What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Capute-Rimoin-Konigsmark-Esterly-Richardson Syndrome
- NSML (Noonan Syndrome with Multiple Lentigines)
- Progressive Cardiomyopathic Lentiginosis
What is LEOPARD Syndrome? (Definition/Background Information)
- LEOPARD Syndrome is a very rare genetic disorder characterized by abnormalities of the skin, heart, inner ear, head, face, and the genitals. It may be accompanied with mild mental retardation
- The term “LEOPARD” denotes:
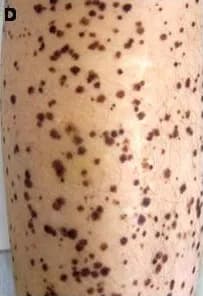
- Lentigines, which are multiple black or dark brown spots on the skin
- Electrocardiographic conduction defects in the heart
- Ocular hypertelorism, where there is widely-spaced eyes
- Pulmonary stenosis due to narrowing of the pulmonary valve, resulting in obstruction of the normal outflow of blood from the right ventricle of the heart
- Abnormalities of the genitals
- Retarded growth resulting in short stature
- Deafness or hearing loss, due to malfunction of the inner ear
- LEOPARD Syndrome is an autosomal dominant disorder caused by a mutation in the protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 11 gene (PTPN11)
- The affected individuals require treatment by a team of endocrinologists, cardiologists, urologists, dermatologists, and other specialists depending on their presentations (signs and symptoms)
- Most individuals diagnosed with LEOPARD Syndrome lead normal lives, but death may occur due to complications of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy or cardiac conduction defects
Who gets LEOPARD Syndrome? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- The actual prevalence of LEOPARD Syndrome is not known due to under-diagnosis of this rare disorder. But, currently around 200 cases have been reported worldwide
- Both males and females are affected
What are the Risk Factors for LEOPARD Syndrome? (Predisposing Factors)
The following are the risk factors for LEOPARD Syndrome:
- The most common risk factor is the presence of LEOPARD Syndrome in either one of the parents, siblings, or other blood relatives
- The presence of Noonan syndrome in family members, where there is mutation in either PTPN11, SOS1, KRAS, NRAS, RAF1, BRAF, or MEK1 gene, with mutation in PTPN11 occurring in nearly 85% of the cases
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of LEOPARD Syndrome? (Etiology)
LEOPARD Syndrome is a complex genetic condition that may be inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern.
- Nearly 85% of the cases are caused by a mutation in the protein coding region of the PTPN11 gene
- Recently point mutations in the RAF1 gene have been found in 2 out of 6 PTPN11-negative LS patients
Autosomal dominant: Autosomal dominant conditions are traits or disorders that are present when only one copy of the mutation is inherited on a non-sex chromosome. In these types of conditions, the individual has one normal copy and one mutant copy of the gene. The abnormal gene dominates, masking the effects of the correctly functioning gene. If an individual has an autosomal dominant condition, the chance of passing the abnormal gene on to their offspring is 50%. Children, who do not inherit the abnormal gene, will not develop the condition or pass it on to their offspring.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of LEOPARD Syndrome?
The signs and symptoms associated with LEOPARD Syndrome are highly variable and may include:
- The presence of characteristic, multiple, dark brown spotted skin lesions called lentigines. Sometimes, lentigines are absent in young children less than 5 years of age, but they eventually appear as the child grows older
- In addition, nearly 20% of the individuals may have large, dark brown discoloration of the skin called café-au-lait spots
- Defect in conduction system of the heart, hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy, or pulmonary stenosis resulting in heart blocks, arrhythmias, breathlessness, chest pain, and even sudden death
- Ocular hypertelorism, where the eyes are widely spaced apart and may be accompanied with other abnormalities such as strabismus or squint of eyes, drooping of the upper eyelids, the presence of abnormal folds of skin over the inner corners of the eyes, abnormal protrusion of the lower jaw, or low-set prominent ears
- Short stature as a result of growth retardation, which may be associated with skeletal abnormalities such as funnel chest, pigeon chest, or abnormal curvature of the spine
- Sensorineural deafness leading to abnormal speech
How is LEOPARD Syndrome Diagnosed?
A diagnosis of LEOPARD Syndrome includes:
- A detailed medical history
- A thorough physical examination to check for the presence of lentigines or café-au-lait spots
- Cardiac examination
- Urogenital examination
- Echocardiography and ECG to rule out cardiac abnormalities
- Pelvic ultrasound to rule out abnormalities of the gonads and urinary tract
- X-ray of the spine
- Audiometry and CT scan of ear canal to rule out hearing abnormalities
- Molecular genetic testing for the mutations in PTPN11 and RAF1 genes in order to confirm the diagnosis
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of LEOPARD Syndrome?
Following are the complications of LEOPARD Syndrome:
- Cardiac complications such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, pulmonary stenosis, and conduction defects that include heart blocks are the most common and life-threatening conditions, if not treated appropriately
- Growth retardation and skeletal abnormalities
- Deafness
How is LEOPARD Syndrome Treated?
Treatment of LEOPARD Syndrome is based on the type and severity of symptoms. It involves the coordinated efforts between a multi-specialty team consisting of pediatricians, surgeons, dermatologists, cardiologists, orthopedicians, endocrinologists, and audiologists.
The treatment measures may include:
- Medications for certain cardiac conditions and hormonal therapy to achieve normal sexual functions
- Surgical repair for cardiac, urogenital, and skeletal abnormalities
- Usage of hearing aid for deafness
- Genetic counseling may be provided to the affected individuals and their families
How can LEOPARD Syndrome be Prevented?
- Currently, there are no specific methods or guidelines to prevent LEOPARD Syndrome, since it is a genetic condition
- Genetic testing of the expecting parents (and related family members) and prenatal diagnosis (molecular testing of the fetus during pregnancy) may help in understanding the risks better during pregnancy
- If there is a family history of the condition, then genetic counseling will help assess risks, before planning for a child
- Active research is currently being performed to explore the possibilities for treatment and prevention of inherited and acquired genetic disorders
What is the Prognosis of LEOPARD Syndrome? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- In general, LEOPARD Syndrome is not a life-threatening condition in the absence of cardiac involvement. Thus, individuals with LEOPARD Syndrome should be carefully evaluated for the presence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and other heart-related defects
- Without cardiac involvement, most individuals with the disorder are able to lead a normal life with appropriate medical, surgical, and supportive care
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for LEOPARD Syndrome:
There are many online groups available for individuals diagnosed with LEOPARD Syndrome that provide supportive care, encouragement, and bring a measure of relief to the affected individuals and their families.
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.