What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Carotid Arterial Disease
- Carotid Atherosclerosis
- Carotid Atherosclerotic Disease
What is Carotid Artery Disease? (Definition/Background Information)
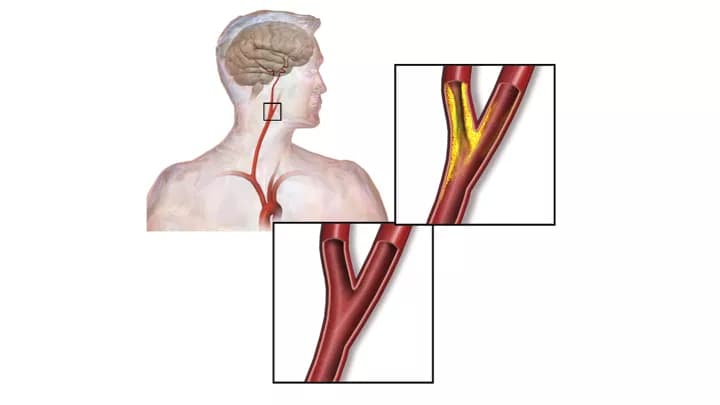
- Blood pumped from the heart travels through the carotid arteries (located on both sides of the neck) to reach parts of the brain, face, and head
- In Carotid Artery Disease, sometimes due to various lifestyle and/or genetic factors, the carotids become clogged with wax-like substances composed of fat called plaque. This can potentially obstruct the free flow of blood causing a stroke, which may further lead to permanent damage of the brain
- The disease develops slowly over time, usually with an advancing age. It requires both active and passive treatment measures to manage the condition; such measures include surgery, medications, and modifications to one's lifestyle
Who gets Carotid Artery Disease? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- It is reported that the incidence of Carotid Artery Disease increases with age
- Gender preference seems to shift with advancing age. Women over 75 years of age, are more prone to the disorder than men. But, if the age is below 75 years, men seem to have a higher risk
- No racial or ethnic preference is observed and the condition is seen worldwide
What are the Risk Factors for Carotid Artery Disease? (Predisposing Factors)
Some of the potential risk factors for Carotid Artery Disease include the following. Most times, multiple risk factors are observed in an individual, thereby creating a greater impact on one's health:
- A diet, high in fat, cholesterol, sugar, and salt, can cause unhealthy body conditions resulting in obesity, high fat (triglyceride) levels, low ‘good’ cholesterol (HDL), and high ‘bad’ cholesterol (LDL) levels
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Advancing age
- Uncontrolled diabetes and high sugar levels, which can increase the risk by almost 4-times. Type 2 diabetes occurs due to the body’s inability to use insulin effectively (termed as insulin-resistance)
- Smoking tobacco: It contributes significantly to the risk factors by creating a cholesterol level imbalance, limiting oxygen supply, and constricting/injuring the blood vessels. This also causes elevated blood pressure levels
- Leading a sedentary life; a lack of physical activities (lack of exercise)
- Certain diseases and disorders may cause narrow carotids and these include connective tissue disorders (such as Marfan syndrome) and fibromuscular dysplasia. This narrowing impedes the blood flow to the brain
- A family medical history of stroke, atherosclerosis, or coronary heart disease may increase one's risk
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases one's chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Carotid Artery Disease? (Etiology)
- The carotid artery, like every other artery, is smooth and resilient permitting easy passage of blood. However, with time, they become rigid and constricted due to plaque deposits along the walls. This results in a condition known as atherosclerosis
- Atherosclerosis causes blockage of the blood flow restricting blood from reaching vital organs in the head. In severe cases, it can even result in a stroke. This is the cause of Carotid Artery Disease that occurs due to genetic and/or lifestyle-related plaque buildup in the arteries
- The plaque consists of microscopic fat particles, cholesterol, calcium, and cell debris. Tiny amounts of blood that accumulates at these deposits, harden, and clot. Sometimes, there is a possibility that these blood clots might be carried by the blood to the brain. This can also lead to a stroke (called embolism-stroke) or potentially result in other complications
- There are many factors that aid in plaque formation and they include food, a sedentary lifestyle, alcohol consumption, smoking tobacco, old age, familial factors, diabetes, and other disorders
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Carotid Artery Disease?
- Mild Carotid Artery Disease can exist without any sign or symptom for a long period of time. Rarely, even in mild cases, there is a possibility that it might suddenly develop into a life-threatening situation
- Stroke is the most frequent indication of carotid arterial blockage. Yet, this is many a times preceded by a condition known as transient ischemic attack (TIA). TIA is a brief stoppage of blood flow to the brain
- A TIA (normally observed for a couple of hours) serves as an early warning sign and key indicator of a possible ‘future’ stroke (near future or far future); and is a far more dangerous condition
Signs and symptoms of TIA (observed for a short while only) and/or stroke includes:
- Vision problems; either blurred vision or loss of vision
- Memory loss
- Speech/language problems, incoherence
- Unexplained and sudden numbness/weakness in one part of the body; loss of sensation
- Confusion, loss of balance, and dizziness
- Intense and sudden headaches
How is Carotid Artery Disease Diagnosed?
Diagnostic tests for Carotid Artery Disease may include:
- Physical exam with evaluation of medical history (also for heart-related conditions)
- Listening to the carotid artery (in the neck) using a stethoscope, to detect any unusual ‘whooshing’ sounds
- Blood test to determine blood sugar, cholesterol, and triglyceride (a type of fat) levels
- Evaluation of basic neurological status by performing tests that estimate the normal intellectual, physical, and mental abilities, of the individual
- Testing blood flow, pressure values, and if any obstruction is present in the artery, using a doppler ultrasound (or sonography) scan
- Carotid angiography: A technique, where a special dye is injected into the veins, to study them on X-ray images
- Other imaging studies used include CT angiography and MR angiography
- A differential diagnosis should be considered to eliminate other related abnormalities
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Carotid Artery Disease?
Complications due to Carotid Artery Disease may include:
- Infrequently blood clots may develop or bits of plaque may become dislodged from the arterial wall and be carried by the blood. These may obstruct blood flow, or travel to other vital organs such as the brain, lungs, and heart
- Stroke, which has the potential to cause irreversible brain damage and paralyze the body (or any part of the body)
- Coronary heart disease or other artery-related disease, due to simultaneous plaque formations at other locations, due to high cholesterol levels in the body
How is Carotid Artery Disease Treated?
The general steps that a physician may consider to manage Carotid Artery Disease are mainly meant to prevent any medical emergencies. These include:
- Use of medications, for mild to moderate atherosclerosis, to lower blood pressure (such as calcium channel blockers, beta blockers, and water pills), prevent blood clots (using anti-platelet drugs), limit progression of plaque buildup (with ACE inhibitors), and lower cholesterol levels (with statins and fibrates)
- Surgical procedures are adopted when the condition is serious with severe blood flow obstruction, or when a TIA/stroke is diagnosed. The two surgical intervention techniques used are:
- Carotid endarterectomy (invasive procedure to remove plaque, replace portion of the artery)
- Carotid angioplasty with stenting (using inflated catheter and placing a stent to prevent narrowing of the artery)
- Passive management of the condition by bringing about changes to the lifestyle, such as through avoidance of smoking, high-fat, and high-salt diets; limiting alcohol consumption; regular exercising; having a healthy diet; and managing stress
How can Carotid Artery Disease be Prevented?
Carotid Artery Disease can be prevented, if the risk factors that lead to the condition are controlled and the progress rate of plaque-formation reduced. The measures to be taken include:
- Smoking has to be completely avoided, and alcohol consumption controlled (limiting to a minimum, when possible)
- Individuals have to minimize their stress levels and always maintain blood pressure within acceptable ranges
- A healthy diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, fish, whole grains, and low in fats and sugar, delays any build-up of plaque
- Being aware of preliminary signs and symptoms of TIA (in particular) and stroke
- Being aware of signs and symptoms of atherosclerosis-related diseases, chiefly if one's age is over 50 years. Having periodic medical health check-ups, more so if the risk factors apply to the individual
- Maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and being physically active
- For diabetics, always having one's blood sugar under control via good food habits and adequate physical exercising
What is the Prognosis of Carotid Artery Disease? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- Carotid Artery Disease may remain asymptomatic and may not be noticed until a medical complication, such as a stroke, develops
- The prognosis is dependent on the intensity of the stroke, establishment of an early treatment procedure, the part of the head/brain that is affected, and many other factors
- An advancing age and genetic parameters cannot be changed; but, healthy modifications to one's lifestyle may keep atherosclerosis from progressing to a life-threatening condition
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Carotid Artery Disease:
Stroke caused by Carotid Artery Disease is a leading killer. More than 50% of strokes that occur are due to plaque build-up in the carotid arteries.
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.