What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Mammary Lipoma
What is Lipoma of Breast? (Definition/Background Information)
- Lipoma of Breast is a common benign tumor of fat tissues (adipose tissues). They are usually observed in adults, both men and women, between the ages 40-60 years. Lipomas can occur in almost any part of the body subcutaneously (just below the skin)
- There may be different subtypes of lipoma that are observed uncommonly in the breast. These include the following:
- Angiolipoma of Breast (that occurs as a painless mass)
- Cellular Angiolipoma of Breast
- Spindle Cell Lipoma of Breast
- Hibernoma of Breast
- Chondrolipoma of Breast
- Adenolipoma of Breast (which some research scientists refer to as a hamartoma)
- The cause and risk factors of Lipoma of Breast is unknown. The signs and symptoms of Lipoma of Breast may include the presence of a slow-growing lump in the breast. Small-sized tumors may be asymptomatic and show no signs and symptoms
- Lipoma of Breast is treated through a surgical excision, per the healthcare provider’s recommendation. The prognosis is excellent with its complete removal, since it is a benign tumor. However, periodic checkups and screening mammograms are advised to look for any recurrence
Who gets Lipoma of Breast? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Adults between 40-60 years are generally affected by Lipoma of Breast, though lipomas may occur at any age. It is one of the most common benign breast tumors
- Both males and females are affected
- All racial and ethnic groups are affected and no specific predilection is seen
What are the Risk Factors for Lipoma of Breast? (Predisposing Factors)
- Currently, no definitive risk factors for Lipoma of Breast are known
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Lipoma of Breast? (Etiology)
- The exact cause of development of Lipoma of Breast is currently not clearly understood
- Certain gene mutations have also been reported in the tumors. Research is being performed to determine how these mutations contribute to the formation of the tumors
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Lipoma of Breast?
The signs and symptoms of Lipoma of Breast may include:
- A benign soft lump in a single breast; typically, only one breast is affected
- This solitary tumor is normally slow-growing and present just below the skin (subcutaneous)
- The tumors can appear as round and well-defined masses; it generally does not exceed 5 cm in size
- The skin over the mass is intact; the mass is usually moveable underneath the skin
In many, these benign lesions are asymptomatic and present no signs and symptoms.
How is Lipoma of Breast Diagnosed?
Lipoma of Breast may be diagnosed in the following manner:
- Complete physical examination with comprehensive medical and family history evaluation
- Breast exam to check for any lumps or unusual signs in the breasts
- Mammogram: A mammogram uses x-rays to provide images of the breast. These benign tumors are identified as a mammogram mass, which may or may not be associated with microcalcification. The mammography findings may raise enough suspicion to warrant a tissue biopsy
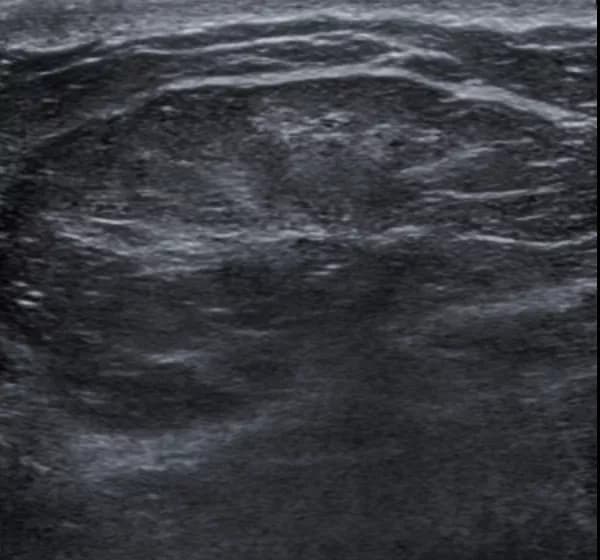
- Breast ultrasound scan: Using high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the breast, the type of tumor, whether fluid-filled cyst or solid mass type, may be identified
- Computerized tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan of the breast
- Breast biopsy:
- A biopsy of the tumor is performed and sent to a laboratory for a pathological examination. A pathologist examines the biopsy under a microscope. After putting together clinical findings, special studies on tissues (if needed) and with microscope findings, the pathologist arrives at a definitive diagnosis. Examination of the biopsy under a microscope by a pathologist is considered to be gold standard in arriving at a conclusive diagnosis
- Biopsy specimens are studied initially using Hematoxylin and Eosin staining. The pathologist then decides on additional studies depending on the clinical situation
- Sometimes, the pathologist may perform additional studies, which may include immunohistochemical stains and molecular studies to assist in the diagnosis
Biopsies are the only methods used to determine whether an abnormality is benign or cancerous. These are performed by inserting a needle into a breast mass and removing cells or tissues, for further examination. There are different types of biopsies:
- Fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) of breast mass: In this method, a very thin needle is used to remove a small amount of tissue. FNAB cannot help definitively diagnose Lipoma of Breast. It only helps determine if the tumor is malignant or benign. This can help the healthcare provider discuss and plan the next steps (with respect to diagnosis and treatment)
- Core needle biopsy of breast mass: A wider needle is used to withdraw a small cylinder of tissue from an abnormal area of the breast
- Open tissue biopsy of breast mass: A surgical procedure used less often than needle biopsies, it is used to remove a part or all of a breast lump for analysis
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Lipoma of Breast?
There may not be any significant complications of Lipoma of Breast.
- However, in some cases, the condition may cause emotional stress due to concerns of malignancy
- Recurrence of lipoma on incomplete removal is known to occur
How is Lipoma of Breast Treated?
The following treatment methods for Lipoma of Breast may be considered:
- A ‘wait and watch’ approach may be considered for asymptomatic lipomas
- A simple surgical excision and removal of the entire tumor is normally sufficient treatment, particularly if the individuals have the following signs and symptoms:
- The tumor is infected, with or without foul-smelling pus discharge
- Sudden increase in size of the lipoma
- If the tumor that was painless, suddenly becomes painful
- If the skin tumor causes cosmetic issues
- Breast lumpectomy:
- The surgical procedure performed is known as a breast lumpectomy. It is a surgical procedure to remove the breast lump, which may be done under a general anesthetic
- During the surgery, a small incision is made in the skin of the breast and a hollow probe that is connected to a vacuum, inserted
- The breast tissue is sucked through the probe, using vacuum, until the lump has been removed
- Follow-up care with frequent breast self-examinations and screening mammograms may be recommended by the healthcare provider
How can Lipoma of Breast be Prevented?
The development of Lipoma of Breast is difficult to prevent. Currently, no specific preventive measures are available to avoid Lipomas of Breast.
In general, however, it is important to be aware of certain risk factors for breast tumors, which include:
- The individual must regularly conduct breast self-exams, to ensure that no lumps are present
- Maintain a healthy body weight and exercise regularly
- Implement and follow a well-balanced diet; a high intake of fiber via fresh fruits and vegetables helps in a healthy lifestyle
- Avoid or completely stop smoking
- Drink alcohol in moderation; limit to one or (maximum) two drinks a day
- Limit combination hormone therapy used to treat symptoms of menopause. It is advised that individuals be aware of the potential benefits and risks of hormone therapy
What is the Prognosis of Lipoma of Breast? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- The prognosis of Lipoma of Breast is excellent through a complete excision of this fat tissue tumor
- The tumor may recur, if it is incompletely removed. And so, periodic follow-up check-ups with screening are recommended
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Lipoma of Breast:
The following DoveMed website links are useful resources for additional information:
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.