What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Fibrous Histiocytoma of Tendon Sheath
- Giant-Cell Synovioma
- Localized Nodular Tenosynovitis
What is Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath? (Definition/Background Information)
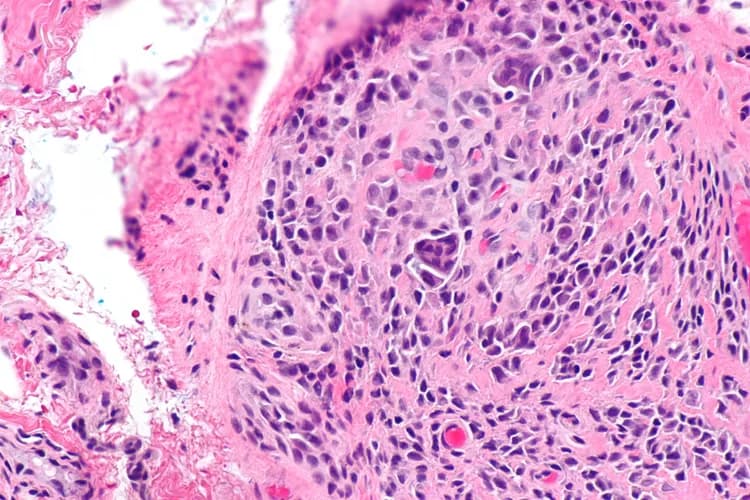
- A Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath (GCTTS) is a benign tumor consisting of many types of polygonal cells in a bed of collagen. It involves the joint fluid sac, tendon sheath, and synovial membrane of the joints
- Synovial fluid is the lubricating fluid found in the joints (like knee, elbow), and synovium refers to the thin membrane that lines or covers the joint space
- GCTTS is a common, painless tumor, frequently appearing on the fingers of the hand. It may take decades to develop and has no metastatic capability
- Surgical excision of the tumor with its entire removal, followed by radiation therapy, remains the standard treatment mode
- GCTTS is potentially known to recur, after its surgical removal. Hence, multiple surgeries may be required to eliminate it completely
Who gets Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- The soft tissue tumor, GCTTS usually affects middle-aged adults (between 30-50 years of age)
- Children below 10 years and elderly individuals above 60 years, are hardly affected
- There is a slight female predominance (female-male ratio 3:2)
- No ethnic or racial preference is seen
What are the Risk Factors for Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath? (Predisposing Factors)
No clear risk factors have been established. Nevertheless, the following are thought to be associated with Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath, in some way:
- Degenerative disorders of the joints; particularly affecting the fingers
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- External trauma
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath? (Etiology)
- The exact cause and formation mechanism of Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath is unknown
- Some of the theories proposed to offer an explanation of its development relate to:
- Metabolic defects
- Infections
- Abnormal body immunity
- Blood vessel anomalies
- However, the generally accepted theory is that GCTTS might form as a reactive process to an injury-related inflammation, leading to cell proliferation
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath?
Signs and symptoms of Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath may include the following:
- The presentations are based on the location of the tumor
- In the initial growing phase of these generally superficial lesions (those located below the skin surface), they may be asymptomatic. The soft tissue tumors grow at an extremely slow rate
- GCTTS are firm, hard, and well-defined. No skin color change is noticed, but swelling may be felt (which in rare cases may be painful)
- Numbing sensation is felt on the hands, feet, and fingers, with locally impaired function, if the lesion is big. Inconvenience and discomfort may be sensed, on account of this
- The right hand ‘long fingers’ (except the thumb and small finger) are the usual site for the tumor, followed by the toe. Most tumors are observed around the joints or bones. The least affected areas are the ankles, knees, and wrists
How is Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath Diagnosed?
A diagnosis of Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath may involve:
- Physical exam with evaluation of medical history
- MRI scan of the site
- Ultrasound studies
- Histopathological studies conducted on a biopsy specimen - the specimen is examined under a microscope by a pathologist, to arrive at a definitive diagnosis
- Differential diagnosis, to eliminate other tumor types is considered, before arriving at a definitive diagnosis
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath?
Complications of Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath may include:
- Complications are dependent on the site and size of the tumor. In some cases, the tumor may infiltrate into adjoining tissues and muscles
- The mobility of the joints may be constrained leading to difficulty in walking, folding hands, etc. affecting the quality of life
- Damage of the fingers, knee, elbow, or even other organs, vital nerves, and blood vessels, during surgery
- GCTTS is known to having a high recurrence rate (9-44%), after its surgical excision and removal. Often, multiple surgeries may be required to completely eliminate the tumor
How is Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath Treated?
Treatment measures for Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath include the following:
- Surgical excision of GCTTS, removal of the entire lesion, followed by radiation therapy, remains the standard treatment mode. If the tumor is not fully removed, then it will recur
- When it is unsafe to surgically remove the lesion on account of weak health condition of the individual; non-invasive procedures (like radiotherapy) may be adopted
- In some cases skin grafting and tendon reconstruction may be required
- Post-operative care is important: A minimum activity level is ensured, until the surgical wound heals
- Follow-up care with regular screening and check-ups are important
How can Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath be Prevented?
- Current medical research has not established a way of preventing Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath
- Regular medical screening at periodic intervals with blood tests, scans, and physical examinations, are mandatory for those who have already endured the tumor, due to its high recurrence rate
- The recurrence risk may be compounded by the presence of other degenerative bone diseases and external injuries
What is the Prognosis of Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- The prognoses are excellent with surgical intervention and complete removal of the lesions, even though they may be deep-seated
- Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath recurrence risk is dependent on surgical efficacy. It does not show any tendency to metastasize
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath:
There are two types of soft-tissue giant cell tumors, namely:
- Common Localized Type of GCTTS
- Rare Diffuse Type of GCTTS
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.