 18 years of age
- Both males and females are affected and no gender preference is noted
- No particular racial or ethnic group preference is seen
The tumor incidence is unknown, but experts inform that it may be more common than previously believed, since an exact diagnosis of the tumor can be challenging. Also, presently, proper diagnostic criteria have not been well-established.
What are the Risk Factors for Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma? (Predisposing Factors)
- Presently, no risk factors are evident or have been identified for Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma formation
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma? (Etiology)
The exact cause and mechanism of Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma formation is unknown. However, the following genetic anomalies have been observed:
- Chromosomal translocations are present in 65% of the cases; the other 25% are known to show ring chromosome anomaly. It is researched that these two factors lead to the fusion of genes
- The tumor regularly shows a gene fusion of either the FUS and CREB3L2 genes (in about 76-96% cases), or of the FUS and CREB3L1 genes (in 4-6% cases). Studies inform that this is a very specific indicator for Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma?
The presentations may be based on the location of the tumor. Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma signs and symptoms can include:
- A painless, slow-growing mass may be observed in the body. Studies indicate that 1 in 6 individuals may have the tumor for a long time period (even 5 years)
- The malignant tumor is present as a well-circumscribed mass
- The size of the tumor ranges from 1-20 cm; average size at diagnosis is about 5 cm
- The tumors may be located just below the skin (in children usually); in a majority, they are seen to arise below the fascial plane (much deeper than the subcutaneous tissues)
- Most common location of LGFS is the arms and legs (proximal location) or chest and back. They may be observed at other locations too
How is Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma Diagnosed?
A diagnosis of Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma is made using the following tools:
- Physical exam with evaluation of the individual’s medical history
- CT scan or MRI scan of the affected region
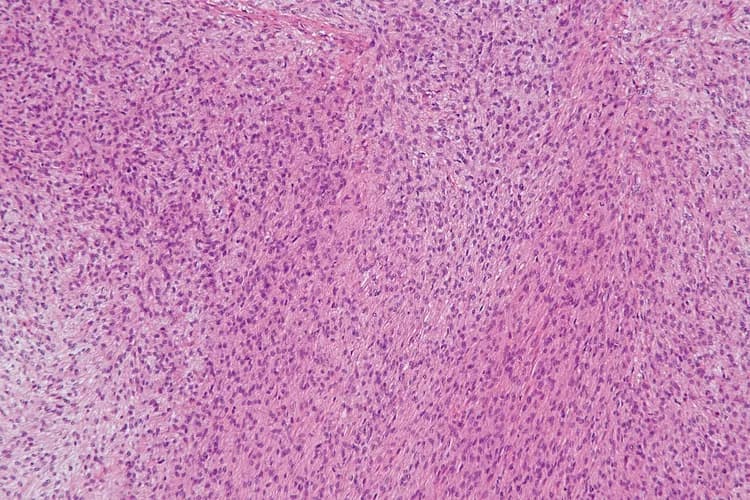
- Tissue biopsy of tumor specimen: A tumor biopsy is performed and sent to a laboratory for a pathological examination. The pathologist examines the biopsy under a microscope. After putting together clinical findings, special studies on tissues (if needed) and with microscope findings, the pathologist arrives at a definitive diagnosis
Note:
- Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma can present diagnostic challenges
- Since, the tumor presents an unusual pattern on microscopic examination, it was previously referred to as Hyalinizing Spindle Cell Tumor with Giant Rosettes
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma?
Complications of Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma may include:
- The tumor has low risk for metastasis and recurrence in the first 5 years following the surgical removal of the main tumor. The rate of metastasis and recurrence is 5% and 10% respectively during this period
- However, with time, the incidence of both metastasis and recurrence increased. Some case reports compiled from healthcare centers shows that the metastasis and recurrence rates could be as high as 45% and 64%. In the same study, the death rate was 42%
- Common metastatic sites include the lungs and pleura
- Damage to vital nerves, blood vessels, and surrounding structures during surgery to remove the tumor
- Side effects from chemotherapy (such as toxicity) and radiation therapy
How is Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma Treated?
Treatment measures for Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma may include the following:
- Wide surgical excision of LGFS with removal of the entire lesion is generally adopted, since it is a malignant tumor with metastasis potential
- Embolization (clotting the vessels in the tumor) may be used to provide temporary relief from the symptoms and reduce blood loss during a surgical procedure
- Radiation therapy and/or chemotherapy may be used to destroy the tumor cells, based on the assessment by the healthcare provider
- Post-operative care is important; a minimum activity level is to be ensured until the surgical wound heals
- Long-term follow-up care with regular screening and check-ups are important
How can Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma be Prevented?
- Current medical research has not established a way of preventing Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma
- Regular medical screening at periodic intervals with blood tests, scans, and physical examinations are mandatory due to its metastasizing potential and chances of recurrence. Often several years of active vigilance is necessary
What is the Prognosis of Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma is a rare low-grade malignancy, with metastasizing potential. The prognosis of the tumor depends upon many factors including the size of the tumor, stage of the tumor, tumor location, age and health status of the individual
- The prognosis of small-sized tumors with complete excision and removal is generally good. Metastasis is not commonly observed, but may take place after a long time interval
- Also tumor behavior is difficult to predict; for it may take an aggressive course, even though LGFS is evidently low-grade
- Following removal of the primary tumor, many cases are observed to either recur and/or metastasize at a much higher rate, after a time period of around 5 years
- Curiously, metastasis was seen to take place, even 45 years after initial tumor diagnosis. Some tumors are known to have caused fatalities even after 15 years
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma:
Please visit our Cancer & Benign Tumor Health Center for more physician-approved health information:
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.