What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- GN (Ganglioneuroma)
What is Ganglioneuroma? (Definition/Background Information)
- Ganglioneuroma is a rare tumor that develops in a special type of nerve cells (the neural crest) belonging to the sympathetic nervous system (autonomic). It commonly occurs in the chest (posterior mediastinum), abdomen (retroperitoneum), paraspinal region (along the spinal cord region) and the adrenal gland. Other uncommon sites include the heart, large bowel, and skin
- Ganglioneuromas are typically benign (non-cancerous) and usually do not cause any symptoms. Or, they cause symptoms due to pressure on other organs adjacent to it
- They grow slowly and are usually discovered when the individuals are examined or imaged for other health reasons. Ganglioneuromas may be occasionally associated with other conditions (such as Multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) type IIb, neurofibromatosis type 1, or Cowden syndrome)
- Surgical removal of the tumor offers cure in most individuals. The prognosis of Ganglioneuroma is generally favorable
Who gets Ganglioneuroma? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Ganglioneuroma is a tumor type that is extremely rare. It usually affects individuals in their late childhood and early adulthood stage
- Both males and females may be affected
- It may occur worldwide and affect individuals of all races and ethnicities
What are the Risk Factors for Ganglioneuroma? (Predisposing Factors)
Currently, there are no known risk factors associated with Ganglioneuroma.
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Ganglioneuroma? (Etiology)
The causative factors of Ganglioneuroma are currently known.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Ganglioneuroma?
Ganglioneuromas are usually asymptomatic, though some exhibit signs and symptoms that depend on its location:
- The tumor may secrete abnormal amounts of hormones causing symptoms such as:
- Abnormal sweating, anxiety
- Diarrhea
- High blood pressure
- Difficulty falling asleep
- Increased body hair growth
- Other signs due to compression of nearby organs include:
- If the tumor is present in the chest, the affected individual may experience chest pain and difficulty breathing
- If the tumor is present in the abdomen, the affected individual may experience fullness or bloating and pain
- If the tumor is present in the spinal cord or brain, the affected individual may experience back or neck pain, tingling and numbness of the arms and/or legs (can be one or both the limbs)
How is Ganglioneuroma Diagnosed?
Diagnostic tools used to diagnose Ganglioneuroma include:
- Thorough evaluation of medical history and complete physical examination
- Various tests can be conducted depending on where the symptoms arise from
Other tests are undertaken done to determine the state and condition of the tumor. These tests include:
- CT or MRI scans of the brain, spine, spinal cord, abdomen, and other regions (as required)
- Blood tests to check for hormone levels
- Urine tests may reveal vanilmandelic acid and homovanillic acid
- Myelogram: It is an x-ray procedure that uses a special dye (contrast material) to show bones and the spaces between them and the spinal cord
- A biopsy or removal of tumor is performed for a definitive diagnosis
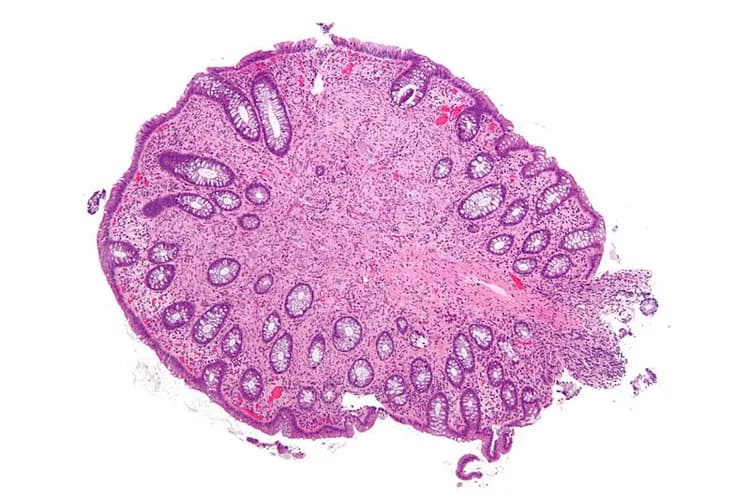
In this biopsy procedure, the physician removes a sample of the tumor tissue (or removes the tumor completely) and sends it to the laboratory for a histopathological examination. The pathologist examines the biopsy under a microscope and arrives at a definitive diagnosis after a thorough evaluation of the clinical and microscopic findings, as well as by correlating the results of special studies on tissues (if required)
The studies may reveal the following:
- Gross appearance: Encapsulated, firm in consistency, and gray-white cut surface
- Microscopically, they may show clusters of mature ganglion cells that are surrounded by Schwann-like fascicles
What are the possible Complications of Ganglioneuroma?
Complications associated with Ganglioneuromas are generally a result of organ compression (adjacent organs) or due to production of hormones. They can also occur during the treatment of the condition. The complications include:
- Pressure caused by an untreated or large tumors may affect the nearby organs and cause specific signs and symptoms due to this
- Constant pressure on the spinal cord has the potential to cause paralysis
- Hormone productions can complications such as hypertension, severe diarrhea, and other signs and symptoms
- Chronic fatigue, weakness, and nausea may be experienced after radiation and chemotherapy
- All tumors have the potential to spread and become cancerous; however, this is not usually observed with Ganglioneuroma
Note: The symptoms may not disappear sometimes, despite removal of the tumor.
How is Ganglioneuroma Treated?
- The treatment option for Ganglioneuroma include, removal of the tumor by surgery, especially if it is causing symptoms
- In some cases, chemotherapy and radiation therapy may be provided
How can Ganglioneuroma be Prevented?
Currently, there are no available methods to prevent Ganglioneuroma occurrence.
What is the Prognosis of Ganglioneuroma? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
Ganglioneuromas are generally slow-growing and benign (non-cancerous). The prognosis is generally good with suitable treatment.
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Ganglioneuroma:
The following DoveMed website link is a useful resource for additional information:
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.