What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Bubonic Plague Lymphadenopathy
- Enlarged Lymph Nodes due to Yersinia Pestis
- Yersinia Pestis Lymphadenitis
What is Bubonic Plague? (Definition/Background Information)
- Plague is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis. Humans are typically infected through rodent or flea bites, or from close contact with the infected animal
- There are 3 main types of Plague, namely:
- Bubonic Plague, when the bacteria infect the lymph nodes
- Septicemic Plague, when the bacteria infect and multiply in blood
- Pneumonic Plague, when the bacteria infect the lungs and cause pneumonia
- Bubonic Plague is the inflammation and often significant enlargement of the lymph nodes (called bubos) due to underlying infection. It is transmitted through the bite of infected rodents or fleas
- There is a higher risk in tropical and sub-tropical regions for Bubonic Plague. The risks also include certain occupations (such as farming), being a veterinarian, coming in close contact with infected animals, hunting, military personnel, and outdoor camping
- The healthcare provider arrives at a diagnosis of Bubonic Plague from assessing the symptoms, studying the affected individual’s work and travel history, and through blood tests to check for the causative organism
- If the underlying infection and associated signs and symptoms are treated in a timely manner, Bubonic Plague is a curable condition. The treatment usually involves the prompt administration of antibiotics
- The prognosis generally depends upon the severity of the underlying signs and symptoms due to this bacterial infection. With early diagnosis and treatment of Bubonic Plague, a full recovery can be attained
- Maintaining personal hygiene, keeping the immediate home and work environment free of rodents (such as by getting rid of potential or existing rodent habitat) and taking precautions while handling animals can help prevent Bubonic Plague
Who gets Bubonic Plague? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Bubonic Plague occurs due to underlying Yersinia pestis infection that can affect individuals of all age groups
- There is no gender preference and both males and females are affected
- Generally, Plague is observed worldwide and all racial and ethnic groups are at risk
- However, the disease spreads rapidly in tropical and sub-tropical places, wherever rodent (rats, mice, and other mammals) population is high
What are the Risk Factors for Bubonic Plague? (Predisposing Factors)
The following risk factors for Bubonic Plague infection are noted:
- Location: Individuals who live in areas where rat population is more and overcrowding is common have a high risk of contracting Yersinia Pestis infection
- Occupation: Individuals, whose occupation necessitates close contact with animals (rodents), such as veterinarians, farmers, and hunters, have a very high risk
- Hobbies: Individuals with hobbies, such as camping, hunting, or hiking, are vulnerable to the disease in Plague-affected areas
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases one's chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Bubonic Plague? (Etiology)
Bubonic Plague is caused by a bacterial infection that results in swollen lymph nodes and other related signs and symptoms.
- The bacterium infects rodents and fleas which in turn, infects humans. Infected flea-bite is the most common cause for the spread of infection
- Bites of infected rodents, such as rats, squirrels, and rabbits, can also spread the disease
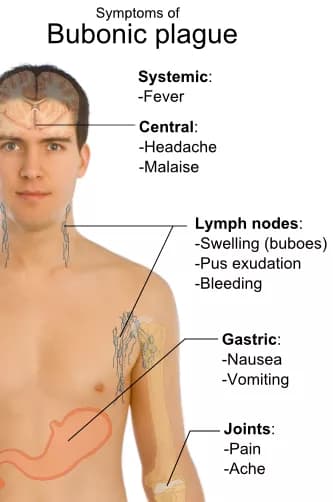
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Bubonic Plague?
The signs and symptoms of Bubonic Plague appear within 3-7 days of infection and may include the following:
- Initially, the lymph nodes closest to the infection site (entry point of bacteria into the body) are affected. If the condition is undetected or untreated, then it spreads to other lymph nodes
- Lymphadenopathy or significantly enlarged lymph nodes, known as bubos appear all over the body; hence the name ‘Bubonic Plague’
- The swollen lymph nodes are generally painful
- The lymph nodes that are commonly involved include lymph nodes in the groin region (inguinal), armpits (axillary), head and neck region (cervical), and upper thigh region (femoral)
- Fever and chills
- Headaches and body aches
- Debilitating weakness
- Vomiting of blood
- Muscle cramps
- Seizures
How is Bubonic Plague Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of Bubonic Plague may involve the following tests and exams:
- Physical examination and examining the signs and symptoms of the affected individual
- Medical history evaluation, including recent travel history
- Recent history of rodent bites (such as from rats or rabbits)
- Blood or sputum tests to check for the presence of the causative bacterium
In majority of the cases, a lymph node biopsy is not performed for Bubonic Plague. However, if the signs and symptoms persist despite suitable treatment, then a biopsy may be undertaken to rule-out other causes of swollen glands (such as a lymphoma).
In case of a lymph node biopsy, the following information may be noted:
- Lymph node biopsy: A lymph node biopsy is performed and sent to a laboratory for a pathological examination. The pathologist examines the biopsy under a microscope. After putting together clinical findings, special studies on tissues (if needed) and with microscope findings, the pathologist arrives at a definitive diagnosis. The pathologist may use special techniques, such as immunohistochemistry stains, to help reveal the presence of the pathogen
- The lymph node biopsy may be performed through any of the following procedures:
- Fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB): A device called a cannula is used to extract tissue or fluid from the lymph nodes
- Lymph node core biopsy of the enlarged lymph node
- Lymph node open biopsy of the enlarged lymph node
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Bubonic Plague?
Bubonic Plague, if left untreated, can lead to certain serious complications such as:
- Gangrene: Blood clots appear in the blood vessels affecting the free flow of blood to the fingers and toes. This may necessitate amputation of the fingers and toes
- Meningitis: An inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord
- Untreated or delayed treatment of Bubonic Plague may develop to affect blood (forming Septicemic Plague) and lungs (forming Pneumonic Plague)
How is Bubonic Plague Treated?
An immediate medical attention is necessary for all forms of Plague. The management of Bubonic Plague may include undertaking treatment of the underlying Yersinia pestis infection. This involves the following measures:
- A dose of powerful antibiotics, such as streptomycin, gentamicin, doxycycline, ciprofloxacin, or chloramphenicol, either individually or in combination, is normally administered
- In some cases, intravenous fluids, oxygen and respiratory support may also be required
How can Bubonic Plague be Prevented?
The prevention of Bubonic Plague may be achieved through the following measures:
- Cleanliness and personal hygiene
- All necessary steps must be taken to ensure that one’s surroundings are free of rodents
- Keeping the residential environment clean is an important preventive method
- Places that can potentially harbor and colonize rodents (especially rats) should be eliminated or sanitized to prevent infestation
- Dead animals and rodents have to be handled extremely carefully and to strict safety standards; ensure that open skin wounds, if any, are kept properly covered and protected
- Follow government advisories on disease outbreaks and schedule travel plans accordingly
- Individuals, such as veterinary doctors, who come in contact with animals on a daily basis, have to take suitable safety measures before treating the infected animals
What is the Prognosis of Bubonic Plague? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- With early diagnosis and proper treatment of Bubonic Plague, it is possible to treat the condition effectively and the prognosis is good
- Without treatment, Bubonic Plague can cause death in about or over 50% of the infected individuals. It can also cause severe and life-threatening complications such as gangrene and meningitis
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Bubonic Plague:
General information on lymph nodes:
The lymph nodes are part of one’s immune system. The lymph nodes are present throughout the body, usually in groups. In normal healthy adults, one cannot feel (see or touch) the lymph nodes readily. However, if they are enlarged, they can be felt either by the individual himself/herself or by the healthcare provider.
Enlarged lymph nodes can occur in both benign and malignant conditions. Hence, the cause of enlarged lymph nodes should be evaluated. If no obvious cause for enlargement of lymph nodes is found, then the possibility of a lymph node malignancy should be ruled out.
In a majority of individuals, a lymph node swelling is caused by a benign process such as an inflammation or infection. In many cases, swollen lymph nodes are part of other signs and symptoms. This can help a healthcare provider arrive at a list of follow-up tests and ensure an accurate diagnosis. Superficial enlarged lymph nodes can be felt by the healthcare provider through palpation. Enlarged lymph nodes deep in the body are often detected by radiological studies such as X-rays, ultrasound scan, CT and MRI scans.
Some enlarged lymph nodes can be painful, while others may be painless. Depending upon the underlying cause, enlarged lymph nodes can be localized to a particular area of the body, or they can be generalized, meaning that they are present throughout the body.
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals


0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.