What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Benign Glomangioma
- Benign Glomangiomyoma
- Benign Glomuvenous Malformation
What is Benign Glomus Tumor? (Definition/Background Information)
- Glomus tumors are a group of uncommon tumors caused by the proliferation of glomus cells, which are found in the glomus body. The glomus body is a small organ found in large numbers all over the body. It controls and helps regulate the body temperature and blood flow
- Based upon the histology features under the microscope, glomus tumors can be classified as:
- Benign Glomus Tumor
- Atypical Glomus Tumor
- Malignant Glomus Tumor
- A great majority of the glomus tumors are Benign Glomus Tumors. They are usually present superficially (on or just below the skin) and are characterized by pain, swelling, and skin discoloration. Some benign tumors may also be located deeper inside the body tissues
- The exact cause of Benign Glomus Tumor is not known, though several genetic mutations have been identified. Most commonly, young adults are affected by these benign tumors
- The diagnosis of Benign Glomus Tumor is undertaken by clinical examination and tumor biopsy. No significant complications are generally observed
- Surgical removal of the tumor is the most effective treatment and is considered for tumors that present significant signs and symptoms. The prognosis of Benign Glomus Tumor is excellent with appropriate treatment
Some of the (mostly) Benign Glomus Tumor types include:
- Glomuvenous Malformation: It is usually benign and seen in multiple locations; a positive family history is often present. Occasionally, the tumor is mixed with smooth muscles, in which cases it is called a Glomangioma. Most Glomangiomas are benign tumors
- Symplastic Glomus Tumor: If a glomus tumor shows atypical nuclear features (nuclear pleomorphism), but does not show abnormal cell proliferation; is less than 2 cm in size and is not located deep in the body, and does not show tumor necrosis, it is called a Symplastic Glomus Tumor
Who gets Benign Glomus Tumor? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Benign Glomus Tumors are very rare tumors. It may affect individuals of any age, though it is frequently observed in young adults
- Glomus tumors can occur in various parts of the body and both male and female genders are equally affected. However, tumors that form under the nail beds (subungual) are much more common in women than men
- All racial and ethnic groups may be affected and no preference is noted
What are the Risk Factors for Benign Glomus Tumor? (Predisposing Factors)
Currently, the risk factors that contribute to Benign Glomus Tumor development are unknown.
- A positive family history is seen when multiple lesions are present; in such cases, there is an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance noted
- Neurofibromatosis type 1 (a genetic disorder) association is seen with tumors that appear on the fingers and toes (subungual glomus tumors), typically when more than one digit is involved
- Bleb nevus syndrome are associated with glomus cell proliferation due to a condition called Glomovenous Malformation
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Benign Glomus Tumor? (Etiology)
The exact cause and mechanism of formation Benign Glomus Tumors is unknown.
- In general, glomus tumors are observed to have a variety of mutations
- Inherited tumors show gene mutations; the glomulin gene in chromosome 1 is involved in such cases
- Multiple glomus tumors are known to be inherited in an autosomal dominant manner
Autosomal dominant: Autosomal dominant conditions are traits or disorders that are present when only one copy of the mutation is inherited on a non-sex chromosome. In these types of conditions, the individual has one normal copy and one mutant copy of the gene. The abnormal gene dominates, masking the effects of the correctly function gene. If an individual has an autosomal dominant condition, the chance of passing the abnormal gene on to their offspring is 50%. Children, who do not inherit the abnormal gene, will not develop the condition or pass it on to their offspring.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Benign Glomus Tumor?
The following are the signs and symptoms of Benign Glomus Tumors:
- A vast majority of the glomus tumors are single; although in 1 in 10 individuals, multiple tumors may be present. Solitary tumors are often found in slightly older adults than multiple tumors (which is found in younger adults)
- The tumors are superficial (occurring on or just below the skin) in a vast majority of cases; they may also be infrequently deep-seated and occur at several locations
- The common sites are the upper extremities, with involvement of the hand, wrist, and fingers. Also, the tumor is commonly seen to affect the foot and toes
- On the skin, the tumors are painful and may appear as blue nodules, usually 1 cm in size or less. The pain may increase on touch or on exposure to cold
- Tumors present inside the body tissues may be irregularly-shaped and have less specific signs and symptoms
- Deep-seated tumors are very rare and may occur in the digestive tract, urinary bladder, male genitals, chest cavity, lungs, and bones. They may occur at any location in the body
- On the finger nail or toenail, the tumor may appear as a very painful, raised swelling with underlying skin discoloration. The nail may be deformed
- Glomus tumors on the arms and legs can be present as papules, or as small, raised swellings
How is Benign Glomus Tumor Diagnosed?
A diagnosis of Benign Glomus Tumor may include the following:
- A thorough physical exam and complete evaluation of medical history
- The following classical triad of symptoms may be noted for superficial glomus tumors:
- Severe pain
- Point tenderness
- Cold sensitivity
- Hildreth’s test: The limb with the tumor is elevated to drain blood away from the site of the tumor. After elevation, a tourniquet is tied and subsequently, the tumor is touched. The pain upon touch should be significantly reduced. But when the tourniquet is removed, the pain on touch suddenly increases
- Love’s pin test: Individuals should experience severe pain and subsequent decrease in pain, when the skin on top of the tumor is pushed using a fine object, such as a paper-clip, a pinhead, a toothpick, or a ball-point pen tip
- CT scan or MRI scan of the affected region, for deep-seated tumors
- Tissue biopsy of tumor specimen:
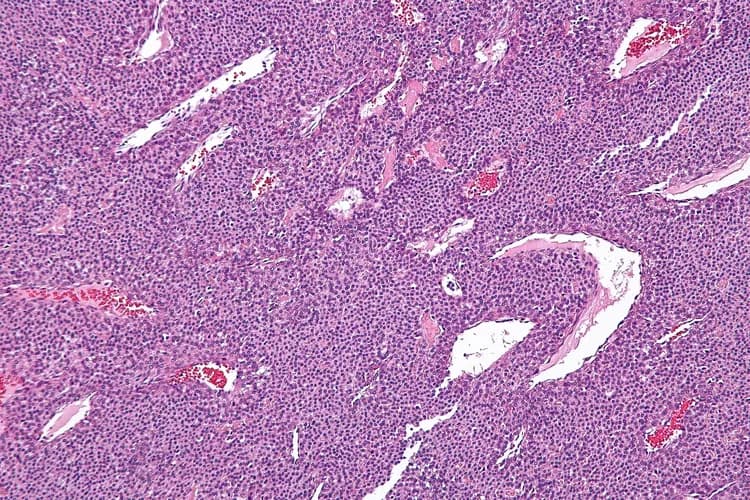
- A biopsy of the tumor is performed and sent to a laboratory for a pathological examination. A pathologist examines the biopsy under a microscope. After putting together clinical findings, special studies on tissues (if needed) and with microscope findings, the pathologist arrives at a definitive diagnosis. Examination of the biopsy under a microscope by a pathologist is considered to be gold standard in arriving at a conclusive diagnosis
- Biopsy specimens are studied initially using Hematoxylin and Eosin staining. The pathologist then decides on additional studies depending on the clinical situation
- Sometimes, the pathologist may perform special studies, which may include immunohistochemical stains, molecular testing, and very rarely, electron microscopic studies, to assist in the diagnosis
Note: For most benign tumors that do not cause significant signs and symptoms, the diagnosis is often delayed.
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Benign Glomus Tumor?
Generally, Benign Glomus Tumors are not associated with any serious complications. However, in some cases, the following may be noted:
- Superficial lesions may present severe pain and emotional stress
- The tumor can recur after its surgical removal
How is Benign Glomus Tumor Treated?
The treatment of Benign Glomus Tumor may involve the following measures:
- The healthcare provider may recommend a ‘wait and watch’ approach for small, asymptomatic tumors in superficial locations
- Simple excision and complete removal of the tumor: It is the most effective treatment available for the benign tumors
- Multiple tumors may be treated through any of the following means:
- Laser therapy
- Injection of hypertonic saline
- Sclerotherapy
- Generally, medical therapy (treatment using medications) is not effective for treating glomus tumors
- Follow-up care with regular screening and check-ups are important
How can Benign Glomus Tumor be Prevented?
Currently, there are no effective preventative methods available for Benign Glomus Tumor. Avoiding exposure to severe cold may reduce aggravation of the signs and symptoms.
What is the Prognosis of Benign Glomus Tumor? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- With appropriate treatment, the prognosis of Benign Glomus Tumor is typically excellent
- Following a simple excision and tumor removal, the pain and accompanying symptoms are known to subside
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Benign Glomus Tumor:
Please visit our Cancer & Benign Tumor Health Center for more physician-approved health information:
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.